JDBC
作者:互联网
JDBC
Java Database Connectivity
java连接数据库的技术
sun公司的一批工程师希望一统数据库连接的江湖
也就是说这帮人希望实现一套API能够连接市面所有的数据库
发现不可能,因为每一个数据库的实现方式是完全不一样的
方案:
1.放弃这个项目
2.自己只设计接口,然后要求每一个数据库厂商自己实现接口
最后选择了方案2
所以:
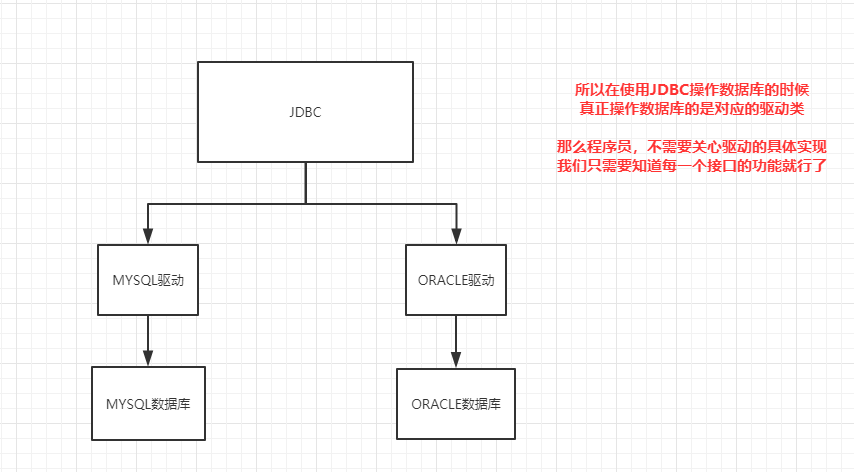
JDBC只是一套接口,没有具体的实现类
数据库厂商提供的实现类,称之为驱动
所以要使用JDBC连接指定数据库,必须先引入对应的驱动
一、JDBC核心接口
(1)Connection
表示与数据库的连接
也就是说如果能获取到Connection实现类的对象,就说明我们连上了数据库
连数据库需要提供的数据:
1. 连接的路径
2. 用户名
3. 密码
(2)StateMent
用来执行sql语句
(3)ResultSet
如果执行的是DQL,则自动使用ResultSet的实现类对象来封装结果集的所有信息
所以使用JDBC的过程:
1.先获取Connection对象
2.使用StateMent执行指定的sql语句
3.可能需要使用ResultSet接收结果集
二、第一个JDBC程序
1.导包
注意:导包的时候一定要导入对应版本的jar包
2.注册驱动
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
3.获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
4.创建Statement
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
5.CRUD
String sql = "INSERT INTO dept VALUES(50, '公关部', '肖家河大厦')";
6.操作结果集
int result = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
7.关闭连接
connection.close()
package com.qianfeng.jdbcDemo;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/*
第一个jdbc程序
测试使用JDBC做插入数据
*/
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//获取Connection
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
/*
执行sql语句
1.定义sql语句: 向dept表插入一条数据
2.创建Statement接口的实现类对象
3.调用Statement接口的实现类对象的方法执行sql语句
*/
String sql = "INSERT INTO dept VALUES(50, '公关部', '肖家河大厦')";
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//返回值代表在表中影响的行数
int result = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(result);
}
}
三、中文问题
如果使用jdbc向数据库插入中文数据,有可能出现乱码的情况
出现乱码的原因:肯定是因为编码与解码的格式不一致
涉及到字符集的地方:
1.数据库
2.开发环境(IDEA)
3.传输过程
以上三个地方都要讲字符集设置为utf-8
设置传输过程的字符编码:
在url后添加参数
jdbc:mysql://locolhost:3306/java2103?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
主要:是utf8不是utf-8
如果是使用的mysql8,则url写为:
jdbc:mysql://locolhost:3306/java2103?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=GMT&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
练习:
使用JDBC对dept表分别做DELETE/UPDATE操作
四、使用JDBC做DQL操作
(1)ResultSet的使用

(2)查询单行数据
package com.qianfeng.jdbcDemo;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Dept dept = findDeptByDeptno(10);
System.out.println(dept);
}
public static Dept findDeptByDeptno(int deptno) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Dept dept = null;
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=GMT";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
String sql = "SELECT * FROM dept WHERE deptno = " + deptno;
Statement stmt = connection.createStatement();
/*
executeUpdate 执行DML操作 返回值是影响的函数
executeQuery 执行DQL操作 返回值是结果集
*/
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
/*
将rs的数据取出,然后封装成Dept对象并返回
*/
if(rs.next()){//如果后面有记录,则返回true,并使指针往下移动一行,指向指向记录
int dno = rs.getInt(1);//取出当前行第一列的数据
String dname = rs.getString("dname");//取出当前行列名为dname的数据
String loc = rs.getString("loc");//取出当前行列名为loc的数据
dept = new Dept();
dept.setDeptno(dno);
dept.setDname(dname);
dept.setLoc(loc);
}
return dept;
}
}
(3)查询多行数据
package com.qianfeng.jdbcDemo;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/*
查询多行记录
*/
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
List<Dept> allDepts = findAllDepts();
System.out.println(allDepts);
}
public static List<Dept> findAllDepts() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
ArrayList<Dept> list = new ArrayList<>();
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=GMT";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
String sql = "SELECT * FROM dept";
Statement stmt = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){//控制指针指向每一行记录
int deptno = rs.getInt("deptno");
String dname = rs.getString(2);
String loc = rs.getString("loc");
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setDeptno(deptno);
dept.setDname(dname);
dept.setLoc(loc);
list.add(dept);
}
return list;
}
}
五、要求(重要)
一定要会写增删改查!!!
六、SQL注入
用户在输入数据时,如果输入的数据被用来执行sql语句,则该数据可能绕过我们指定的sql验证
例如 登录案例:
用户输入: 用户名 密码
正常情况:只有用户名与密码都正确才能登录成功
sql注入:完全不指定你的用户名与密码,但是还是能登录成功
package com.qianfeng.jdbcDemo;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
演示登录案例
模拟sql注入
*/
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
/*
sql注入:
如果我们用户名随便写
但是密码写:a' OR '1' = '1
会发现还是可以登录成功
原因:
因为使用用户输入的用户名与密码,拼接成的sql语句的内容如下:
SELECT * FROM user WHERE uname='sfdsfds' AND password='a' OR '1' = '1'
而这个sql语句的条件永远成立,所以肯定能登录成功
这就是所谓的sql注入
根据分析可得:
sql注入产生的原因:使用用户输入的值来拼接操作数据库的sql语句
*/
String username = scanner.nextLine();
String password = scanner.nextLine();
if(login(username, password)){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}
/*
模拟登录的场景
登录的业务逻辑:
如果用户输入的用户名与密码都存在指定表中的同一行记录中,则登录成功
*/
public static boolean login(String username, String password) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=GMT";
String uname = "root";
String pwd = "123456";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, uname, pwd);
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE uname='" +username + "' AND password='" +password +"'";
System.out.println(sql);
Statement stmt = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
if(rs.next()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
七、PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement是Statement的子接口
所以我们可以认为PreparedStatement是对Statement的扩展
PreparedStatement扩展了预编译功能
预编译:
先将需要指定值的sql先交给PreparedStatement来处理,
然后在将需要的值交给PreparedStatement
使用方式:
public static boolean login(String username, String password) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
....
/*
被预编译的sql语句可以使用占位符
占位符的效果:相当于告诉PreparedStatement 使用占位符的位置需要使用指定的值
*/
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE uname=? AND password=?";
PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepraedStatement(sql);
/*
在执行sql语句之前,使用指定的值替换占位符
使用pstmt.setXxx(占位符索引, 给占位符的值),索引从1开始取
Xxx表示对应的类型
*/
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, password);
//执行sql语句:不用指定sql语句
pstmt.executeQuery();
}
根据上面写法可得:
就没有使用拼接字符串的方式拼接sql语句了,从根源上就杜绝了sql注入
在实际开发中,建议都使用PreparedStatement
(1)PreparedStatement的执行原理
在预编译的时候,会将带占位符的sql语句解析为一个函数,占位符会被解析为该函数的形参
当使用setXxx方法时,相当于使用实参给形参赋值
当调用executeUpdate()/executeQuery()方法相当于在指向这个函数
(2)PreparedStatement的优势
1.安全,不可能出现sql注入
2.效率高, 函数具备复用性
package com.qianfeng.jdbcDemo;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
演示登录案例
模拟sql注入
*/
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
/*
sql注入:
如果我们用户名随便写
但是密码写:a' OR '1' = '1
会发现还算可以登录成功
原因:
业务使用用户输入的用户名与密码,拼接成的sql语句的内容如下:
SELECT * FROM user WHERE uname='sfdsfds' AND password='a' OR '1' = '1'
而这个sql语句的条件永远成立,所以肯定能登录成功
这就是所谓的sql注入
根据分析可得:
sql注入产生的原因:使用用户输入的值来拼接操作数据库的sql语句
*/
String username = scanner.nextLine();
String password = scanner.nextLine();
// if(login(username, password)){
// System.out.println("登录成功");
// }else{
// System.out.println("登录失败");
// }
/*
使用PreparedStatement就不可能出现sql注入了!
*/
if(loginPlus(username, password)){
System.out.println("登录成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败");
}
}
/*
模拟登录的场景
登录的业务逻辑:
如果用户输入的用户名与密码都存在指定表中的同一行记录中,则登录成功
*/
public static boolean login(String username, String password) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=GMT";
String uname = "root";
String pwd = "123456";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, uname, pwd);
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE uname='" +username + "' AND password='" +password +"'";
System.out.println(sql);
Statement stmt = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
if(rs.next()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static boolean loginPlus(String username, String password) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&serverTimezone=GMT";
String uname = "root";
String pwd = "123456";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, uname, pwd);
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE uname = ? AND password = ?";
PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, username);
pstmt.setString(2, password);
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
八、批量处理
将大量的sql语句存在一起,统一处理
批量处理的优势:效率非常高
使用方式:
1.打开批处理
在url中添加一个参数:rewriteBatchedStatements=true
2.将需要执行的sql语句添加到队列中
preparedStatement.addBatch()
3.将所有添加的sql语句一次性的执行完
preparedStatement.executeBatch()
测试:
package com.qianfeng.jdbcDemo;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/*
批量处理
向demo5表中插入1000条数据
*/
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
addNormal();
//addBatch();
}
/*
使用非批量处理,插入1000条数,花的时间:4秒以上
*/
public static void addNormal() throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8";
String uname = "root";
String pwd = "123456";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, uname, pwd);
String sql = "INSERT INTO demo5 VALUES (NULL, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
pstmt.setString(1, "jay" +i);
pstmt.setString(2, "123" +i);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
/*
使用批量处理:插入10万条数据
花的时间:不到1秒
*/
public static void addBatch() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?rewriteBatchedStatements=true";
String uname = "root";
String pwd = "123456";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, uname, pwd);
String sql = "INSERT INTO demo5 VALUES (NULL, ?, ?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
pstmt.setString(1, "jay" + i);
pstmt.setString(2, "123" + i);
pstmt.addBatch();//将当前sql添加到批量处理的队列中
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//上面的for循环在批量处理的队列添加了10000条需要被执行的sql,一次性处理完
pstmt.executeBatch();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}
九、注册驱动的原理
注册驱动:
只有在mysql3之前才需要主动的注册驱动
现在我们使用的版本基本上都是5、8
原则上来说可以不用注册驱动
如果你手动的注册了,则提高了你的代码的兼容性
注册驱动的代码:
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
这行代码明明是获取Driver类的类对象,为什么成为注册驱动呢?
原因是:获取类对象时,加载类信息,则执行该类的静态代码块
该类的源码如下:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package com.mysql.jdbc;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
//注册驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}
十、JDBC的规范写法
1.所有的异常都应该处理
2.所有资源应该关闭
Connection 、Statement、 ResultSet
package com.qianfeng.jdbcDemo;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
String uname = "root";
String pwd = "123456";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, uname, pwd);
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE uid = ?";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, 1);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt("uid"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("uname"));
}
}catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(pstmt != null){
try {
pstmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
十一、JdbcUtilV1(工具类的使用)
实际开发中使用JDBC的时候,如果都按照最规范的方法编写代码,编码效率太低,因为重复代码太多了
解决方案:
将重复的代码封装到一个工具类中
然后调用该工具类的方法就行了!
重复的代码有哪些:
1.获取连接
2.关闭资源
package com.qianfeng.utils;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 处理使用Jdbc时重复的代码问题
*/
public class JdbcUtilV1 {
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
private static String username = "root";
private static String password = "123456";
static {
//加载驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取连接
* @return 获取到的连接对象
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
/**
* 关闭指定的JDBC资源
* @param rs
* @param stmt
* @param connection
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stmt, Connection connection){
if(rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(stmt!=null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
测试:
package com.qianfeng.jdbcDemo;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV1;
import java.sql.*;
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
/*
使用工具类来完成test1方法相同的功能
*/
public static void test2(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
connection = JdbcUtilV1.getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE uid = ?";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, 1);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt("uid"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("uname"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtilV1.close(null, pstmt, connection);
}
}
/*
查询user表的单行记录
*/
public static void test1(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/java2103?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
String uname = "root";
String pwd = "123456";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, uname, pwd);
String sql = "SELECT * FROM user WHERE uid = ?";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, 1);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt("uid"));
System.out.println(rs.getString("uname"));
}
}catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(pstmt != null){
try {
pstmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
作业
创建user表,有uid,username,password字段
创建对应的java类
使用JDBC对user表进行增、删、改、查当行记录封装成User对象、查所有记录封装成List集合
要求:
1.不使用工具类
2.使用PreparedStatement
十二、事务的特点(常见的面试题)
ACID
A:原子性
属于事务的多行sql语句作为一个整体,要么全部执行成功,要么全部执行失败
C:一致性
在事务执行之前与事务执行之后,状态一致(数据总和保持一致)
I:隔离性
一个事务在操作某个数据时,其他的事务不允许操作
至于做哪些操作的时候,其他事务不允许操作,可以通过设置数据库的隔离级别来进行设置
D:持久性
一个事务执行完成之后,数据无论如何都不能消失
(1)隔离级别(了解)
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 读未提交 | √ | √ | √ |
| 读已提交 | × | √ | √ |
| 不可重复读 | × | × | √ |
| 串行化 | × | × | × |
脏读:读取到其他事务操作了但是没有提交的数据
可重复读:一个事务多次读取一个数据,但是读取到的值不一致
幻读:一个事务在操作一个表格的数据时,操作的过程中表格中新增了或者减少记录
(2)事务的提交
当我们开启了事务后,属于事务的sql语句执行之后,必须进行提交后才会真正的写入数据库
当提交了事务之后,事务就结束了
例如:
开启事务
sql语句1:修改a用户余额减少100
sql语句2:修改b用户余额增加100
提交事务
(3)mysql操作事务
相应的sql语句
START TRANSACTION; # 开启事务
COMMIT; # 提交事务
ROLLBACK; # 回滚事务
提交事务/回滚事务 都有结束事务的效果
提交事务:将操作的数据都写入数据库
回滚事务:将事务中所有的操作都撤销
示例:
创建一个account表,表示账户,来模拟转账
CREATE TABLE account(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
username VARCHAR(50),
balance DOUBLE(7,1)
);
INSERT INTO account VALUES(NULL, "jay", 100000);
INSERT INTO account VALUES(NULL, "kl", 500);
# 使用jay的账户给kl的账户转100块, 使用事务提交
# 效果:事务中的所有sql语句都生效了
START TRANSACTION;
UPDATE account SET balance = balance - 100 WHERE id = 1;
UPDATE account SET balance = balance + 100 WHERE id = 2;
COMMIT;
# 使用jay的账户给kl的账户转100块, 使用事务回滚
# 效果:事务中的所有sql语句都没有生效
START TRANSACTION;
UPDATE account SET balance = balance - 100 WHERE id = 1;
UPDATE account SET balance = balance + 100 WHERE id = 2;
ROLLBACK;
(4)jdbc操作事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);// 开启事务
connection.commit();//提交事务
connection.rollback();//回滚事务
因为数据默认开启了自动提交:将每一行sql语句当做一个独立的事务,然后sql一执行完,自动提交该事务
所以将自动提交关闭,将相当于开启了事务
如果开启了事务之后,既不提交也不回滚,mysql会在默认时间后自动的回滚该事务
示例:
package com.qianfeng.jdbcDemo;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV2;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/*
测试jdbc操作事务
*/
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
testTransaction();
}
public static void testTransaction(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try{
connection = JdbcUtilV2.getConnection();
String sql = "UPDATE account SET balance = balance + ? WHERE id = ?";
//开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setDouble(1, -100.0);
pstmt.setInt(2, 1);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
/*
主动抛出异常:模拟事务的执行过程中出现了意外
如果将此代码注释掉,则事务就会顺利的提交
否则就会执行事务的回滚
*/
//System.out.println(1/0);
pstmt.setDouble(1, 100.0);
pstmt.setInt(2, 2);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
//如果代码能执行到这儿:说明整个事务中没有出现意外,则提交事务
System.out.println("事务提交了.....");
connection.commit();
}catch (Exception e){
//如果代码执行大这儿:说明执行事务的过程中出现意外了,需要回滚事务
try {
if(connection != null) {
System.out.println("事务回滚了.....");
connection.rollback();
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}finally {
JdbcUtilV2.close(null, pstmt, connection);
}
}
}
十三、转账案例
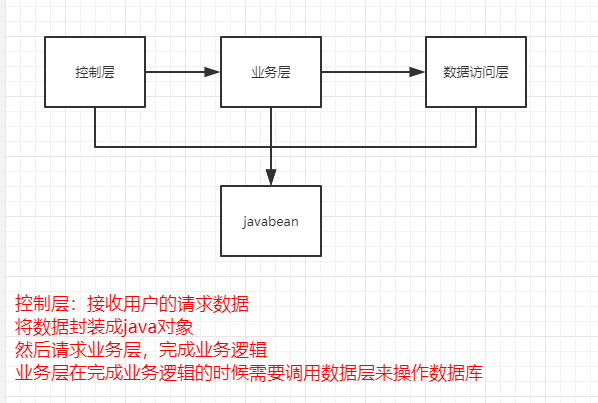
使用分层的思想来完成这个案例
控制层:用接收数据并调用业务层
业务层:专门用来处理业务逻辑
数据层:专门用来处理数据库
模型层:用来存放数据,其实就是javabean
关系:
控制层---依赖于-->业务层---依赖于--> 数据层
(1)Account类
作为Model层,用来存放数据
package com.qianfeng.caseDemo;
public class Account {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Double balance;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
}
(2)AccountDao
package com.qianfeng.caseDemo;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV2;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/*
操作Account相关信息的数据层
只用来操作与Account相关的数据库
*/
public class AccountDao {
/**
* 更新account表的数据类型
* @param account
*/
public void updateAccount(Account account, Connection connection){
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try{
String sql = "UPDATE account SET username=?, balance=? WHERE id=?";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, account.getUsername());
pstmt.setDouble(2, account.getBalance());
pstmt.setInt(3, account.getId());
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}catch (SQLException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
JdbcUtilV2.close(null, pstmt, null);
}
}
/**
* 根据指定的id查找对应的账户
* @param id 指定的账户id
* @return 查询出来的记录转换成的java对象
*/
public Account findAccountById(Integer id) {
Account account = null;
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
connection = JdbcUtilV2.getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM account WHERE id = ?";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, id);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//如果结果集中有记录,则将这一行记录解析为Account对象
if(rs.next()){
int acountId = rs.getInt("id");
String username = rs.getString("username");
double balance = rs.getDouble("balance");
account = new Account();
account.setId(acountId);
account.setUsername(username);
account.setBalance(balance);
}
}catch (SQLException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
JdbcUtilV2.close(rs, pstmt, connection);
}
return account;
}
}
(3)AccountService
package com.qianfeng.caseDemo;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV2;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 用来处理与Account相关的业务逻辑
*/
public class AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDao();
/**
* 转账的业务逻辑
* 将from账户的余额减去money
* 将to账户的余额增长money
*
* @param fromId 转出去的账户Id
* @param toId 接收的账户Id
* @param money 转出去的金额
*/
public void tranfer(Integer fromId, Integer toId, double money) {
Account from = accountDao.findAccountById(fromId);
Account to = accountDao.findAccountById(toId);
Connection connection = null;
try {
/*
注意:开启事务的Connection对象与操作sql的Connection对象
必须是同一个对象
*/
connection = JdbcUtilV2.getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);//开启事务
from.setBalance(from.getBalance() - money);
accountDao.updateAccount(from, connection);
if (from.getBalance() < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("你有钱吗你就转账! 如果转完之后你的余额是:" + from.getBalance());
}
to.setBalance(to.getBalance() + money);
accountDao.updateAccount(to, connection);
connection.commit();
connection.close();
}catch (Exception e){
try {
connection.rollback();
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
(4)AccountController
package com.qianfeng.caseDemo;
/*
处理与Account相关的调度问题
接收数据,响应数据
*/
public class AccountController {
private AccountService accountService = new AccountService();
public void transfer(Integer fromId, Integer toId, double money){
try {
accountService.tranfer(fromId, toId, money);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
System.err.println("转账出现意外!!!");
}
}
}
(5)Main
package com.qianfeng.caseDemo;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入需要转账的账户id");
Integer formId = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入需要接收转账的账户id");
Integer toId = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入转账金额");
Double money = scanner.nextDouble();
AccountController controller = new AccountController();
controller.transfer(formId, toId, money);
}
}
十四、JdbcUtilV4
V4版本解决V3版本的两个问题
1.事务不能重复开启
2.不能支持多线程的情况
解决方案:每一个线程进来,为该线程单独提供一个Connection
使用ThreadLocal可以达到这个效果
package com.qianfeng.utils;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class JdbcUtilV4 {
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
private static String driverClass;
private static String url;
private static String username;
private static String password;
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties"));
driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driverClass);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 一个线程如果是第一次调用此方法,说明没有开启过事务
* 则为该线程单独创建一个Connection对象
* 但是如果一个线程不是第一次调用此方法,则直接将为该线程创建好的Connection对象返回
* @return
*/
public static Connection getTranConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
if(connection == null){
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
threadLocal.set(connection);
}
return connection;
}
/**
* 开启事务
*/
public static void startTrans() throws SQLException {
//同一个Connection对象不能在结束事务之前,多次开启事务
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
if(connection != null){
throw new RuntimeException("事务不能重复开启");
}
connection = getTranConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
}
/**
* 提交事务
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void commit() throws SQLException {
//如果没有开启过事务,则不允许提交
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
if(connection == null){
throw new RuntimeException("请先开启事务再提交!");
}
connection.commit();//提交事务
connection.close();//关闭连接
threadLocal.remove();//将Connection对象从threadLocal中删除
}
/**
* 回滚事务
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static void rollback() throws SQLException{
//如果没有开启过事务,则不允许回滚
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
if(connection == null){
throw new RuntimeException("请先开启事务再回滚!");
}
connection.rollback();//回滚事务
connection.close();//关闭连接
threadLocal.remove();//将Connection对象从threadLocal中删除
}
/*
获取普通的连接对象
*/
public static Connection getNormalConn() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
/**
* 关闭资源
* @param rs
* @param stmt
* @param conn
*/
public static void close(ResultSet rs, Statement stmt, Connection conn){
if(rs != null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(stmt != null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
使用此工具类修改业务层以及数据层
(1)AccountDao
package com.qianfeng.caseDemo;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV2;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV3;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV4;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/*
操作Account相关信息的数据层
只用来操作与Account相关的数据库
*/
public class AccountDao {
/**
* 更新account表的数据类型
* @param account
*/
public void updateAccount(Account account){
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
Connection connection = null;
try{
connection = JdbcUtilV4.getTranConnection();
String sql = "UPDATE account SET username=?, balance=? WHERE id=?";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, account.getUsername());
pstmt.setDouble(2, account.getBalance());
pstmt.setInt(3, account.getId());
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}catch (SQLException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
JdbcUtilV2.close(null, pstmt, null);
}
}
/**
* 根据指定的id查找对应的账户
* @param id 指定的账户id
* @return 查询出来的记录转换成的java对象
*/
public Account findAccountById(Integer id) {
Account account = null;
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
connection = JdbcUtilV2.getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM account WHERE id = ?";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, id);
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//如果结果集中有记录,则将这一行记录解析为Account对象
if(rs.next()){
int acountId = rs.getInt("id");
String username = rs.getString("username");
double balance = rs.getDouble("balance");
account = new Account();
account.setId(acountId);
account.setUsername(username);
account.setBalance(balance);
}
}catch (SQLException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
JdbcUtilV2.close(rs, pstmt, connection);
}
return account;
}
}
(2)AccountService
package com.qianfeng.caseDemo;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV2;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV3;
import com.qianfeng.utils.JdbcUtilV4;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 用来处理与Account相关的业务逻辑
*/
public class AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao = new AccountDao();
/**
* 转账的业务逻辑
* 将from账户的余额减去money
* 将to账户的余额增长money
*
* @param fromId 转出去的账户Id
* @param toId 接收的账户Id
* @param money 转出去的金额
*/
public void tranfer(Integer fromId, Integer toId, double money) {
Account from = accountDao.findAccountById(fromId);
Account to = accountDao.findAccountById(toId);
try {
/*
注意:开启事务的Connection对象与操作sql的Connection对象
必须是同一个对象
*/
JdbcUtilV4.startTrans();
from.setBalance(from.getBalance() - money);
accountDao.updateAccount(from);
if (from.getBalance() < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("你有钱吗你就转账! 如果转完之后你的余额是:" + from.getBalance());
}
to.setBalance(to.getBalance() + money);
accountDao.updateAccount(to);
JdbcUtilV4.commit();
}catch (Exception e){
try {
JdbcUtilV4.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
标签:JDBC,String,rs,connection,sql,public,pstmt 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/snail05/p/16468293.html