56.Django项目实例详解(一)
作者:互联网
在本节我们继续以项目实例的形式带领小伙伴们使 Django 进行相关的 Web 开发任务,在《Django HTML表单实例应用》一节中,我们使用 HTML 表单完成了 书籍的查询功能。在本节我们将以完整的逻辑呈现图书的管理操作,本节的代码会较多,希望小伙伴们多加领悟,善于总结,并有所收获。下面我们正式开始本节的内容。
1. 获取全量书籍信息
将书籍的信息以表格的信息呈现的前端页面,通过页面中的的增加、删除按钮对表中的每条数据进行操作。这是本节要实现的主体功能。我们首先将书籍的信息按照表格的形式展现出来。在 index\templates 中编写 book_table.html 页面,代码如下所示:
- <html lang="en">
- <head>
- <meta charset="UTF-8">
- <title>书籍信息表</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <table border="1">
- <tr>
- <th>id</th>
- <th>title</th>
- <th>price</th>
- <th> retail_price</th>
- <th>public</th>
- <th>option</th>
- </tr>
- {% for book in all_book %}
- <tr>
- <td>{{ book.id }}</td>
- <td>{{ book.title }}</td>
- <td>{{ book.price }}</td>
- <td>{{ book.retail_price }}</td>
- <td>{{ book.pub.pubname }}</td>
- <td>
- <a href="/index/update_book/{{ book.id }}">更新</a>
- <a href="/index/delete_book/{{ book.id }}">删除</a>
- </td>
- </tr>
- {% endfor %}
- </table>
- </body>
- </html>
上述代码中我们我们构建了一个有关书籍信息表的表格,下面就需要在 index.views.py 文件中编写视图层代码逻辑了,代码如下所示:
- """
- time: 22/6
- item: Book CURD
- """
- def book_table(request):
- try:
- all_book=Book.objects.all().order_by('-price')
- if not all_book:
- return HttpResponse('书籍信息表为空,请录入!')
- except Exception as e:
- print(e)
- return render(request, 'index/book_table.html', locals())
并配置路由映射关系,最后访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/index/all_book/ 可得如下界面显示:
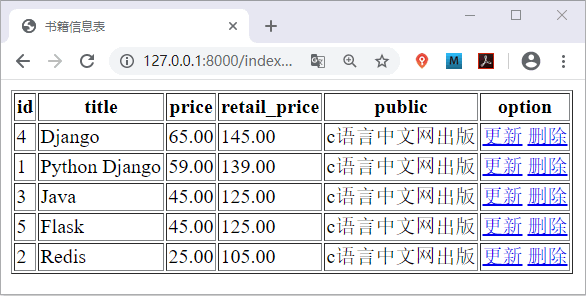
图1:Django实例书籍信息表
2. 实现添加书籍信息
接下来实现书籍信息的添加功能,编写 add_book.html 页面,代码如下所示:
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html lang="en">
- <head>
- <meta charset="UTF-8">
- <title>添加书籍信息</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <form action="/index/add_book/" method="post">
- {% csrf_token %}
- <p>
- title : <input type="text" name="title">
- </p>
- <p>
- price : <input type="text" name="price">
- </p>
- <p>
- retail_price : <input type="text" name="retail_price">
- </p>
- <p>
- public : <input type="text" name="pub">
- </p>
- <p>
- <!--按钮的值提交--> <input type="submit" value="提交">
- </p>
- </form>
- </body>
- </html>
上述我们编写完成了添加书籍信息的页面,然后需要在视图层 index\views.py 中编写提交书籍信息的逻辑代码。如下所示:
- def add_book(request):
- if request.method == 'GET':
- return render(request, 'index/add_book.html')
- elif request.method == 'POST':
- #添加书籍
- title = request.POST.get('title')
- if not title:
- return HttpResponse('请给出一个正确的title')
- pub = request.POST.get('pub')
- price = float(request.POST.get('price','999.99'))
- if not price:
- return HttpResponse('请输入价格')
- try:
- retail_price = float(request.POST.get('retail_price'))
- if not retail_price:
- return HttpResponse('请输入市场价')
- except Exception as e:
- print(e)
- #判断title是不是已经存在了
- old_book = Book.objects.filter(title=title)
- if old_book:
- return HttpResponse('你输入的书籍系统已经存在 !')
- try:
- pub1=PubName.objects.get(pubname=str(pub))
- Book.objects.create(title=title,price=price,retail_price=retail_price,pub=pub1)
- except Exception as e:
- print('Add ErrorReason is %s'%(e))
- return HttpResponseRedirect('/index/all_book')
- return HttpResponse('请使用正确Http请求方法 !')
最后将路由映射关系配置完成,通过上面的代码我们就完成书籍信息的添加的功能,访问 127.0.0.1/index/add_book,可得如下界面:
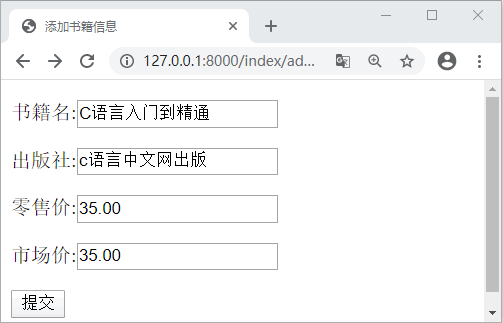
图2:Django实例图书添加功能
输入完上述信息点击添加按钮,会自动跳转到图书浏览目录页面,如下所示:
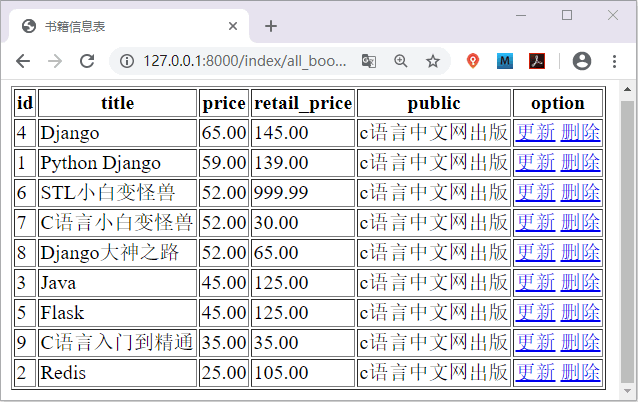
图3:Django实例图书添加功能
在本节中,我们实现了书籍的全量展示功能以及图书的添加功能。上述代码理解起来会比较的直观简单,但是实际编写起来,会有很多需要注意的细节,需要开发者做到思维缜密,当然这个能力并非一蹴而就,需要大家不断的练习与自我提升才可以。在下一节中,我们将继续讲解 Django 项目的实例应用,希望大家通过讲解能够熟练的使用Django 并将其作为 Web 开发的工具。
标签:return,title,price,56,request,Django,book,书籍,详解 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/55zjc/p/16544064.html