课程研讨|数据库原理1|第二周-4
作者:互联网
研讨题目
什么是关系型数据库?什么是非关系型数据库?它们有什么区别?各举1个典型产品简单介绍他们特点?
研讨内容
关系型数据库
关系型数据库是建立在关系模型基础上的资料库。
What is a Relational Database?
Relational databases maintain data in tables, providing an efficient, intuitive, and flexible way to store and access structured information. Tables, also known as relations, consist of columns containing one or more data categories, and rows, also known as table records, containing a set of data defined by the category. Applications access data by specifying queries, which use operations such as project to identify attributes, select to identify tuples, and join to combine relations. The relational model for database management was developed by IBM computer scientist Edgar F. Codd in 1970.
关系数据库将数据保存在表中,从而提供了一种有效、直观且灵活的方式来存储和访问结构化信息。表,也称为关系,由包含一个或多个数据类别的列和包含表项定义的一组数据的行(也称为表记录)组成。应用程序通过指定查询来访问数据,查询使用诸如项目之类的操作来标识属性,选择来标识元组并联结以合并关系。
How do Relational Databases Work?
Relational databases provide an environment from which data can be accessed or reassembled in a variety of different ways without needing to reorganize the database tables. Each table has a unique identifier, or primary key, which identifies the information in the table, and each row contains a unique instance of data for the categories defined by the columns. For instance, the table might have a primary key of ‘First Names’ and rows with specific examples such as ‘John, Paul, George and Ringo.’
关系数据库提供了一种可以以各种不同的方式访问或重组数据,而无需重新组织数据库表的环境。每个表只都有一个唯一的标识符或主键,用于标识表中的信息,并且每一行都包含由列定义的类别的数据的唯一实例。
The logical connection between different tables can then be established with the use of foreign keys - a field in a table that connects to the primary key data of another table. Relational Database Management Systems often employ SQL or structured query language for gathering data for reports and for interactive queries. So in our example, First Names might be linked to a Role table with data roles of Lead Vocals, Bass Guitar, Drums and Lead Guitar.
可以使用外键建立不同表之间的逻辑连接,外键是表中的字段,该字段连接到另一个表的主键数据。关系型数据库管理系统通常采用SQL或结构化查询语言来手机报告数据和交互式查询。
How is Data in a Relational Database System Organized?
The relational model of the relational database separates logical data structures from physical storage structures, enabling database administrators to manage physical data storage without affecting access to that data as a logical structure. The distinction also applies to database operations – logical operations allow an application to specify the content it needs, and physical operations determine how that data should be accessed, then carries out the task.
关系数据库的关系模型将逻辑数据结构与物理存储结构分开,使数据库管理员可以管理物理数据存储而不会影响对作为逻辑结构的数据的访问。逻辑操作允许应用程序指定其所需内容,而物理操作则确定应如何访问数据然后执行任务。
What are the Advantages of a Relational Database?
The main advantage of a relational database is its formally described, tabular structure, from which data can be easily stored, categorized, queried, and filtered without needing to reorganize database tables. Further benefits of relational databases include:
- Scalability: New data may be added independent of existing records.
- Simplicity: Complex queries are easy for users to perform with SQL.
- Data Accuracy: Normalization procedures eliminate design anomalies.
- Data Integrity: Strong data typing and validity checks ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Security: Data in tables within a RDBMS can limit access to specific users.
- Collaboration: Multiple users can access the same database concurrently.
关系数据库的主要优点是它的形式化描述的表格结构,可以从中轻松存储,分类,查询和过滤数据,而无需重新组织数据库表。关系数据库的其他好处包括:
- 可伸缩性:可以独立于现有记录添加新数据
- 简便性:复杂的查询使用户易于使用SQL执行
- 数据准确性:归一化程序可以消除设计异常
- 数据完整性:强大的数据键入和有效性检查可确保准确性和一致性
- 安全性:RDBMS中表中的数据可以限制对特定用户的访问
- 协作:多个用户可以同时访问同一数据库
What is a Relational Database Management System?
A Relational Database Management System is a tabular based collection of programs and capabilities that provides an interface between users and applications and the database, offering a systematic way to create, update, delete, manage, and retrieve data. Most relational database management systems use the SQL programming language to access the database and many follow the ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties of the database:
- Atomicity: If any statement in the transaction fails, the entire transaction fails and the database is left unchanged.
- Consistency: The transaction must meet all protocols defined by the system – no partially completed transactions.
- Isolation: No transaction has access to any other transaction that is unfinished. Each transaction is independent.
- Durability: Once a transaction has been committed, it will remain committed through the use of transaction logs and backups.
关系数据库管理系统是基于表格的程序和功能的集合,可在用户和应用程序与数据库之间提供接口,从而提供了一种创建,更新,删除,管理和检索数据的系统方法。大多数关系数据库管理系统使用SQL编程语言来访问数据库,并且许多遵循数据库的ACID属性。
-
原子性
如果事务中的任何语句失败,则整个事务都会失败,并且数据库将保持不变。
所有操作要么全部成功,要么全部失败回滚,且操作失败不能对数据库由任何影响。
-
一致性
交易必须符合系统定义的所有协议,不能部分完成交易。
一个事务执行之前和执行之后都必须处于一致性状态。
-
隔离性
没有事务可以访问任何其他未完成的事务。每笔交易都是独立的。
多个用户并发访问数据库时,数据库为每一个用户开启的事务,不能被其他事务的操作所干扰,多个并发事务之间要相互隔离。
-
持久性
提交事务后,将通过使用事务日志和备份来保持提交。
事务一旦被提交了,数据的改变是永久性的,即便在数据库系统遇到故障的情况下也不会丢失提交事务的操作。
非关系型数据库
非关系数据库以非表格形式存储数据,并且比传统的基于SQL的关系数据库结构更灵活。它不遵循传统关系数据库管理系统提供的关系模型。
Non-relational databases (often called NoSQL databases) are different from traditional relational databases in that they store their data in a non-tabular form. Instead, non-relational databases might be based on data structures like documents. A document can be highly detailed while containing a range of different types of information in different formats. This ability to digest and organize various types of information side-by-side makes non-relational databases much more flexible than relational databases.
Non-relational databases are often used when large quantities of complex and diverse data need to be organized. For example, a large store might have a database in which each customer has their own document containing all of their information, from name and address to order history and credit card information. Despite their differing formats, each of these pieces of information can be stored in the same document.
Non-relational databases often perform faster because a query doesn’t have to view several tables in order to deliver an answer, as relational datasets often do. Non-relational databases are therefore ideal for storing data that may be changed frequently or for applications that handle many different kinds of data. They can support rapidly developing applications requiring a dynamic database able to change quickly and to accommodate large amounts of complex, unstructured data.
非关系数据库与传统关系数据库的不同之处在于,它们以非表格形式存储数据。相反,非关系数据库可能基于文档之类的数据结构。文档可以高度详细,同时包含各种格式的不同类型的信息。并排消化和组织各种类型信息的能力使非关系数据库比关系数据库更加灵活。
当需要组织大量复杂多样的数据时,通常使用非关系数据库。非关系数据库的执行速度通常更快,这是因为查询时不必像提供关系数据集那样查看多个表。因此,非关系数据库是存储可能经常更改的数据或处理许多不同类型数据的应用程序的理想选择。它们可以支持快速开发的应用程序,这些应用程序,这些应用程序要求动态数据库能够快速更改并容纳大量复杂的非结构化数据。
A NoSQL (originally referring to “non-SQL” or “non-relational”) database provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases. Such databases have existed since the late 1960s, but the name “NoSQL” was only coined in the early 21st century,triggered by the needs of Web 2.0 companies.NoSQL databases are increasingly used in big data and real-time web applications.NoSQL systems are also sometimes called “Not only SQL” to emphasize that they may support SQL-like query languages or sit alongside SQL databases in polyglot-persistent architectures.
Motivations for this approach include: simplicity of design, simpler “horizontal” scaling to clusters of machines (which is a problem for relational databases), finer control over availability and limiting the object-relational impedance mismatch. The data structures used by NoSQL databases (e.g. key–value pair, wide column, graph, or document) are different from those used by default in relational databases, making some operations faster in NoSQL. The particular suitability of a given NoSQL database depends on the problem it must solve. Sometimes the data structures used by NoSQL databases are also viewed as “more flexible” than relational database tables.
The Benifits of a non-relational database
Today’s applications collect and store increasingly vast quantities of ever-more complex customer and user data. The benefits of this data to businesses, of course, lies in its potential for analysis. Using a non-relational database can unlock patterns and value even within masses of variegated data.
There are several advantages to using non-relational databases, including:
-
Massive dataset organization
In the age of Big Data, non-relational databases can not only store massive quantities of information, but they can also query these datasets with ease. Scale and speed are crucial advantages of non-relational databases. -
Flexible database expansion
Data is not static. As more information is collected, a non-relational database can absorb these new data points, enriching the existing database with new levels of granular value even if they don’t fit the data types of previously existing information. -
Multiple data structures
The data now collected from users takes on a myriad of forms, from numbers and strings, to photo and video content, to message histories. A database needs the ability to store these various information formats, understand relationships between them, and perform detailed queries. No matter what format your information is in, non-relational databases can collate different information types together in the same document. -
Built for the cloud
A non-relational database can be massive. And as they can in some cases grow exponentially, they need a hosting environment that can grow and expand with. The cloud’s inherent scalability makes it an ideal home for non-relational databases.
当今的应用程序收集和存储越来越多的客户和越来越复杂的用户数据。使用非关系数据库可以在大量杂色数据中解锁模式和价值。
-
大规模数据集组织
在大数据时代,非关系数据库不仅可以存储大量信息,而且可以轻松查询这些数据集。规模和速度是非关系数据库的关键优势。
-
灵活的数据库扩展
数据不是静态的。随着收集到更多信息,非关系数据库可以吸收这些新数据点,从而使现有数据库具有新的粒度值,即使它们不适合先前现有信息的数据类型。
-
多种数据结构
从用户那里收集的数据具有多种形式,从数字和字符串到照片和视频内容再到消息历史记录。数据库。数据库需要具有存储这些各种信息格式,了解它们之间的关系以及执行详细查询的能力。无论您的信息采用哪种格式,非关系数据库都可以在同一文档中整理不同的信息类型。
-
专为云而建
非关系数据库可能非常庞大。并且由于它们在某些情况下可以加倍增长,因此需要一个可以随其扩展和扩展的托管环境。云的固有可扩展性使其成为非关系数据库的理想之处。
Non-relational databases and application development
Applications must be able to query data efficiently and deliver results almost instantly. Non-relational databases are a natural choice for this kind of environment. They offer both security and agility, allowing for rapid development of applications in an agile environment. Easier and less complex to manage than relational databases, they can also yield lower data management costs while providing superior performance and speed.
Naturals for agile development, non-relational databases can accommodate the complexity of data inputs more efficiently than structured databases. In an age of increasing data complexity, non-relational databases provide the flexibility in database design that has become increasingly indispensable. Especially when paired with the cloud, non-relational databases lift the limits on your data collection, organization, and analysis, allowing you to get the most out of your data.
应用程序必须能够有效查询数据并几乎立即交付结果。对于这种环境,非关系数据库是自然的选择。它们同时提供安全性和敏捷性,从而允许在敏捷环境中快速开发应用程序。与关系数据库相比,它们更易于管理,管理起来也不那么复杂,它们还可以降低数据管理成本,同时提供卓越的性能和速度。
与结构化数据库相比,非关系数据库对于敏捷开发是很自然的,它可以更有效地适应数据输入的复杂性。在数据复杂性日益增长的时代,非关系型数据库提供了越来越不可缺少的数据库设计灵活性。尤其是与云配对时,非关系型数据库将解除对数据收集,组织和分析的限制,使您能够充分利用数据。
Types of NoSQL Databases
Over time, four major types of NoSQL databases emerged: document databases, key-value databases, wide-column stores, and graph databases. Let’s examine each type.
-
Document databases store data in documents similar to JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) objects. Each document contains pairs of fields and values. The values can typically be a variety of types including things like strings, numbers, booleans, arrays, or objects, and their structures typically align with objects developers are working with in code. Because of their variety of field value types and powerful query languages, document databases are great for a wide variety of use cases and can be used as a general purpose database. They can horizontally scale-out to accomodate large data volumes. MongoDB is consistently ranked as the world’s most popular NoSQL database according to DB-engines and is an example of a document database.
-
Key-value databases are a simpler type of database where each item contains keys and values. A value can typically only be retrieved by referencing its key, so learning how to query for a specific key-value pair is typically simple. Key-value databases are great for use cases where you need to store large amounts of data but you don’t need to perform complex queries to retrieve it. Common use cases include storing user preferences or caching. Redis and DynanoDB are popular key-value databases.
-
Wide-column stores store data in tables, rows, and dynamic columns. Wide-column stores provide a lot of flexibility over relational databases because each row is not required to have the same columns. Many consider wide-column stores to be two-dimensional key-value databases. Wide-column stores are great for when you need to store large amounts of data and you can predict what your query patterns will be. Wide-column stores are commonly used for storing Internet of Things data and user profile data. Cassandra and HBase are two of the most popular wide-column stores.
-
Graph databases store data in nodes and edges. Nodes typically store information about people, places, and things while edges store information about the relationships between the nodes. Graph databases excel in use cases where you need to traverse relationships to look for patterns such as social networks, fraud detection, and recommendation engines. Neo4j and JanusGraph are examples of graph databases.
-
文档数据库
将数据存储在类似于JSON对象的文档中。每个文档包含成对的字段和值。这些值通常可以是多种类型,包括字符串,数字,布尔值,数组或对象之类的东西,并且它们的结构通常与开发人员在代码中使用的对象保持一致。由于它们的字段值类型和强大的查询语言多种多样,因此文档数据库非常适合各种各样的用例,并且它们的结构通常与开发人员在代码中使用的对象保持一致。由于它们的字段值类型和强大的查询语言多种多样,因此文档数据库非常适合各种各样的用例,并且可以用作通用数据库。它们可以水平扩展以适应大数据量。
-
典型应用场景
Web应用
-
不适用场景
在不同的文档上添加事务。Document-Oriented数据库并不支持文档间的事务,如果对这方面有需求则不应该选用这个解决方案。
-
-
键值数据库
是一种较简单的数据库,其中每个项目都包含键和值。通常只能通过引用其键来检索值,因此学习如何查询特定键值对通常很简单。键值数据库非常适合需要存储大量数据但无需执行复杂查询来检索数据的用例。
支持搜索功能
键值存储使用关系数组作为其基本数据模型。在此模型中,数据表示为键-值对的集合,这样每个可能的键在集合中最多出现一次。
键值模型是最简单的非平凡数据模型之一,并且更丰富的数据模型通常是对其进行扩展的。键值模型可以扩展为按词典顺序维护键的离散排序模型。此扩展具有强大的计算功能,因为它可以有效地检索选择性键范围。
键值存储区可以使用从最终一致性到可序列化性的一致性模型。一些数据库支持键的排序。有各种硬件实现方式,有些用户将数据存储在内存中,而其他用户则存储在固态驱动器或旋转磁盘上。
-
典型应用场景
内容缓存,主要用于处理大量数据的高访问负载,也用于一些日志系统等等
-
不适用场景
- 取代通过键查询,而是通过值来查询。Key-Value数据库中根本没有通过值查询的途径。
- 需要储存数据之间的关系。在Key-Value数据库中不能通过两个或以上的键来关联数据。
- 事务的支持。在Key-Value数据库中故障产生时不可以进行回滚。
-
-
列存储数据库
将数据存储在表、行和动态列中。列存储提供了比关系数据库有了更大的灵活性,因为不需要每一行都具有相同的列。许多人认为列存储是二维键值数据库。列存储非常适合需要存储大量数据并且可以预测查询模式的情况。列存储通常用于存储物联网数据和用户配置文件数据。
-
典型应用场景
分布式的文件系统
-
不适用场景
- 如果我们需要ACID事务。Vassandra就不支持事务。
- 原型设计。如果我们分析Cassandra的数据结构,我们就会发现结构是基于我们期望的数据查询方式而定。在模型设计之初,我们根本不可能去预测它的查询方式,而一旦查询方式改变,我们就必须重新设计列族。
-
-
图形数据库
将数据存储在节点和边中。节点通常存储有关人物,地点和事物的信息,而边缘则存储有关节点之间的关系的信息。在需要遍历关系以查找模式的用例中,图形数据库就十分出色。
图形数据库是为数据的关系而设计的,它的关系很好地表示为由有限数量的关系连接的元素组成的图。数据示例包括社会关系,公共交通连接,路线图,网络拓扑等。
-
典型应用场景
社交网络,推荐系统等。专注于构建关系图谱。
-
不适用场景
不适合的数据模型。图数据库的适用范围很小,因为很少有操作涉及到整个图。
-
| Data model | Performance | Scalability | Flexibility | Complexity | Functionality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key–value store | high | high | high | none | variable (none) |
| Column-oriented store | high | high | moderate | low | minimal |
| Document-oriented store | high | variable (high) | high | low | variable (low) |
| Graph database | variable | variable | high | high | graph theory |
| Relational database | variable | variable | low | moderate | relational algebra |
二者区别与比较
Non Relational Databases, or NoSQL databases, store and organize data in means other than the tabular relations model used in relational databases. Where relational databases store data in rows and columns, have strict rules concerning data variety and table relationships, and follow strict ACID properties, non relational databases offer a more flexible data structure based on the BASE (Basically Available, Soft state, Eventual consistency) model: Basically Available guarantees the availability of the data - there will be a response to any request, but without any consistency guarantee; Soft State guarantees that the state of the system could change over time; and Eventual Consistency guarantees that the system will eventually become consistent once it stops receiving inputs.
非关系数据库以与关系数据库中使用的表格关系模型不同的方式存储和组织数据。关系数据库在行和列中存储数据,具有关于数据种类和表关系的严格规则并遵循严格的ACID属性的情况下,非关系数据库基于BASE(基本可用,软状态,最终一致性)模型提供更灵活的数据结构:基本上可用保证数据的可用性——将对任何请求作出响应,但不提供任何一致性保证;软状态保证系统的状态可用随时间变化;最终一致性可确保系统一旦停止接收输入,最终将变得一致。
-
数据存储方式不同
关系型和非关系型数据库的主要差异是数据存储的方式。关系型数据天然就是表格式的,因此存储在数据表的行和列中。数据表可以彼此关联协作存储,也很容易提取数据。
与其相反,非关系型数据不适合存储在数据表的行和列中,而是大块组合在一起。非关系型数据通常存储在数据集中,就像文档、键值对或者图结构。你的数据及其特性是选择数据存储和提取方式的首要影响因素。
-
扩展方式不同
SQL和NoSQL数据库最大的差别可能是在扩展方式上,要支持日益增长的需求当然要扩展。
要支持更多并发量,SQL数据库是纵向扩展,也就是说提高处理能力,使用速度更快速的计算机,这样处理相同的数据集就更快了。
因为数据存储在关系表中,操作的性能瓶颈可能涉及很多个表,这都需要通过提高计算机性能来客服。虽然SQL数据库有很大扩展空间,但最终肯定会达到纵向扩展的上限。而NoSQL数据库是横向扩展的。
而非关系型数据存储天然就是分布式的,NoSQL数据库的扩展可以通过给资源池添加更多普通的数据库服务器(节点)来分担负载。
-
对事务性的支持不同
如果数据操作需要高事务性或者复杂数据查询需要控制执行计划,那么传统的SQL数据库从性能和稳定性方面考虑是你的最佳选择。SQL数据库支持对事务原子性细粒度控制,并且易于回滚事务。
虽然NoSQL数据库也可以使用事务操作,但稳定性方面没法和关系型数据库比较,所以它们真正闪亮的价值是在操作的扩展性和大数据量处理方面。
-
存储方式
SQL数据存储于特定结构的表中;NoSQL更加灵活和可扩展,存储方式可用是JSON文档、哈希表或者其他方式。
-
表/数据集合的数据的关系
在SQL中必须定义好表和字段结构后才能添加数据。表结构可以在被定义之后更新,但是如果有比较大的结构变更的话就会变得比较复杂。在NoSQL中,数据可以在任何时候任何地方添加,不需要先定义表。NoSQL可以在数据集中建立索引,NoSQL更适合初始化数据还不明确或者未定的项目中。
-
外部数据存储
SQL中如何需要增加外部关联数据的话,规范化做法是在原表中增加一个外键,关联外部数据表;在NoSQL中除了这种规范化的外部数据表做法以外,还能用非规范化方式把外部数据直接放到原数据集中,以提高查询效率。
-
SQL中的JOIN查询
SQL中科院使用JOIN表链接方式将多个关系数据表中的数据用一条简单的查询语句查询出来。NoSQL暂未提供类似JOIN的查询方式对多个数据集中的数据做查询。
-
数据耦合性
SQL中不允许删除已经被使用的外部数据;而NoSQL中则没有这种强耦合的概念,可以随时删除任何数据。
-
事务
SQL中如果多张表数据需要同批次被更新,即如果其中一张表更新失败的话其他表也不能更新成功。这种场景可以通过事务来控制,可以在所有命令完成后再统一提交事务。而NoSQL中没有事务这个概念,每一个数据集的操作都是原子级的。
关系型数据库适合存储结构化数据,如用户的帐号、地址:
- 这些数据通常需要做结构化查询(嗯,好像是废话),比如join,这时候,关系型数据库就要胜出一筹
- 这些数据的规模、增长的速度通常是可以预期的
- 事务性、一致性
NoSQL适合存储非结构化数据,如文章、评论:
- 这些数据通常用于模糊处理,如全文搜索、机器学习
- 这些数据是海量的,而且增长的速度是难以预期的
- 根据数据的特点,NoSQL数据库通常具有无限(至少接近)伸缩性按
- key获取数据效率很高,但是对join或其他结构化查询的支持就比较差
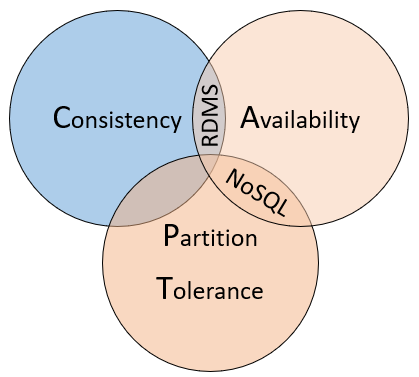
CAP定理
对于一个分布式计算系统,不可能同时满足以下三点:
-
Consistency 一致性
所有节点访问同一份最新的数据副本
即使系统必须阻止请求,直到所有副本更新,集群中的每个节点都以最新数据响应。如果在一致的系统中查询当前正在更新的项目,则将等待该响应,直到所有副本都成功更新为止,但将收到最新的数据。
-
Availability 可用性
每次请求都能获取到非错的响应——但是不保留获取的数据为最新数据
每个节点都会返回立即响应。即使该响应不是最新数据也是如此。如果在可用系统中查询正在更新的项目,那么将获得该服务当时提供的最佳答案。
-
Partition tolerance 分区容错性
以实际效果而言,分区相当于对通信的时限要求。系统如果不能在时限内达成数据一致性,就意味着发生了分区的情况,必须就当前操作在C和A之间做出选择。
即使复制的数据节点发生故障或失去与其他复制的数据节点的连接,也可以确保系统继续运行。
Many relational database systems support built-in replication features where copies of the primary database can be made to other secondary server instances. Write operations are made to the primary instance and replicated to each of the secondaries. Upon a failure, the primary instance can fail over to a secondary to provide high availability. Secondaries can also be used to distribute read operations. While writes operations always go against the primary replica, read operations can be routed to any of the secondaries to reduce system load.
Data can also be horizontally partitioned across multiple nodes, such as with sharding. But, sharding dramatically increases operational overhead by spitting data across many pieces that cannot easily communicate. It can be costly and time consuming to manage. It can end up impacting performance, table joins, and referential integrity.
If data replicas were to lose network connectivity in a “highly consistent” relational database cluster, you wouldn’t be able to write to the database. The system would reject the write operation as it can’t replicate that change to the other data replica. Every data replica has to update before the transaction can complete.
关系数据库通常提供一致性和可用性,但不提供分区容限。通常将它们配置到单个服务器,并通过向计算机添加更多资源来垂直扩展。许多关系数据库系统支持内置的复制功能,可以在其中将主数据库的副本复制到其他辅助服务器实例。对主实例进行写操作,然后将其复制到每个辅助实例。发生故障时,主实例可以故障转移到辅助实例以提高高可用性。次要对象还可以用于分发读取操作。虽然写操作始终与主副本相反,但可以将读操作路由到任何辅助副本,以减少系统负载。数据也可以在多个节点之间进行水平分区,例如使用分片。但是分片会将数据分散在许多不易通信的数据块上,从而大大增加了操作开销。管理起来可能既昂贵又费时。最终可能会影响性能,表链接和参照完整性。如果数据副本在高度一致的关系数据库群集中失去网络连接,则将无法写入数据库。系统将拒绝写操作,因为它无法将更改复制到其他数据副本。每个数据副本都必须先更新,然后事务才能完成。
NoSQL databases typically support high availability and partition tolerance. They scale out horizontally, often across commodity servers. This approach provides tremendous availability, both within and across geographical regions at a reduced cost. You partition and replicate data across these machines, or nodes, providing redundancy and fault tolerance. The downside is consistency. A change to data on one NoSQL node can take some time to propagate to other nodes. Typically, a NoSQL database node will provide an immediate response to a query - even if the data that is presented is stale and hasn’t updated yet.
If data replicas were to lose connectivity in a “highly available” NoSQL database cluster, you could still complete a write operation to the database. The database cluster would allow the write operation and update each data replica as it becomes available.
This kind of result is known as eventual consistency, a characteristic of distributed data systems where ACID transactions aren’t supported. It’s a brief delay between the update of a data item and time that it takes to propagate that update to each of the replica nodes. Under normal conditions, the lag is typically short, but can increase when problems arise. For example, what would happen if you were to update a product item in a NoSQL database in the United States and query that same data item from a replica node in Europe? You would receive the earlier product information, until the cluster updates the European node with the product change. By immediately returning a query result and not waiting for all replica nodes to update, you gain enormous scale and volume, but with the possibility of presenting older data.
NoSQL数据库通常支持高可用性和分区容限。它们通常在商品服务器之间横向扩展。这种方法以低成本在地理区域内核地理区域内提供了巨大的可用性。可以在这些计算机或节点之间分区和复制数据,从而提供冗余和容错能力。缺点是一致性。一个NoSQL节点上的数据更改可能需要一些时间才能传播到其他节点。通常,NoSQL数据库节点将提供对查询的立即响应——即使所提供的的数据过时且未更新。
如果数据副本将在高度可用的NoSQL数据库群集中失去连接,则仍可用完成对数据库的写操作。数据库集群将允许写操作,并在每个数据副本可用时更新它们。
这种结果称为最终一致性,这是不支持ACID事务的分布式数据系统的特征。在数据项的更新与将更新传播到每个副本节点所花费的时间之间存在短暂的延迟。在正常情况下,滞后通常很短,但是当出现问题时滞后会增加。例如,如果要在美国的NoSQL数据库中更新产品项并从欧洲的副本节点查询相同的数据项,会发生什么情况?将收到较早的产品信息,直到集群使用产品更改更新欧洲节点。通过立即返回查询结果而不等待所有副本节点更新,将获得巨大的规模和数量,但有可能预示较旧的数据。
| Consider a NoSQL datastore when: | Consider a relational database when: |
|---|---|
| You have high volume workloads that require large scale | Your workload volume is consistent and requires medium to large scale |
| Your workloads don’t require ACID guarantees | ACID guarantees are required |
| Your data is dynamic and frequently changes | Your data is predictable and highly structured |
| Data can be expressed without relationships | Data is best expressed relationally |
| You need fast writes and write safety isn’t critical | Write safety is a requirement |
| Data retrieval is simple and tends to be flat | You work with complex queries and reports |
| Your data requires a wide geographic distribution | Your users are more centralized |
| Your application will be deployed to commodity hardware, such as with public clouds | Your application will be deployed to large, high-end hardware |
典型产品
SQL Server
由Microsoft开发的关系数据库管理系统。作为数据库服务器,是一种软件产品,其主要功能是根据其他软件应用程序的请求来存储和检索数据,这些软件可以在同一台计算机上运行,也可以在网络上的另一台计算机上运行。
- 易用性
- 适合分布式组织的可伸缩性
- 用于决策支持的数据仓库功能
- 与相关软件紧密关联的集成性
- 良好的性价比
MongoDB
MongoDB is a cross-platform document-oriented database program. Classified as a NoSQL database program, MongoDB uses JSON-like documents with optional schemas. MongoDB is developed by MongoDB Inc. and licensed under the Server Side Public License (SSPL).
MongoDB是一个跨平台的面向文档的数据库,具有可伸缩性和灵活性,可用于所需的查询和索引编制。
- 将数据存储在类似于JSON的灵活文档中,这意味着字段随文档的不同而不同,并且数据结构可以随时间而变化
- 文档模型映射到应用程序代码中的对象,从而使数据易于使用
- 临时查询,索引编制和实时聚合提供了访问和分析数据的强大方法
- MongoDB以分布式数据库为核心,因此内置了高可用性,水平扩展和地理分布并且易于使用
- MongoDB是免费使用的
高性能、易部署、易使用、存储数据非常方便
-
模式少
MongoDB是一个文档数据库,其中一个集合包含不同的文档。一个文档之间的字段数,内容和文档大小可能会有所不同。
-
单个对象的结构清晰
-
没有复杂的联接
-
深入的查询能力
MongoDB支持使用与SQL几乎一样强大的基于文档的查询语言对文档进行动态查询
-
易于扩展
-
不需要将应用程序对象转换/映射到数据库对象
-
使用内部存储器存储工作集,从而可以更快地访问数据
参考资料
[1] https://www.omnisci.com/technical-glossary/relational-database
[2] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relational_database
[3] https://www.mongodb.com/non-relational-database
[4] https://www.mongodb.com/nosql-explained
[5] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NoSQL
[6] https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/architecture/cloud-native/relational-vs-nosql-data
[7] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAP_theorem
[8] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microsoft_SQL_Server
[9] https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/sql-server/sql-server-2019-features
[10] https://www.mongodb.com/what-is-mongodb
标签:database,data,数据库,第二周,研讨,databases,relational,数据 来源: https://blog.csdn.net/Smoothie_/article/details/112309965