LeetCode 2090. K Radius Subarray Averages
作者:互联网
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/k-radius-subarray-averages/
题目:
You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers, and an integer k.
The k-radius average for a subarray of nums centered at some index i with the radius k is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return an array avgs of length n where avgs[i] is the k-radius average for the subarray centered at index i.
The average of x elements is the sum of the x elements divided by x, using integer division. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
- For example, the average of four elements
2,3,1, and5is(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75, which truncates to2.
Example 1:
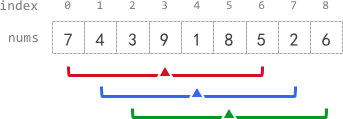
Input: nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3 Output: [-1,-1,-1,5,4,4,-1,-1,-1] Explanation: - avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements before each index. - The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37. Using integer division, avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5. - For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4. - For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4. - avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements after each index.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [100000], k = 0 Output: [100000] Explanation: - The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000. avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [8], k = 100000 Output: [-1] Explanation: - avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i], k <= 105
题解:
Have a window to maintain the sum. Window size is 2 * k + 1, save it as len.
if nums.length < len. Then we could simply return array containing only -1.
Move runner, update sum. When runner - walker = len, we need to update the result.
res[walker + k] = average.
Then move walker by 1 and substract the corresponding value from sum.
Note: there could be overflow. The sum type is long.
Time Complexity: O(n). n = nums.length.
Space: O(1). regardless res.
AC Java:
1 class Solution {
2 public int[] getAverages(int[] nums, int k) {
3 if(nums == null || nums.length == 0 || k == 0){
4 return nums;
5 }
6
7 long sum = 0;
8 int [] res = new int[nums.length];
9 Arrays.fill(res, -1);
10 int len = 2 * k + 1;
11 if(nums.length < len){
12 return res;
13 }
14
15 int walker = 0;
16 int runner = 0;
17 while(runner < nums.length){
18 sum += nums[runner++];
19 if(runner - walker == len){
20 res[walker + k] = (int)(sum / len);
21 sum -= nums[walker++];
22 }
23 }
24
25 return res;
26 }
27 }
标签:index,nums,int,sum,length,Radius,Subarray,avg,Averages 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/Dylan-Java-NYC/p/16378016.html