CF446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
作者:互联网
CF446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers
题目描述
In mathematical terms, the sequence F_{n}*F**n* of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation
F_{1}=1; F_{2}=1; F_{n}=F_{n-1}+F_{n-2} (n>2). DZY loves Fibonacci numbers very much. Today DZY gives you an array consisting of nn integers: a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{n}a1,a2,...,*a**n* . Moreover, there are mm queries, each query has one of the two types:
- Format of the query " 1 l r1 l r ". In reply to the query, you need to add F_{i-l+1}Fi−l+1 to each element a_{i}ai , where l<=i<=rl<=i<=r .
- Format of the query " 2 l r2 l r ". In reply to the query you should output the value of
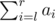 modulo 1000000009 (10^{9}+9) .
modulo 1000000009 (10^{9}+9) .
Help DZY reply to all the queries.
输入格式
The first line of the input contains two integers nn and mm ( 1<=n,m<=3000001<=n,m<=300000 ). The second line contains nn integers a_{1},a_{2},...,a_{n} (1<=a_{i}<=10^{9}) — initial array aa .
Then, mm lines follow. A single line describes a single query in the format given in the statement. It is guaranteed that for each query inequality 1<=l<=r<=n1<=l<=r<=n holds.
输出格式
For each query of the second type, print the value of the sum on a single line.
题意翻译
题面大意:给出一个数列,每次可以选取一个区间,按顺序加上第i个Fibonacci Numbers(斐波那契数)进行更新,也可以查询某一个区间的总和。
感谢@char32_t 提供的翻译
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
输出 #1复制
说明/提示
After the first query, a=[2,3,5,7]a=[2,3,5,7] .
For the second query, sum=2+3+5+7=17sum=2+3+5+7=17 .
After the third query, a=[2,4,6,9]a=[2,4,6,9] .
For the fourth query, sum=2+4+6=12sum=2+4+6=12 .
题解:
2019.11.5模拟赛T3 40分场
\(O(n^2)\)的做法能水10分,普通线段树毫无优化能跑30分。感谢出题人@littleseven
一看是黑题顿时毫无思路。因为这道题涉及到的知识点:线段树+\(Fibonacci\)数列是联赛范围内,所以它就这样被收进了联赛模拟赛中。
介绍一下正解:
首先我们能想到,区间修改区间查询一定需要线段树。而且这道题难住我们的点就是如何维护修改操作,换句话说,如何进行下传标记。
但是我们稍微动动脑能发现这个性质:(我在考场上也推出来了)
对于一个要修改的区间\([l,r]\)中的第\(x\)项,它需要加上这一项:\(fib_{x-l+1}\)。\(fib\)表示斐波那契数列。
而斐波那契数列有这样的性质:(很重要,虽然蒟蒻也是做了这道题才知道)
\[
fib[n+m]=fib[n+1]fib[m]+fib[n]fib[m-1]
\]
那么对于这个位置\(x\),设\(n=-l,m=x+1\),它加上了:
\[
fib[x-l+1]=fib[1-l]fib[x+1]+fib[x]fib[-l]
\]
那么对于线段树上的节点,我们需要维护两个标记:\(add1[i],add2[i]\),分别统计对于一个区间为\([l,r]\)的节点,\(add1(fib_{l+1}+fib_{l+2}+\cdots+fib_{r+1})\),\(add2(fib_{l}+fib_{l+1}+\cdots+fib_{r})\)。
修改的时候,给\(add1\)加上\(fib_{-l+1}\),给\(add2\)加上\(fib_{-l}\),然后进行线段树的正常\(pushdown\)操作即可。
代码:
#include<cstdio>
#define lson pos<<1
#define rson pos<<1|1
using namespace std;
const int maxn=3*1e5+10;
const int mod=1e9+9;
char *p1,*p2,buf[100000];
#define nc() (p1==p2&&(p2=(p1=buf)+fread(buf,1,100000,stdin),p1==p2)?EOF:*p1++)
int read()
{
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=nc();
while(ch<48){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=nc();}
while(ch>47) x=(((x<<2)+x)<<1)+ch-48,ch=nc();
return x*f;
}
int n,m;
int a[maxn],sum[maxn],fib[maxn],ffib[maxn];
int tree[maxn<<2],add1[maxn<<2],add2[maxn<<2];
void fibonacci()
{
fib[1]=fib[2]=sum[1]=ffib[1]=1;
sum[2]=2;
ffib[2]=mod-1;
for(int i=3;i<=n+1;i++)
{
fib[i]=(fib[i-1]+fib[i-2])%mod;
sum[i]=(sum[i-1]+fib[i])%mod;
ffib[i]=(i&1)?fib[i]:mod-fib[i];
}
}
void build(int pos,int l,int r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(l==r)
{
tree[pos]=a[l]%mod;
return;
}
build(lson,l,mid);
build(rson,mid+1,r);
tree[pos]=(tree[lson]+tree[rson])%mod;
}
void mark(int pos,int l,int r,int a1,int a2)
{
add1[pos]=(add1[pos]+a1)%mod;
add2[pos]=(add2[pos]+a2)%mod;
tree[pos]=(tree[pos]+1ll*(sum[r+1]-sum[l]+mod)%mod*a1%mod)%mod;
tree[pos]=(tree[pos]+1ll*(sum[r]-sum[l-1]+mod)%mod*a2%mod)%mod;
}
void pushdown(int pos,int l,int r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
mark(lson,l,mid,add1[pos],add2[pos]);
mark(rson,mid+1,r,add1[pos],add2[pos]);
add1[pos]=add2[pos]=0;
}
void update(int pos,int l,int r,int x,int y,int a1,int a2)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(x<=l && r<=y)
{
mark(pos,l,r,a1,a2);
return;
}
pushdown(pos,l,r);
if(x<=mid)
update(lson,l,mid,x,y,a1,a2);
if(y>mid)
update(rson,mid+1,r,x,y,a1,a2);
tree[pos]=(tree[lson]+tree[rson])%mod;
}
int query(int pos,int l,int r,int x,int y)
{
int ret=0;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if(x<=l && r<=y)
return tree[pos]%mod;
pushdown(pos,l,r);
if(x<=mid)
ret=(ret+query(lson,l,mid,x,y))%mod;
if(y>mid)
ret=(ret+query(rson,mid+1,r,x,y))%mod;
return ret%mod;
}
int main()
{
n=read();m=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
a[i]=read();
fibonacci();
build(1,1,n);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int opt,l,r;
opt=read();l=read();r=read();
if(opt==1)
update(1,1,n,l,r,ffib[l-1],ffib[l]);
else
printf("%d\n",query(1,1,n,l,r));
}
return 0;
}标签:CF446C,int,tree,pos,fib,Fibonacci,DZY,query,mod 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/fusiwei/p/11799491.html