「JOISC 2019 Day3」穿越时空 Bitaro
作者:互联网
「JOISC 2019 Day3」穿越时空 Bitaro
数据结构,线段树
考虑每次行动
显然暴力贪心走是正确的
但时间的流逝很麻烦
可以将每对 \([L_i, R_i] \longrightarrow [L_i - i, R_i - i]\)
这样就可以抵消掉时间流动的问题,就像这样
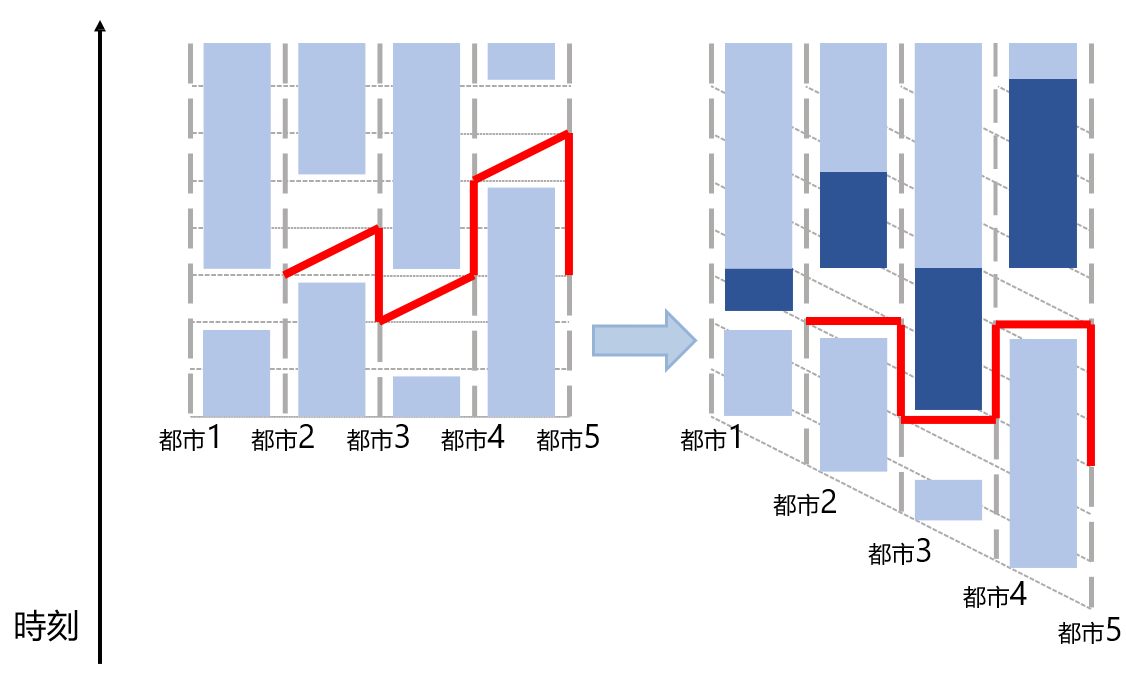
对于当前时间 \(t\) ,当前这条路时间 \([L_i, R_i]\)
- \(t \in [L_i, R_i]\) ,直接走
- \(t < L_i\) 等到 \(L_i\) 走
- \(t > R_i\) 操作一下把时间调至 \(R_i\) 再走
现在每次操作是 \(O(n)\),总\(O(nq)\) ,可以获得 \(\color{lightgreen}4\) 分的好成绩
接下来考虑多次询问和修改
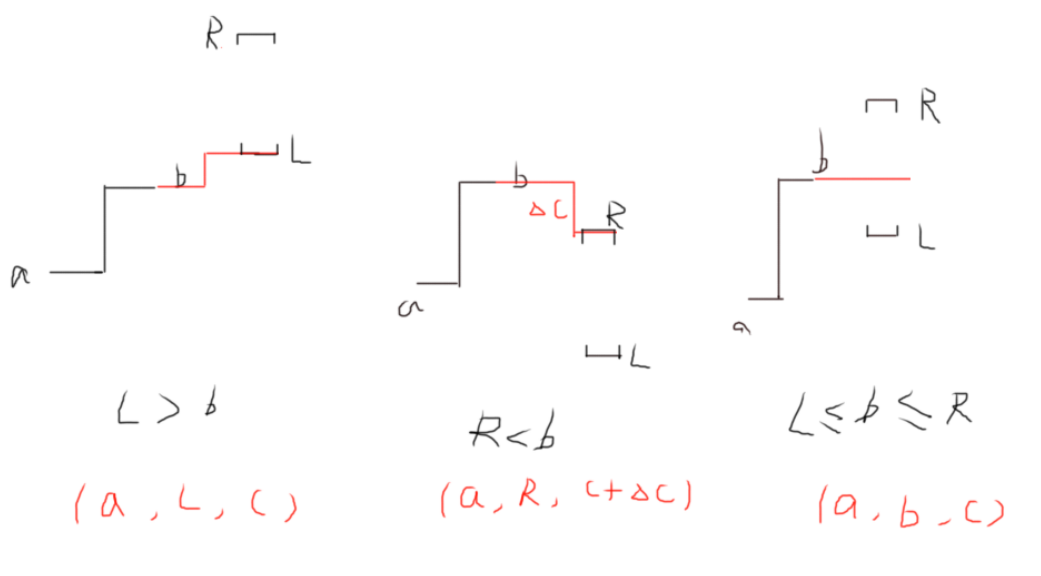
我们可以用一个三元组 \((a, b, c)\) 来表示一次行动,其中 \(a\) 表示开始时刻,\(b\) 表示结束时刻,\(c\) 表示倒流时间数
显然,对于每次询问,我们只需求出对应三元组的 \(c\) 即可
试着将一个三元组拆成两个有序的更小的三元组,这样我们可以将询问的三元组一直拆下去,直到可知为止
反过来考虑将两个三元组 \((a_1, b_1, c_1)\) 和 \((a_2, b_2, c_2)\) 按序合并为一个三元组
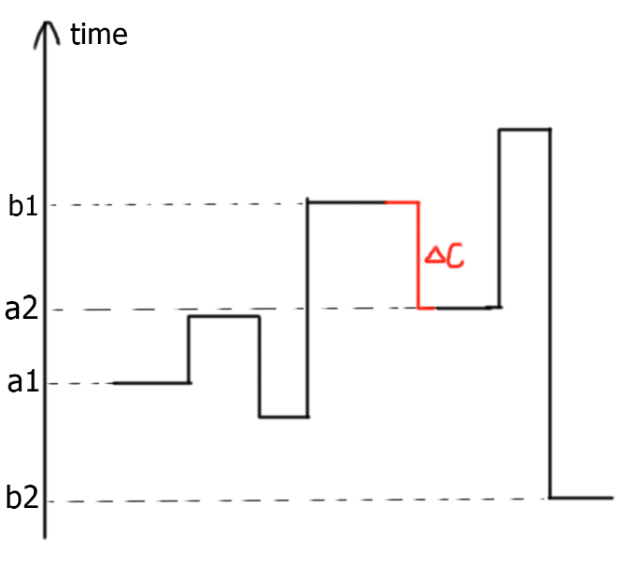
如图,前后两次行动可以接上中间的差值,合并为一次行动
\((a_1, b_1, c_1) + (a_2, b_2, c_2) \longrightarrow (a_1, b_2, c_1 + c_2 + \Delta c)\)
但是题目给的是一个二元区间 \([L_i, R_i]\) ,考虑合并两个二元区间会变成什么
当两个区间有交集时,合并和便是个更小的区间,也就是指只有在这个更小的区间才能通过这两个区间,比如

图中转化为:
\([L_1, R_1] + [L_2, R_2] \longrightarrow [\max(L_1, L_2), \min(R_1, R_2)]\)
当两个区间无交集时,遍合并为了三元组,表示通过这两个区间需要代价(等待或者时间倒流),比如
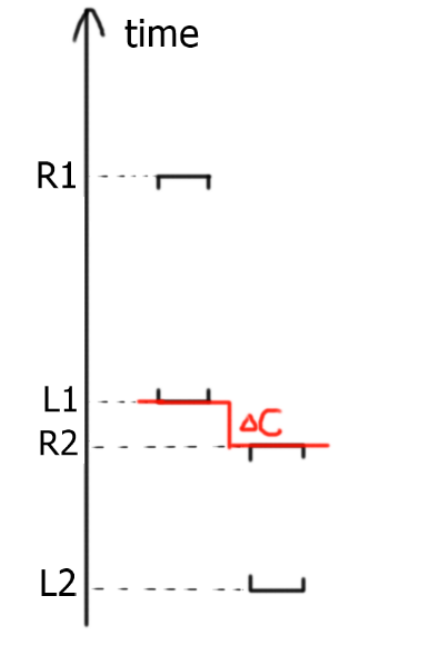
图中转化为:
\([L_1, R_1] + [L_2, R_2] \longrightarrow (L_1, R_2, L_1 - R_2)\)
现在考虑二元与三元合并
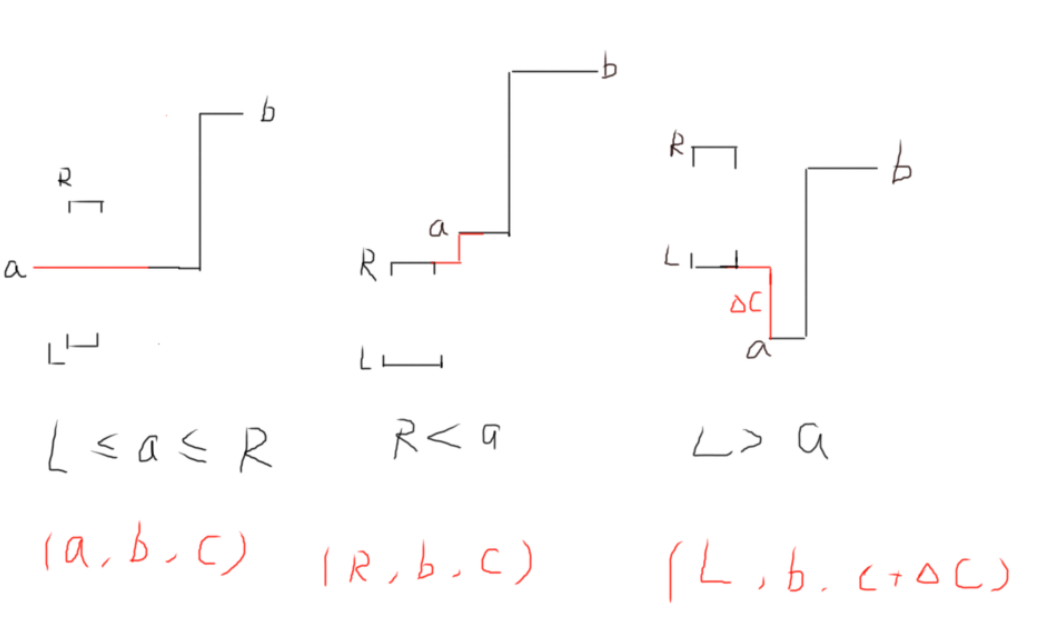
红色的是合并后的三元组
以及三元与二元合并
合并,修改,查询,想到用线段树维护
所以每次查询 \(A, B, C, D\),只需将范围内的所有区间合并起来就行了,但由于起点终点有时间限制,所有在构造两个区间与之并起来,就能得到此次行动的三元组
\([B - A, B - A] + \text{query}(A, C- 1) + [D - C, D - C]\)
减 \(A\) 减 \(C\) 是减去位置,抵消流动时间
特别注意的地方,就是询问中会有反向的,也就是从后边的城市到前面的城市
对于这些询问,只需将其提出来,反向建线段树再做就行了
可以获得 \(\color{red}{100}\) 分的好成绩
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define re register
// #define int long long
// #define pair pair<int, int>
#define File(a) freopen(a".in", "r", stdin), freopen(a".out", "w", stdout);
#define getchar() (p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 1 << 21, stdin), p1 == p2) ? EOF : *p1++)
char buf[1 << 21], *p1 = buf, *p2 = buf;
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
re int x = 0, f = 0;
re char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch)) {if (ch == '-') f = 1; ch = getchar();}
while (isdigit(ch)) {x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + ch - 48; ch = getchar();}
return f ? -x : x;
}
inline string getstr()
{
string res = "";
re char ch = getchar();
while (isspace(ch)) ch = getchar();
while (!isspace(ch)) res.push_back(ch), ch = getchar();
return res;
}
const int N = 3e5 + 5, P = 1e9 + 9;
int n;
struct node
{
long long a, b, c;
inline node operator + (const node &x) const
{
node res;
if (a == 0 && b == 0 && c == 0) return x;
if (x.a == 0 && x.b == 0 && x.c == 0) return *this;
if (c == -1 && x.c == -1)
{
if (a > x.b) res = {a, x.b, a - x.b};
else if (b < x.a) res = {b, x.a, 0};
else res = {max(a, x.a), min(b, x.b), -1};
}
else if (c == -1)
{
if (b < x.a) res = {b, x.b, x.c};
else if (a > x.a) res = {a, x.b, x.c + a - x.a};
else res = x;
}
else if (x.c == -1)
{
if (b < x.a) res = {a, x.a, c};
else if (b > x.b) res = {a, x.b, c + b - x.b};
else res = *this;
}
else res = {a, x.b, max(b - x.a, 0ll) + c + x.c};
return res;
}
};
node tr[N << 2], A[N];
inline void built(int p, int l, int r)
{
if (l > r) return;
if (l == r) return void(tr[p] = {A[l].a - l, A[l].b - l - 1, -1});
int mid = l + r >> 1;
built(p << 1, l, mid);
built(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
tr[p] = tr[p << 1] + tr[p << 1 | 1];
}
inline void update(int p, int l, int r, int LR, node val)
{
if (l == r) return void(tr[p] = val);
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (LR <= mid) update(p << 1, l, mid, LR, val);
else update(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, LR, val);
tr[p] = tr[p << 1] + tr[p << 1 | 1];
}
inline node ask(int p, int l, int r, int L, int R)
{
if (L <= l && r <= R) return tr[p];
int mid = l + r >> 1;
node res = {0, 0, 0};
if (L <= mid) res = res + ask(p << 1, l, mid, L, R);
if (mid < R) res = res + ask(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, L, R);
return res;
}
long long ans[N];
struct
{
int op, A, C, B, D;
}q[N];
signed main()
{
bool flag = 1;
n = read(); int T = read();
for (re int i = 1; i < n; ++i) A[i] = {read(), read(), -1};
built(1, 1, n - 1);
for (re int i = 1; i <= T; ++i)
{
ans[i] = -1;
q[i].op = read(), q[i].A = read(), q[i].B = read(), q[i].C = read();
if (q[i].op == 1) update(1, 1, n - 1, q[i].A, {q[i].B - q[i].A, q[i].C - q[i].A - 1, -1});
else
{
q[i].D = read();
if (q[i].A == q[i].C) {ans[i] = max(0, q[i].B - q[i].D); continue;}
if (q[i].A > q[i].C) {flag = 1; continue;}
node res = ask(1, 1, n - 1, q[i].A, q[i].C - 1);
res = node{q[i].B - q[i].A, q[i].B - q[i].A, -1} + res;
res = res + node{q[i].D - q[i].C, q[i].D - q[i].C, -1};
ans[i] = res.c;
}
}
if (flag)
{
reverse(A + 1, A + n);
built(1, 1, n - 1);
for (re int i = 1; i <= T; ++i)
{
if (q[i].op != 1) q[i].C = n - q[i].C + 1, q[i].A = n - q[i].A + 1;
else q[i].A = n - q[i].A;
}
for (re int i = 1; i <= T; ++i)
{
if (ans[i] != -1) continue;
if (q[i].op == 1) update(1, 1, n - 1, q[i].A, {q[i].B - q[i].A, q[i].C - q[i].A - 1, -1});
else
{
node res = ask(1, 1, n - 1, q[i].A, q[i].C - 1);
res = node{q[i].B - q[i].A, q[i].B - q[i].A, -1} + res;
res = res + node{q[i].D - q[i].C, q[i].D - q[i].C, -1};
ans[i] = res.c;
}
}
}
for (re int i = 1; i <= T; ++i) if (q[i].op != 1) printf("%lld\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
标签:res,合并,Day3,else,JOISC,2019,区间,三元组,define 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/After-glow/p/15836763.html