5. Lab: Copy-on-Write Fork for xv6
作者:互联网
1. 要求
Your task is to implement copy-on-write fork in the xv6 kernel. You are done if your modified kernel executes both the cowtest and usertests programs successfully.
Here's a reasonable plan of attack.
- Modify uvmcopy() to map the parent's physical pages into the child, instead of allocating new pages. Clear PTE_W in the PTEs of both child and parent.
- Modify usertrap() to recognize page faults. When a page-fault occurs on a COW page, allocate a new page with kalloc(), copy the old page to the new page, and install the new page in the PTE with PTE_W set.
- Ensure that each physical page is freed when the last PTE reference to it goes away -- but not before. A good way to do this is to keep, for each physical page, a "reference count" of the number of user page tables that refer to that page. Set a page's reference count to one when kalloc() allocates it. Increment a page's reference count when fork causes a child to share the page, and decrement a page's count each time any process drops the page from its page table. kfree() should only place a page back on the free list if its reference count is zero. It's OK to to keep these counts in a fixed-size array of integers. You'll have to work out a scheme for how to index the array and how to choose its size. For example, you could index the array with the page's physical address divided by 4096, and give the array a number of elements equal to highest physical address of any page placed on the free list by kinit() in kalloc.c.
- Modify copyout() to use the same scheme as page faults when it encounters a COW page.
Some hints:
- The lazy page allocation lab has likely made you familiar with much of the xv6 kernel code that's relevant for copy-on-write. However, you should not base this lab on your lazy allocation solution; instead, please start with a fresh copy of xv6 as directed above.
- It may be useful to have a way to record, for each PTE, whether it is a COW mapping. You can use the RSW (reserved for software) bits in the RISC-V PTE for this.
- usertests explores scenarios that cowtest does not test, so don't forget to check that all tests pass for both.
- Some helpful macros and definitions for page table flags are at the end of kernel/riscv.h.
- If a COW page fault occurs and there's no free memory, the process should be killed.
简单来说就是实现写时复制。
传统的fork()系统调用直接把所有的资源复制给新创建的进程。这种实现过于简单并且效率低下,因为它拷贝的数据也许并不共享,更糟的情况是,如果新进程打算立即执行一个新的映像,那么所有的拷贝都将前功尽弃。Linux 的 fork() 使用写时拷贝(copy-on-write)页实现。写时拷贝是一种可以推迟甚至免除拷贝数据的技术。内核此时并不复制整个进程地址空间,而是让父进程和子进程共享同一个拷贝。只有在需要写入的时候,数据才会被复制,从而使各个进程拥有各自的拷贝。也就是说,资源的复制只有在需要写入的时候才进行,在此之前,只是以只读方式共享。
2. 分析
需要修改的点有如下:
uvmcopy()的功能是拷贝父进程的页表给子进程,此处需要把拷贝操作替换成,子进程和父进程都映射同一个页面,并且将页属性PTE_W置为 0,这样写页面时,可以触发缺页异常,进而处理数据复制。- 触发
pagefault的时候,可以在usertrap()处理缺页异常,通过r_scause()获取中断号,如果 15 表示为写异常。当触发写异常时,需要判断这个异常页是否为通过fork操作特意取消掉PTE_W权限,以便确定该操作是需要进行copy-on-write,而不是错误。页的属性中有 2 位保留位,RSW 位。可以供我们使用作于标记。
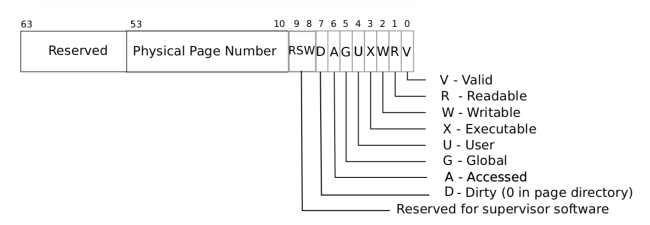
- 由于单个物理页可能会有多个虚拟页进行映射,因此,在释放进程的内存时,需要判断对应的页是否还有其它进程在占用。可以通过增加引用计数,
kalloc()分配内存的时候,增加引用技术,kfree()释放内存时,减少引用计数,当计数为 0 时,释放该物理页。 - 由于内核和用户进程使用的不是同一个页表,当有数据要拷贝到用户进程时,通常利用
copyout接口,该接口在内核执行时,会先根据用户页表和目标虚拟地址,翻译出该虚拟地址的实际物理地址,由于内核的内存空间是直接映射(虚拟地址 == 物理地址),因此内核可以直接将数据 copy 到该翻译出来的物理地址上。但是此处需要考虑到该目标虚拟地址可能是不可写的,因此copyout需要复刻下usertrap()处理缺页异常时的操作。
3. 实现
3.1 初始化引用计数
由于 xv6 初始化内存时,使用了 kfree 接口,因此 reset_page_ref() 初始化时会将引用技术先置为 1。其次引用计数对应的引用数组大小,参考 xv6 内存布局。内存只到 PHYSTOP,约 128GB 内存。
void reset_page_ref();
struct {
struct spinlock lock;
int ref[(PHYSTOP - KERNBASE) / PGSIZE];
} page_ref;
void kinit()
{
initlock(&kmem.lock, "kmem");
reset_page_ref();
freerange(end, (void*)PHYSTOP);
}
void reset_page_ref()
{
int cnt = sizeof(page_ref.ref) / sizeof(int);
printf("cnt = %d\n", cnt);
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++)
{
page_ref.ref[i] = 1;
}
}
int get_pa_index(uint64 pa)
{
return ((pa & ~(PGSIZE - 1)) - KERNBASE) / PGSIZE;
}
void inc_page_ref(uint64 pa)
{
acquire(&page_ref.lock);
int idx = get_pa_index(pa);
page_ref.ref[idx] += 1;
release(&page_ref.lock);
}
void dec_page_ref(uint64 pa)
{
acquire(&page_ref.lock);
int idx = get_pa_index(pa);
page_ref.ref[idx] -= 1;
release(&page_ref.lock);
}
int get_ref_cnt(uint64 pa)
{
int idx = get_pa_index(pa);
return page_ref.ref[idx];
}
void kfree(void *pa)
{
struct run *r;
if(((uint64)pa % PGSIZE) != 0 || (char*)pa < end || (uint64)pa >= PHYSTOP)
panic("kfree");
acquire(&kmem.lock);
int ref_cnt = get_ref_cnt((uint64)pa);
if (ref_cnt == 0){
release(&kmem.lock);
panic("ref cnt == 0"); // release page double times
}
if(ref_cnt == 1){
// Fill with junk to catch dangling refs.
memset(pa, 1, PGSIZE);
r = (struct run*)pa;
r->next = kmem.freelist;
kmem.freelist = r;
}
dec_page_ref((uint64)pa);
release(&kmem.lock);
}
// Allocate one 4096-byte page of physical memory.
// Returns a pointer that the kernel can use.
// Returns 0 if the memory cannot be allocated.
void * kalloc(void)
{
struct run *r;
acquire(&kmem.lock);
r = kmem.freelist;
if(r){
kmem.freelist = r->next;
inc_page_ref((uint64)r);
}
release(&kmem.lock);
if(r)
memset((char*)r, 5, PGSIZE); // fill with junk
return (void*)r;
}
3.2 处理 fork 拷贝
这里需要注意几点:
- 当页是可写权限时,父进程的写权限也要去除,如果不去除会导致,
fork之后,父进程修改某个数据,而子进程会依旧同步到该数据。此外还要加上PTE_RSW权限,用于标志该页是否需要被拷贝。 - 映射完页面之后,需要增加引用计数
int uvmcopy(pagetable_t old, pagetable_t new, uint64 sz)
{
pte_t *pte;
uint64 pa, i;
for(i = 0; i < sz; i += PGSIZE){
if((pte = walk(old, i, 0)) == 0)
panic("uvmcopy: pte should exist");
if((*pte & PTE_V) == 0)
panic("uvmcopy: page not present");
pa = PTE2PA(*pte);
int flags = PTE_FLAGS(*pte); // copy flag , remove write permission and add rsw flag
if (flags & PTE_W){
flags = (flags & (~PTE_W)) | PTE_RSW;
if(mappages(old, i, PGSIZE, (uint64)pa, flags) != 0){ // modify old page attr
goto err;
}
}
if(mappages(new, i, PGSIZE, (uint64)pa, flags) != 0){
goto err;
}
inc_page_ref(pa);
}
return 0;
err:
uvmunmap(new, 0, i / PGSIZE, 1);
return -1;
}
3.3 处理缺页异常
这里需要注意如下:
- 检查是否有
PTE_RSW位,如果没有表示该异常不是通过 copy-on-write 操作引发的,需要 kill 掉该进程。 - 一些常规的边界检查
- 从旧页面拷贝到新页面时,需要整页拷贝,因为分配新页面时,里面都是垃圾数据,如果只拷贝修改的数据,会导致其他数据异常。
- 拷贝完毕,建立完新页面和进程页表的映射之后,还需要做如下操作:
- 执行释放旧物理页的操作,因为进程不再使用该页面了,需要减少引用计数
- 清除
PTE_RSW位,因为此时已不在需要 copy-on-write 操作了,可以直接写入。
void usertrap(void)
{
// ... some code
else if (r_scause() == 15){ // write page fault
uint64 va = r_stval();
if(va >= MAXVA || (va <= PGROUNDDOWN(p->trapframe->sp) && va >= PGROUNDDOWN(p->trapframe->sp) - PGSIZE)){
p->killed = 1;
} else {
if (pagefault(p->pagetable, va) < 0)
p->killed = 1;
}
}
// ... some code
}
// vm.c
int pagefault(pagetable_t pagetable, uint64 fault_va)
{
pte_t* pte = walk(pagetable, fault_va, 0);
if ((*pte & PTE_RSW) == 0)
return -1;
// step 1 : copy origin page
uint64 fault_pa = walkaddr(pagetable, fault_va);
void* dst_pa = kalloc();
if (dst_pa == 0){
return -1;
}
memmove(dst_pa, (void*)fault_pa, PGSIZE);
// step 2 : copy page flag and allow write
int flag = (PTE_FLAGS(*pte) | PTE_W) & ~PTE_RSW; // remove rsw flag
*pte = PA2PTE(dst_pa) | flag;
//printf("page fault, stval=%x\n", fault_va);
kfree((void*)fault_pa);
return 0;
}
4. 小结
- 该实验思路整体较为简单,但是需要注意一些边界条件,防止执行
usertests的时候不通过 - 需要对地址翻译映射过程比较了解,可以参考 lab3-pgtbl 的预备内容。
标签:Fork,uint64,PTE,Write,pa,void,Copy,ref,page 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/lawliet12/p/16101519.html