大数据技术之Flume 第3章 Flume进阶
作者:互联网
第3章 Flume进阶
3.1 Flume事务
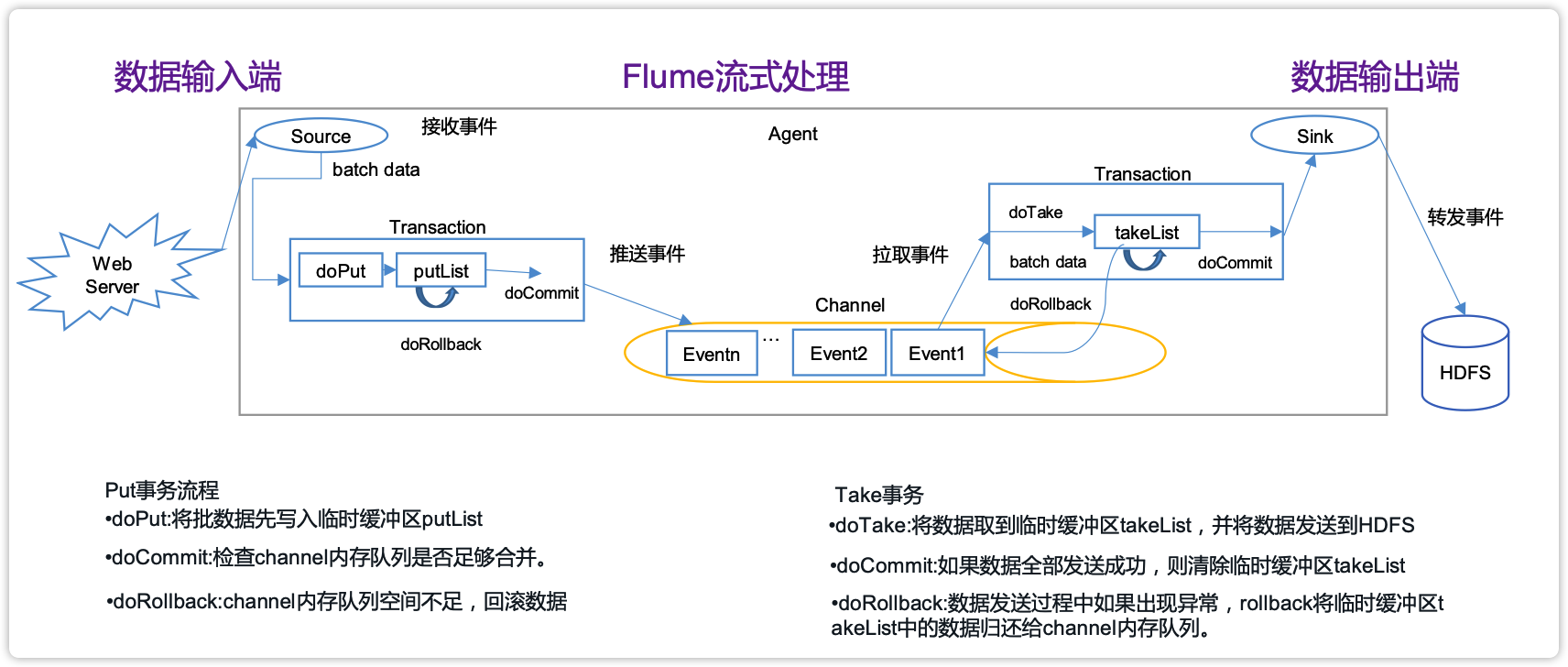
3.2 Flume Agent内部原理
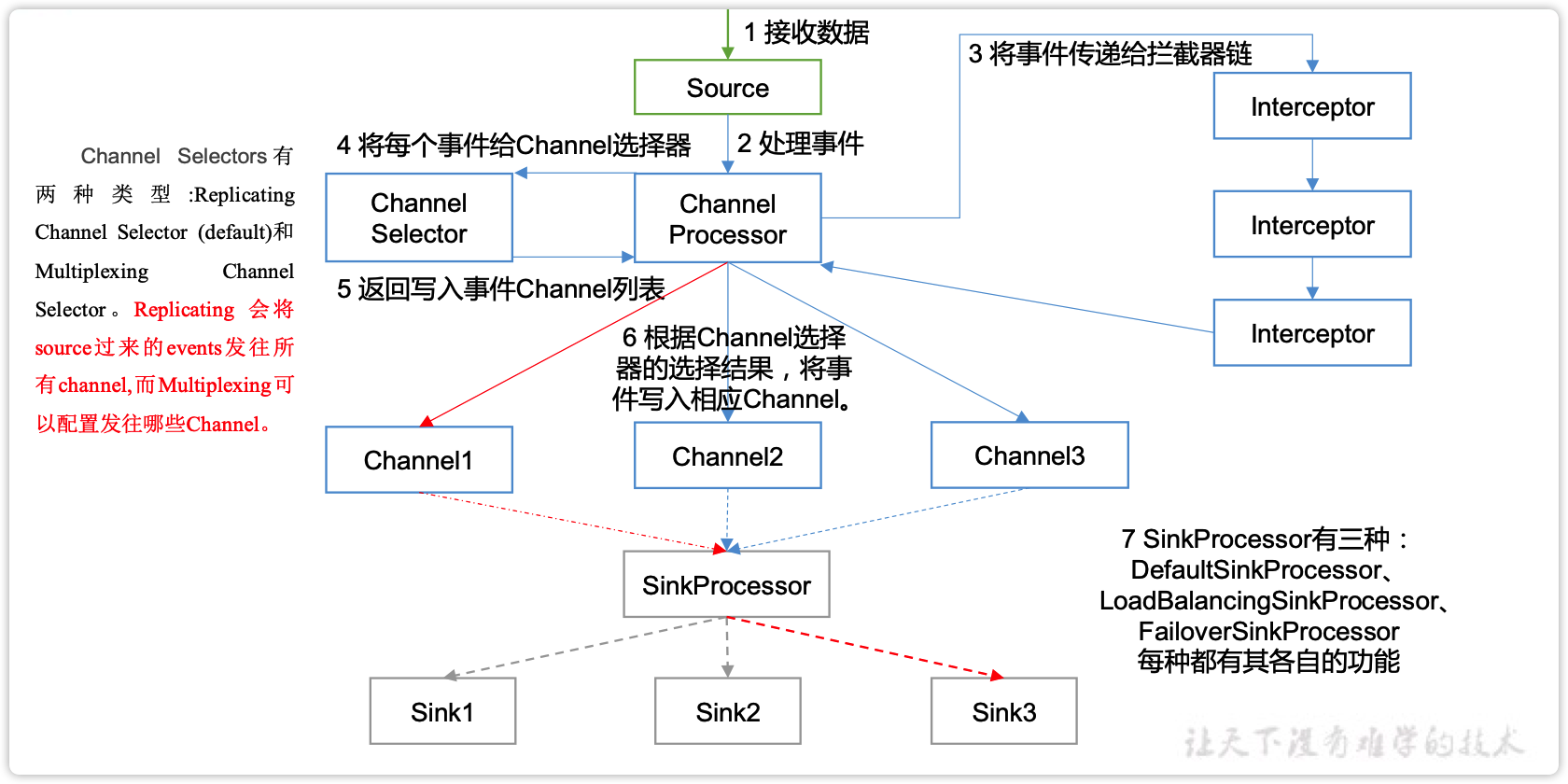
重要组件:
1)ChannelSelector
ChannelSelector的作用就是选出Event将要被发往哪个Channel。其共有两种类型,分别是Replicating(复制)和Multiplexing(多路复用)。
ReplicatingSelector会将同一个Event发往所有的Channel,Multiplexing会根据相应的原则,将不同的Event发往不同的Channel。
2)SinkProcessor
SinkProcessor共有三种类型,分别是DefaultSinkProcessor、LoadBalancingSinkProcessor和FailoverSinkProcessor
DefaultSinkProcessor对应的是单个的Sink,LoadBalancingSinkProcessor和FailoverSinkProcessor对应的是Sink Group,LoadBalancingSinkProcessor可以实现负载均衡的功能,FailoverSinkProcessor可以错误恢复的功能。
3.3 Flume拓扑结构
3.3.1 简单串联
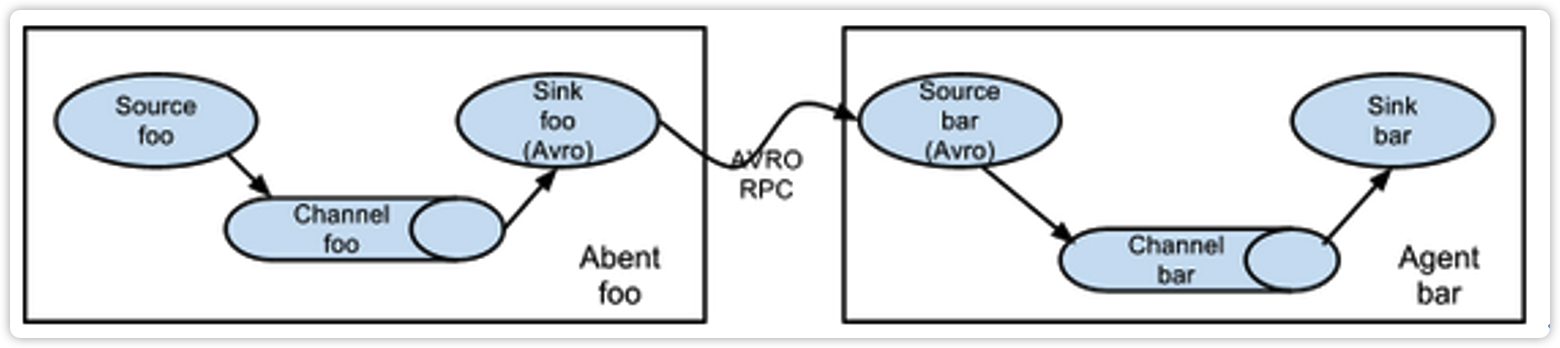
这种模式是将多个flume顺序连接起来了,从最初的source开始到最终sink传送的目的存储系统。此模式不建议桥接过多的flume数量, flume数量过多不仅会影响传输速率,而且一旦传输过程中某个节点flume宕机,会影响整个传输系统。
3.3.2 复制和多路复用
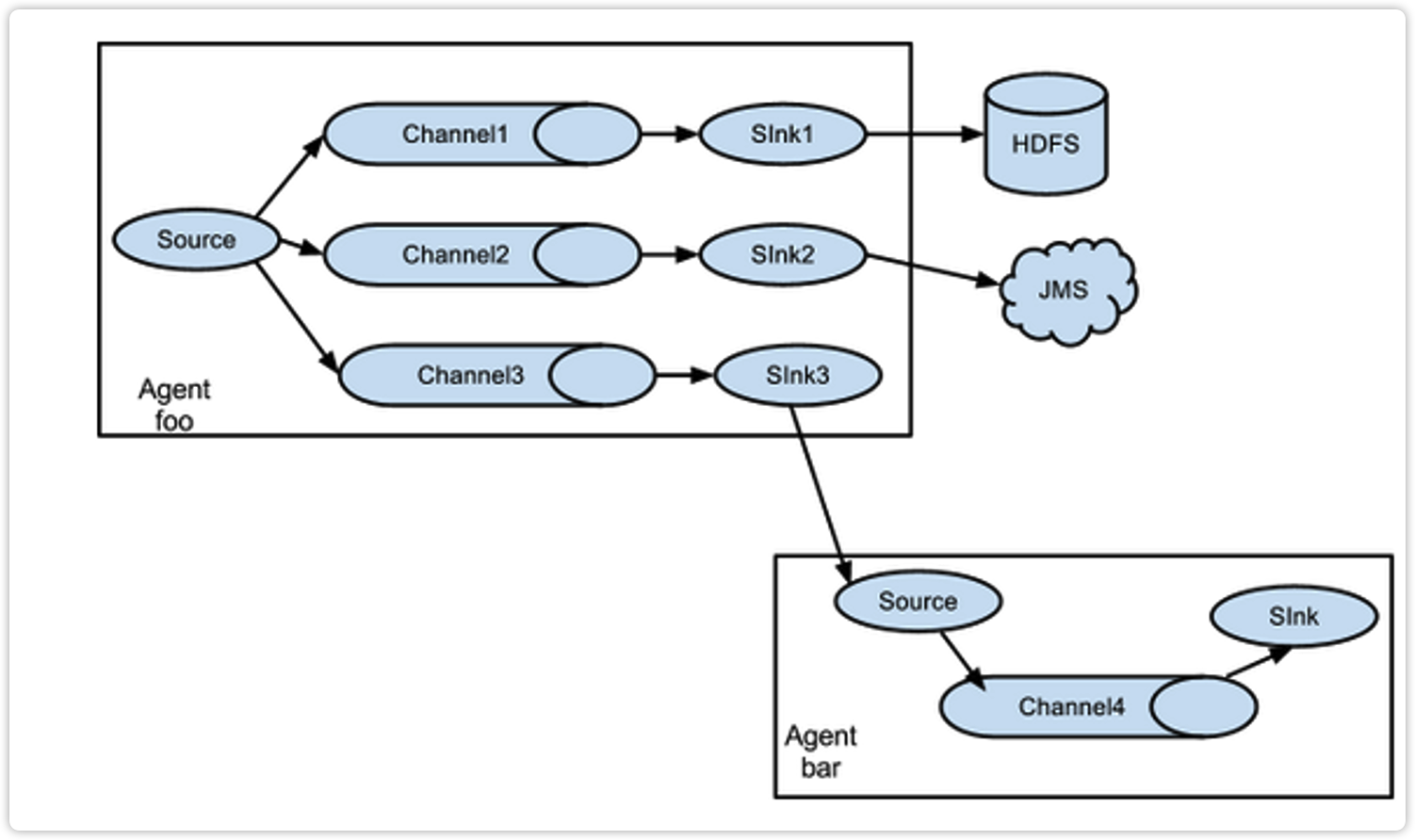
Flume支持将事件流向一个或者多个目的地。这种模式可以将相同数据复制到多个channel中,或者将不同数据分发到不同的channel中,sink可以选择传送到不同的目的地。
3.3.3 负载均衡和故障转移
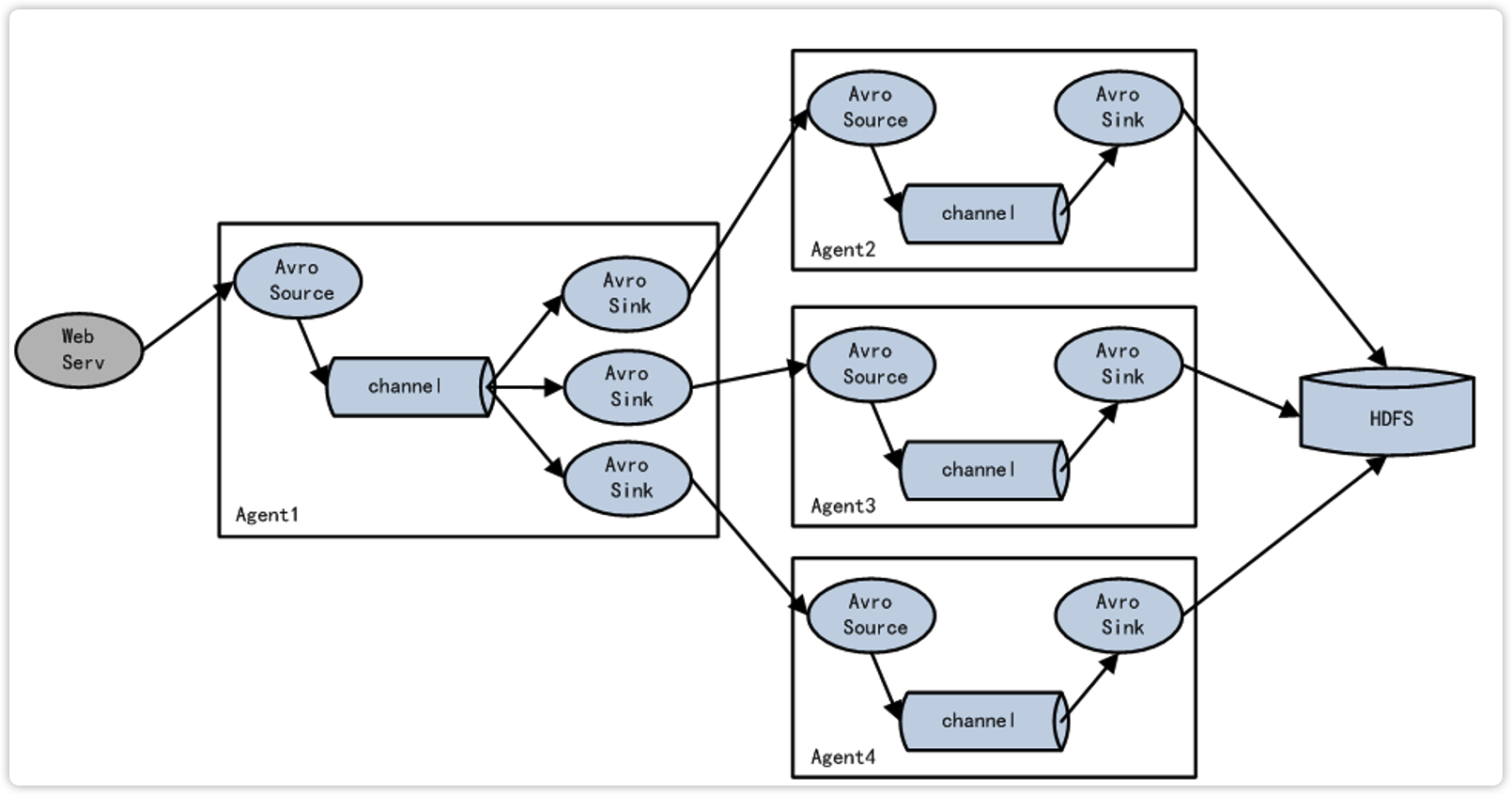
Flume支持使用将多个sink逻辑上分到一个sink组,sink组配合不同的SinkProcessor可以实现负载均衡和错误恢复的功能。
3.3.4 聚合
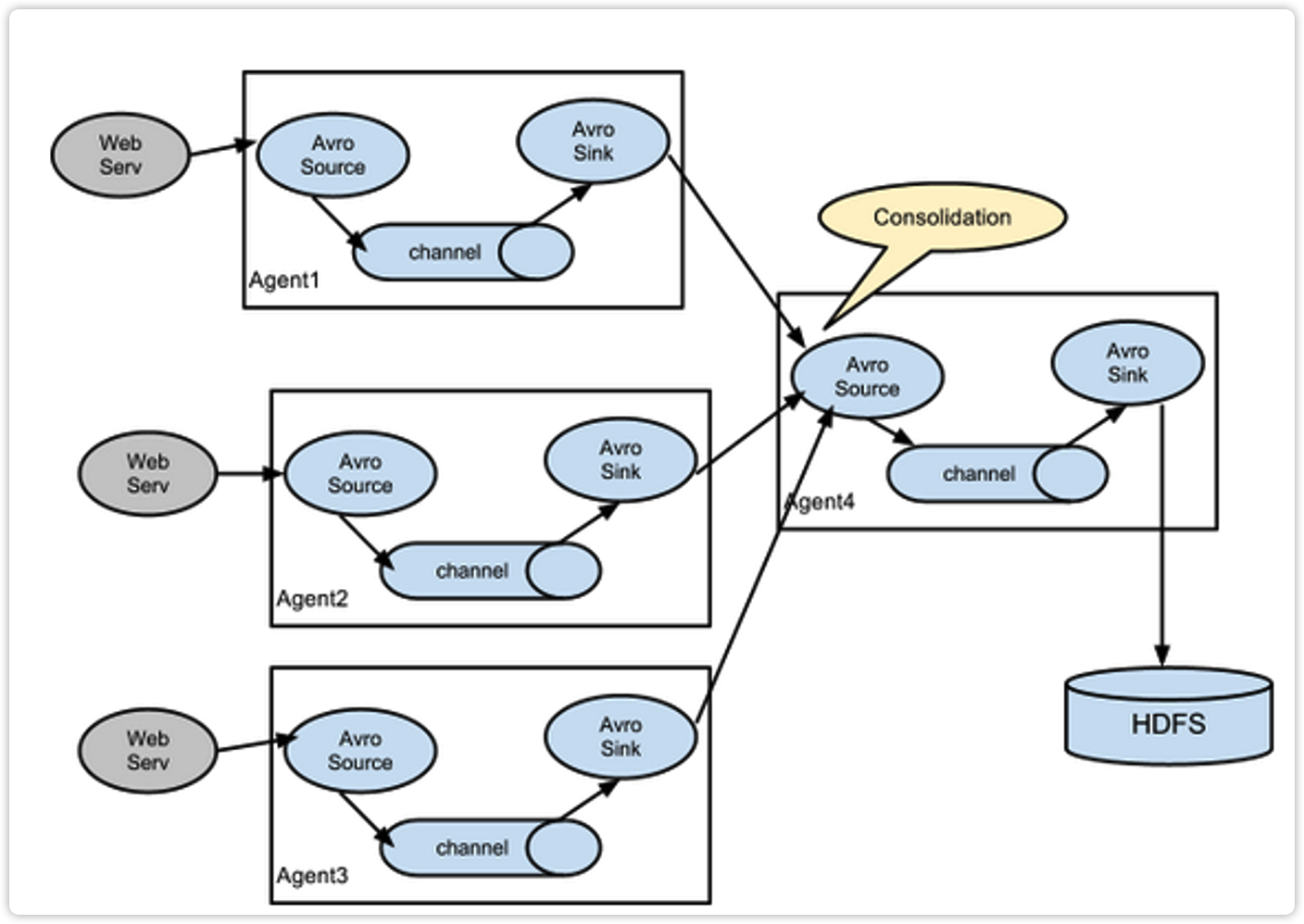
这种模式是我们最常见的,也非常实用,日常web应用通常分布在上百个服务器,大者甚至上千个、上万个服务器。产生的日志,处理起来也非常麻烦。用flume的这种组合方式能很好的解决这一问题,每台服务器部署一个flume采集日志,传送到一个集中收集日志的flume,再由此flume上传到hdfs、hive、hbase等,进行日志分析。
3.4 Flume企业开发案例
3.4.1 复制和多路复用
1)案例需求
使用Flume-1监控文件变动,Flume-1将变动内容传递给Flume-2,Flume-2负责存储到HDFS。同时Flume-1将变动内容传递给Flume-3,Flume-3负责输出到Local FileSystem。
2)需求分析:
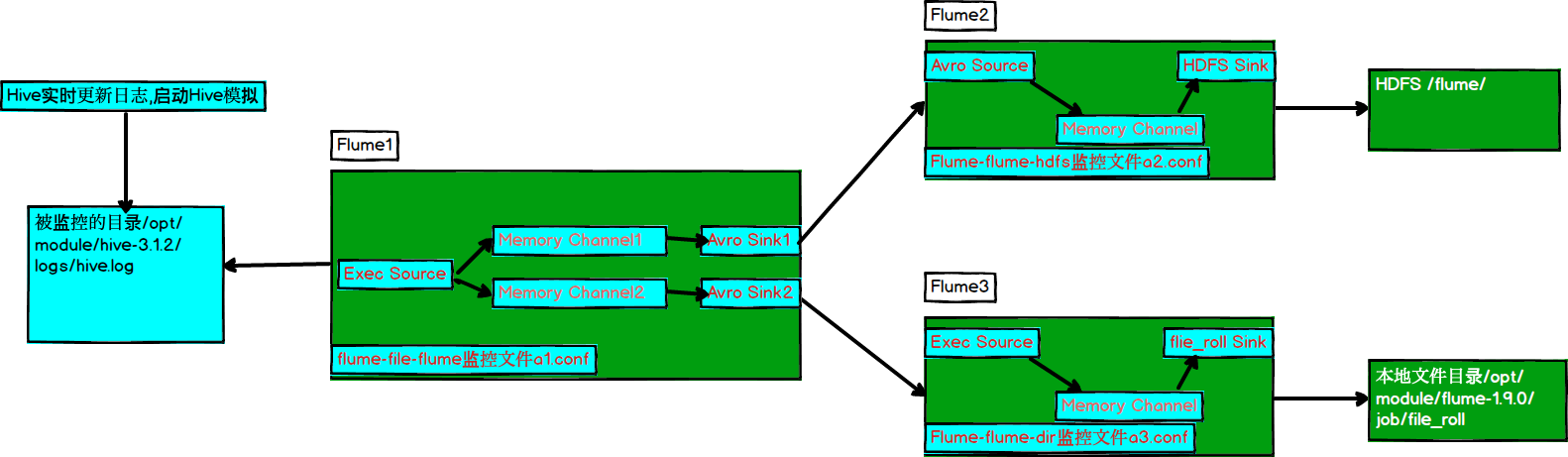
3)实现步骤:
(1)准备工作
在/opt/module/flume-1.9.0/job/目录下创建replicating文件夹
[wolffy@hadoop102 job]$ mkdir replicating
在/opt/module/flume-1.9.0/job/目录下创建file_roll文件夹
[wolffy@hadoop102 job]$ mkdir file_roll
(2)创建a1.conf
配置1个接收日志文件的source和两个channel、两个sink,分别输送给a2和a3。
编辑配置文件
[wolffy@hadoop102 group1]$ vim a1.conf
添加如下内容
# Name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
# source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /opt/module/hive-3.1.2/logs/hive.log
# sink1
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
# sink2
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k2.port = 6666
# Channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Channel
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
# Channel Selector
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating
# bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
(3)创建a2.conf
配置上级Flume输出的Source,输出是到HDFS的Sink。
编辑配置文件
[wolffy@hadoop102 group1]$ vim a2.conf
添加如下内容
# Name
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
# source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a2.sources.r1.port = 5555
# sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoop102:9820/flume/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = logs-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 30
#设置每个文件的滚动大小
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
# Channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(4)创建a3.conf
配置上级Flume输出的Source,输出是到本地目录的Sink。
编辑配置文件
[wolffy@hadoop102 group1]$ vim flume-flume-dir.conf
添加如下内容
# Name
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c1
# source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a3.sources.r1.port = 6666
# sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = file_roll
a3.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /opt/module/flume-1.9.0/job/file_roll
# Channel
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
提示:输出的本地目录必须是已经存在的目录,如果该目录不存在,并不会创建新的目录。
(5)执行配置文件
分别启动对应的flume进程:a3.conf,a2.conf,a1.conf。
[wolffy@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/replicating/a3.conf
[wolffy@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/replicating/a2.conf
[wolffy@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/replicating/a1.conf
(6)启动Hadoop和Hive
[wolffy@hadoop102 hadoop-2.7.2]$ sbin/start-dfs.sh
[wolffy@hadoop103 hadoop-2.7.2]$ sbin/start-yarn.sh
[wolffy@hadoop102 hive]$ bin/hive
hive (default)>
(7)检查HDFS上数据
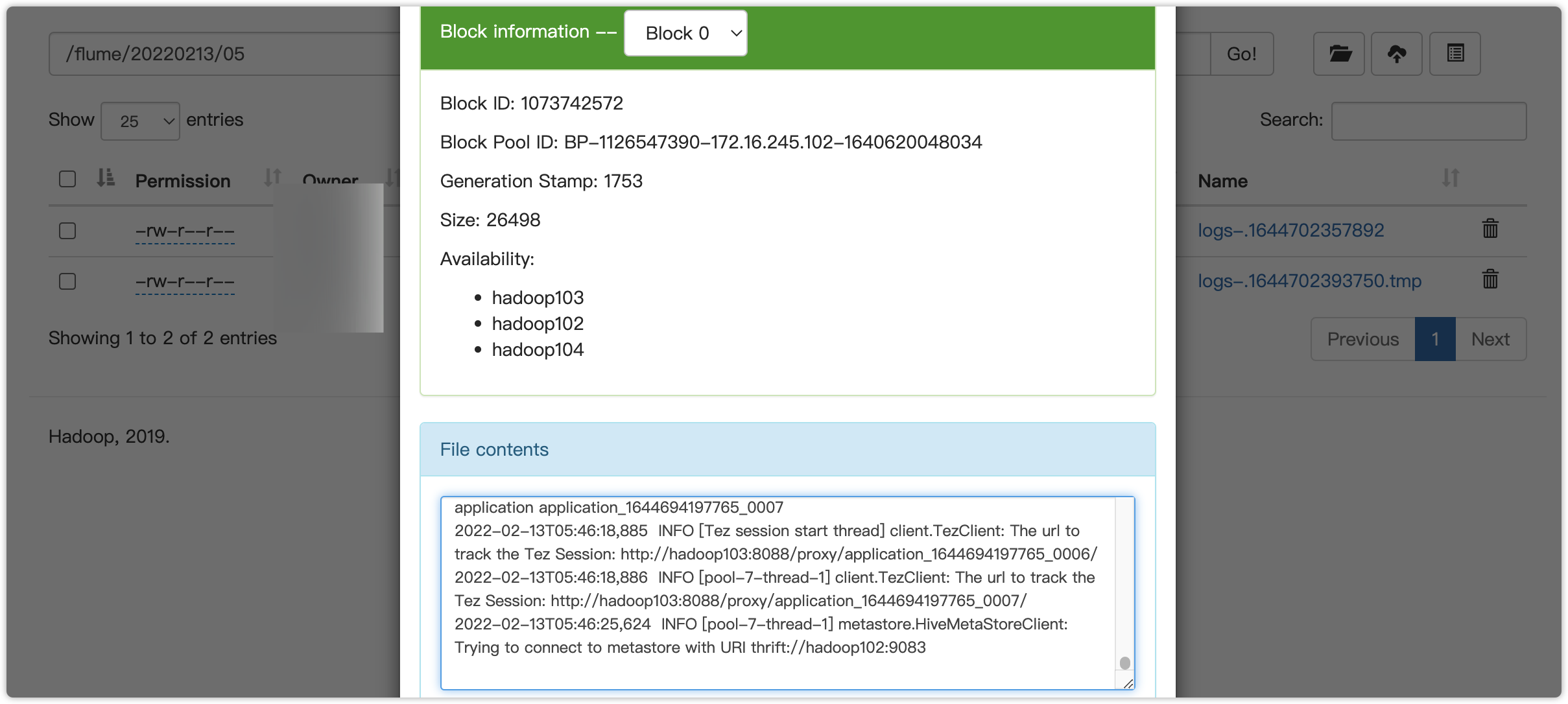
(8)检查/opt/module/datas/flume3目录中数据
[wolffy@hadoop102 flume3]$ ll
总用量 8
-rw-rw-r--. 1 wolffy wolffy 5942 5月 22 00:09 1526918887550-3
3.4.2 负载均衡和故障转移
1)案例需求
使用Flume1监控一个端口,其sink组中的sink分别对接Flume2和Flume3,采用FailoverSinkProcessor,实现故障转移的功能。
2)需求分析
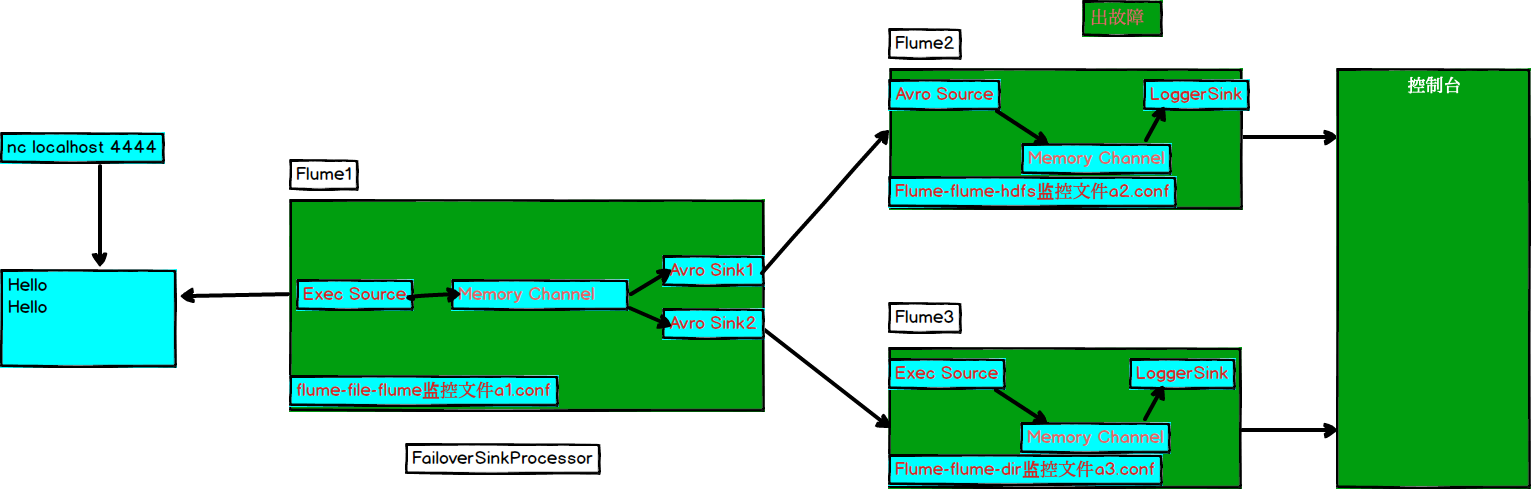
3)实现步骤
(1)准备工作
在/opt/module/flume-1.9.0/job/目录下创建failover文件夹
[wolffy@hadoop102 job]$ mkdir failover/
[wolffy@hadoop102 job]$ cd failover/
(2)创建a1.conf
配置1个netcat source和1个channel、1个sink group(2个sink),分别输送给a2.conf和a3.conf。
编辑配置文件
[wolffy@hadoop102 group2]$ vim a1.conf
添加如下内容
# Name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1
# source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a1.sources.r1.port = 4444
# sink1
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
# sink2
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k2.port = 6666
# sink processor
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 5
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 10
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 10000
# Channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1
(3)创建a2.conf
配置上级Flume输出的Source,输出是到本地控制台。
编辑配置文件
[wolffy@hadoop102 group2]$ vim a2.conf
添加如下内容
# Name
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
# source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a2.sources.r1.port = 5555
# sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(4)创建a3.conf
配置上级Flume输出的Source,输出是到本地控制台。
编辑配置文件
[wolffy@hadoop102 group2]$ vim a3.conf
添加如下内容
# Name
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c1
# source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a3.sources.r1.port = 6666
# sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Channel
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(5)执行配置文件
分别开启对应配置文件:a3.conf,a2.conf,a1.conf。
[wolffy@hadoop102 lume-1.9.0]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/failover/a3.conf -Dflume.wolffy.logger=INFO,console
[wolffy@hadoop102 flulume-1.9.0me]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/failover/a3.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[wolffy@hadoop102 lume-1.9.0]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/failover/a1.conf
(6)使用netcat工具向本机的44444端口发送内容
[wolffy@hadoop102 failover]$ nc hadoop102 4444
(7)查看Flume2及Flume3的控制台打印日志
(8)将Flume2 kill,观察Flume3的控制台打印情况。
2022-02-13 06:40:14,235 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 68 65 6C 6C 6F hello }
注:使用jps -ml查看Flume进程。
3.4.3 负载均衡
a1.conf
# Name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1
# source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a1.sources.r1.port = 4444
# sink1
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k1.port = 5555
# sink2
a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoop102
a1.sinks.k2.port = 6666
# sink processor
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = round_robin
# 退避
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true
# Channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1
a2.conf
# Name
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
# source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a2.sources.r1.port = 5555
# sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a3.conf
# Name
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c1
# source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoop102
a3.sources.r1.port = 6666
# sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Channel
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
3.4.4 聚合
1)案例需求:
hadoop102上的Flume-1监控文件/opt/module/group.log,
hadoop103上的Flume-2监控某一个端口的数据流,
Flume-1与Flume-2将数据发送给hadoop104上的Flume-3,Flume-3将最终数据打印到控制台。
2)需求分析
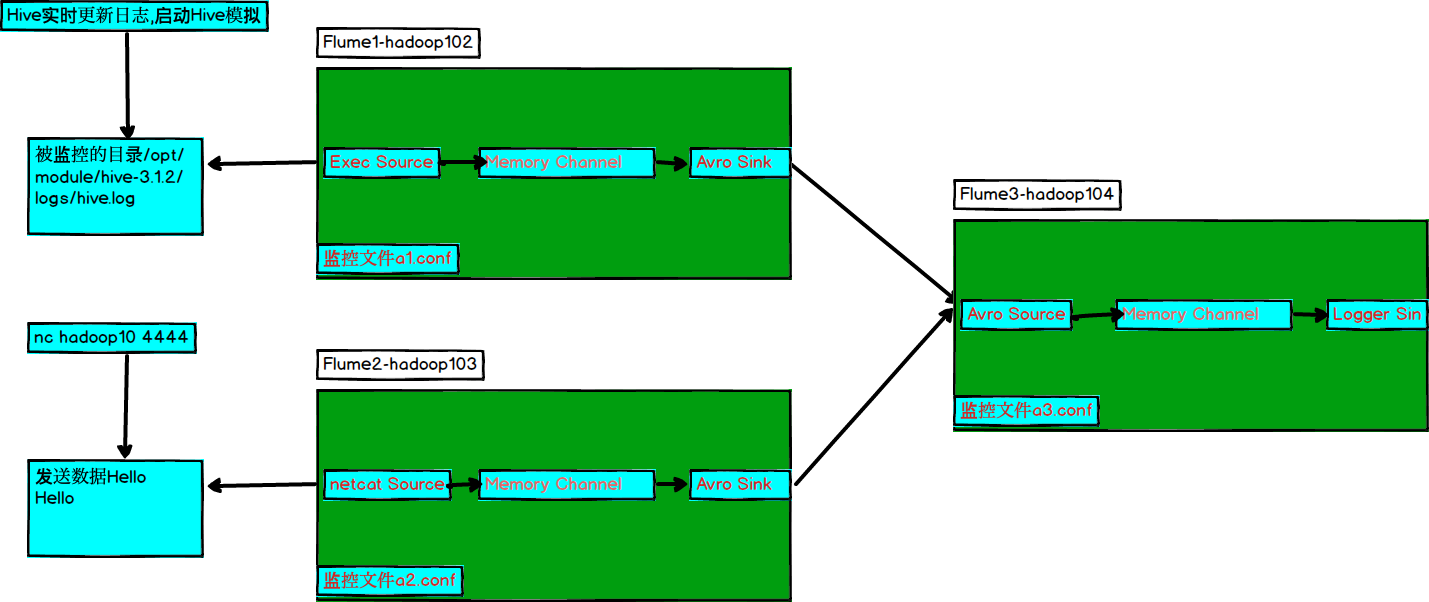
3)实现步骤:
(1)准备工作
分发Flume
[wolffy@hadoop102 module]$ xsync flume-1.9.0
在hadoop102、hadoop103以及hadoop104的/opt/module/flume1.9.0/job目录下创建一个aggre文件夹。
[wolffy@hadoop102 job]$ mkdir aggre
[wolffy@hadoop103 job]$ mkdir aggre
[wolffy@hadoop104 job]$ mkdir aggre
(2)创建flume1-logger-flume.conf
配置Source用于监控hive.log文件,配置Sink输出数据到下一级Flume。
在hadoop102上编辑配置文件
[wolffy@hadoop102 group3]$ vim a1.conf
添加如下内容
[wolffy@hadoop102 aggre]$ cat a1.txt
# Name
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /opt/module/hive-3.1.2/logs/hive.log
# sink1
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop104
a1.sinks.k1.port = 8888
# Channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(3)创建a2conf
配置Source监控端口44444数据流,配置Sink数据到下一级Flume:
在hadoop103上编辑配置文件
[wolffy@hadoop102 group3]$ vim a2.conf
添加如下内容
# Name
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
# source
a2.sources.r1.type = netcat
a2.sources.r1.bind = hadoop103
a2.sources.r1.port = 4444
# sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = avro
a2.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop104
a2.sinks.k1.port = 8888
# Channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(4)创建flume3-flume-logger.conf
配置source用于接收flume1与flume2发送过来的数据流,最终合并后sink到控制台。
在hadoop104上编辑配置文件
[wolffy@hadoop104 group3]$ touch a3.conf
[wolffy@hadoop104 group3]$ vim a3.conf
添加如下内容
# Name
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c1
# source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoop104
a3.sources.r1.port = 8888
# sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Channel
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# bind
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(5)执行配置文件
分别开启对应配置文件:a3.conf,a2.conf,a1.conf。
[root@hadoop104 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/aggre/a3.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[root@hadoop102 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/aggre/a1.conf
[root@hadoop103 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/aggre/a2.conf
(6)在hadoop102上向启动bin/hive
[root@hadoop102 hive-3.1.2]$ bin/hive
Hive Session ID = 1a14279f-53b3-47e9-9504-534fb461235f
Logging initialized using configuration in file:/opt/module/hive-3.1.2/conf/hive-log4j2.properties Async: true
Hive Session ID = a54853cc-e857-43ee-b305-dc644db44b84
hive (default)>
(7)在hadoop103上向4444端口发送数据
[root@hadoop103 flume]$ nc hadoop103 4444
(8)检查hadoop104上数据
2022-02-13 07:31:44,850 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 32 30 32 32 2D 30 32 2D 31 33 54 30 37 3A 33 31 2022-02-13T07:31 }
2022-02-13 07:31:44,850 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 32 30 32 32 2D 30 32 2D 31 33 54 30 37 3A 33 31 2022-02-13T07:31 }
2022-02-13 07:31:45,854 (SinkRunner-PollingRunner-DefaultSinkProcessor) [INFO - org.apache.flume.sink.LoggerSink.process(LoggerSink.java:95)] Event: { headers:{} body: 32 30 32 32 2D 30 32 2D 31 33 54 30 37 3A 33 31 2022-02-13T07:31 } hello }
3.5 自定义Interceptor
1)案例需求
使用Flume采集服务器本地日志,需要按照日志类型的不同,将不同种类的日志发往不同的分析系统。
2)需求分析
在实际的开发中,一台服务器产生的日志类型可能有很多种,不同类型的日志可能需要发送到不同的分析系统。此时会用到Flume拓扑结构中的Multiplexing结构,Multiplexing的原理是,根据event中Header的某个key的值,将不同的event发送到不同的Channel中,所以我们需要自定义一个Interceptor,为不同类型的event的Header中的key赋予不同的值。
在该案例中,我们以端口数据模拟日志,以数字(单个)和字母(单个)模拟不同类型的日志,我们需要自定义interceptor区分数字和字母,将其分别发往不同的分析系统(Channel)。
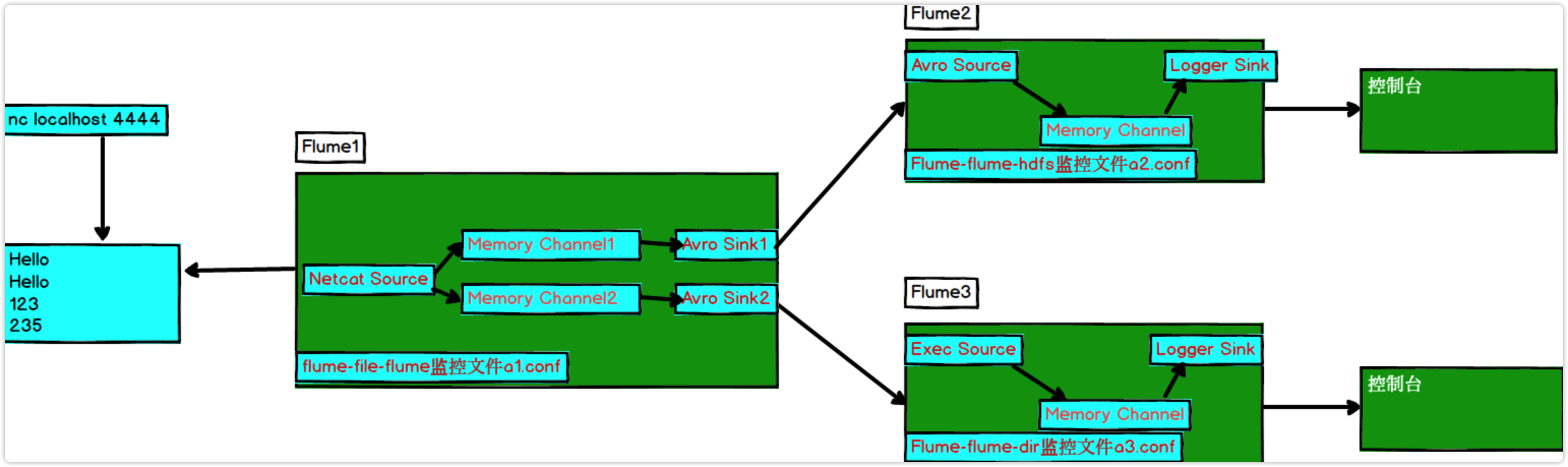
3)实现步骤
(1)创建一个maven项目,并引入以下依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId>
<artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId>
<version>1.9.0</version>
</dependency>
(2)定义CustomInterceptor类并实现Interceptor接口。
package com.bdreasercher.bigdata;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.Event;
import org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor;
import java.util.List;
public class CustomInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public void initialize() {
}
@Override
public Event intercept(Event event) {
byte[] body = event.getBody();
if (body[0] < 'z' && body[0] > 'a') {
event.getHeaders().put("type", "letter");
} else if (body[0] > '0' && body[0] < '9') {
event.getHeaders().put("type", "number");
}
return event;
}
@Override
public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> events) {
for (Event event : events) {
intercept(event);
}
return events;
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
public static class Builder implements Interceptor.Builder {
@Override
public Interceptor build() {
return new CustomInterceptor();
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
}
}
}
打包,把编译好的Jar包房到lib文件夹下。
(3)编辑flume配置文件
为hadoop102上的Flume1配置1个netcat source,1个sink group(2个avro sink),并配置相应的ChannelSelector和interceptor。
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = 0.0.0.0
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = com.bdreasercher.bigdata.CustomInterceptor$Builder
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = type
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.letter = c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.number = c2
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop103
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141
a1.sinks.k2.type=avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoop104
a1.sinks.k2.port = 4242
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
为hadoop103上的Flume4配置一个avro source和一个logger sink。
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = hadoop103
a1.sources.r1.port = 4141
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
为hadoop104上的Flume3配置一个avro source和一个logger sink。
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sources.r1.type = avro
a1.sources.r1.bind = hadoop104
a1.sources.r1.port = 4242
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
(4)分别在hadoop102,hadoop103,hadoop104上启动flume进程,注意先后顺序。
(5)在hadoop102使用netcat向localhost:44444发送字母和数字。
(6)观察hadoop103和hadoop104打印的日志。
3.6 自定义Source
1)介绍
Source是负责接收数据到Flume Agent的组件。Source组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。官方提供的source类型已经很多,但是有时候并不能满足实际开发当中的需求,此时我们就需要根据实际需求自定义某些source。
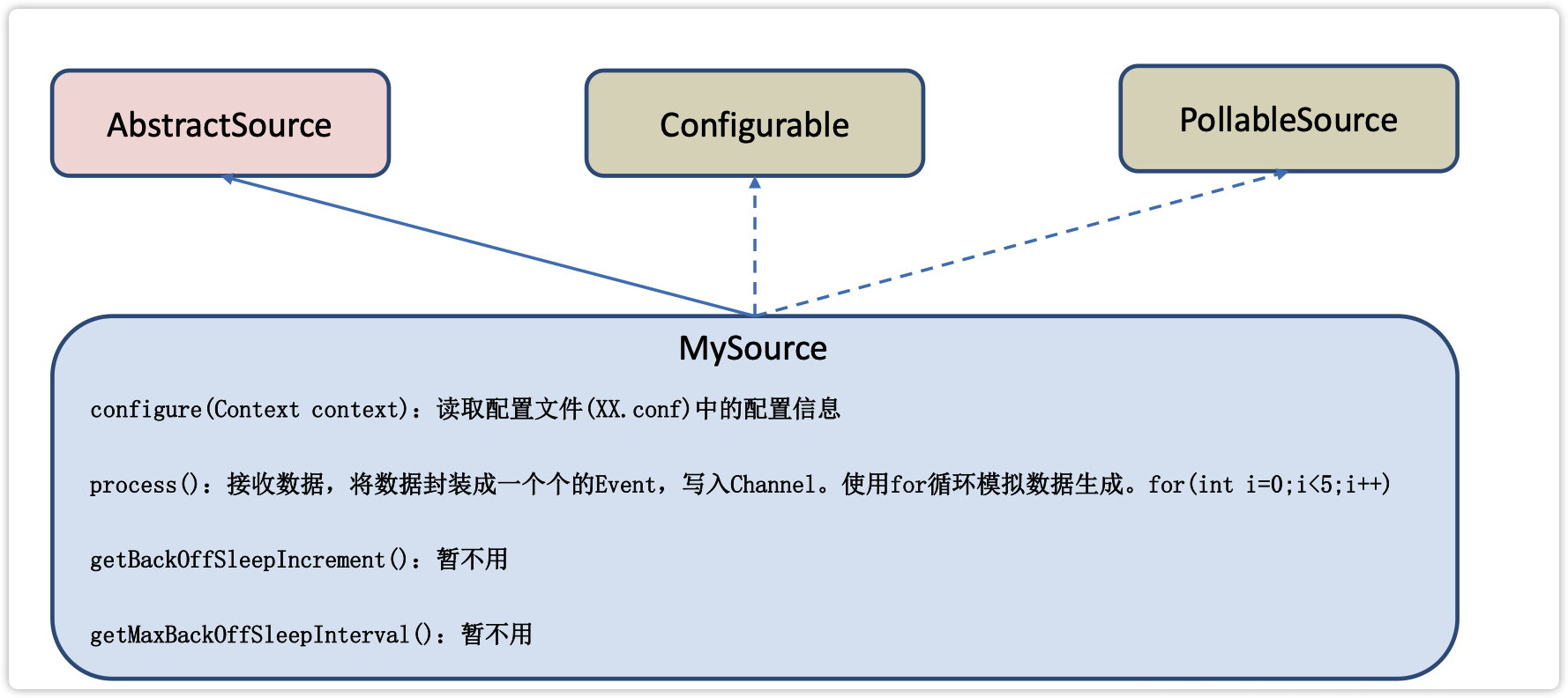
官方也提供了自定义source的接口:https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#source根据官方说明自定义MySource需要继承AbstractSource类并实现Configurable和PollableSource接口。
实现相应方法:
getBackOffSleepIncrement() //backoff 步长
getMaxBackOffSleepInterval()//backoff 最长时间
configure(Context context)//初始化context(读取配置文件内容)
process()//获取数据封装成event并写入channel,这个方法将被循环调用。
使用场景:读取MySQL数据或者其他文件系统。
2)需求
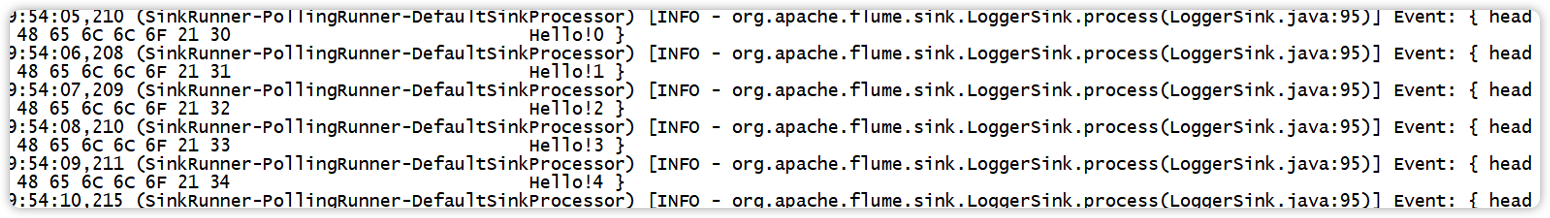
使用flume接收数据,并给每条数据添加前缀,输出到控制台。前缀可从flume配置文件中配置。
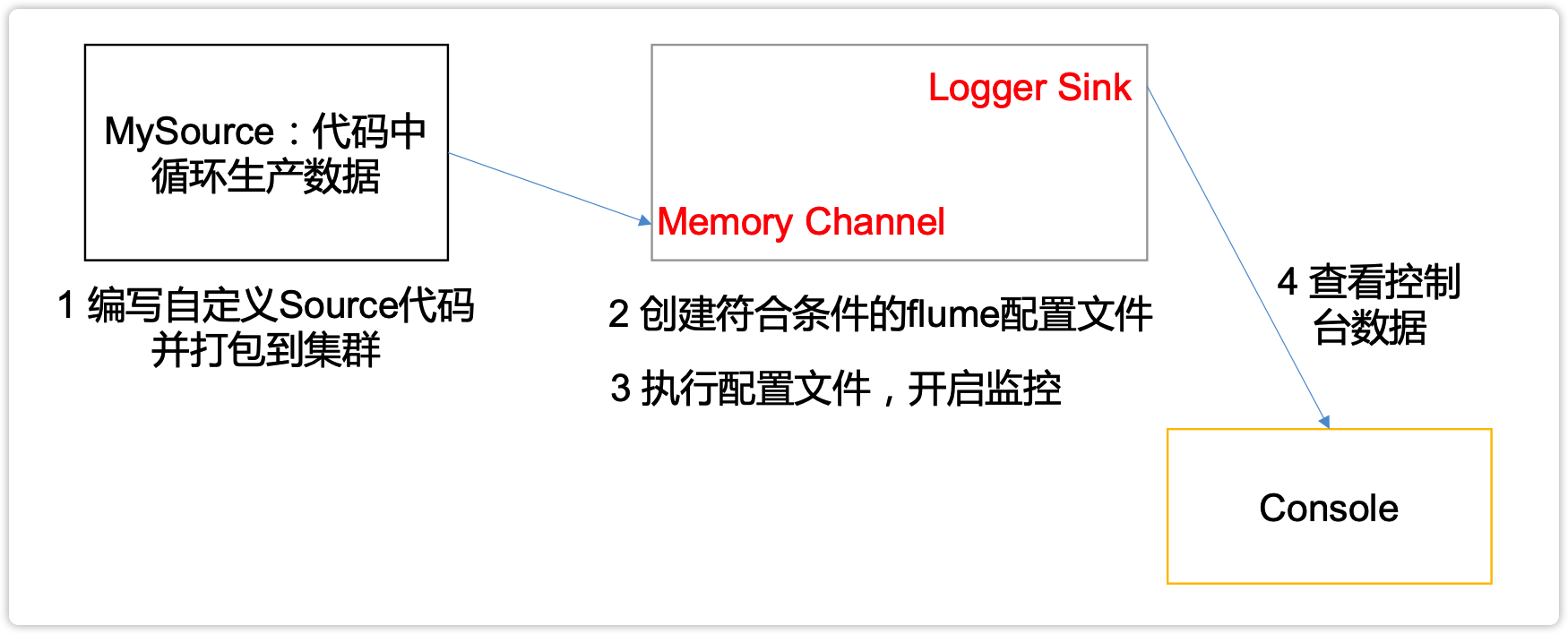
4)编码
(1)导入pom依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId>
<artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId>
<version>1.9.0</version>
</dependency>
(2)编写代码
package com.bdreasercher.bigdata;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException;
import org.apache.flume.PollableSource;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent;
import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MySource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource {
//定义配置文件将来要读取的字段
private Long delay;
private String field;
//初始化配置信息
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
delay = context.getLong("delay");
field = context.getString("field", "Hello!");
}
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
try {
//创建事件头信息
HashMap<String, String> hearderMap = new HashMap<>();
//创建事件
SimpleEvent event = new SimpleEvent();
//循环封装事件
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//给事件设置头信息
event.setHeaders(hearderMap);
//给事件设置内容
event.setBody((field + i).getBytes());
//将事件写入channel
getChannelProcessor().processEvent(event);
Thread.sleep(delay);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return Status.BACKOFF;
}
return Status.READY;
}
@Override
public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() {
return 0;
}
}
5)测试
(1)打包
将写好的代码打包,并放到flume的lib目录(/opt/module/flume-1.9.0/lib)下。
(2)配置文件
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = com.bdreasercher.bigdata.MySource
a1.sources.r1.delay = 1000
#a1.sources.r1.field = root
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(3)开启任务
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ bin/flume-ng agent -c conf/ -f job/mysource.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
(4)结果展示
3.7 自定义Sink
1)介绍
Sink不断地轮询Channel中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个Flume Agent。
Sink是完全事务性的。在从Channel批量删除数据之前,每个Sink用Channel启动一个事务。批量事件一旦成功写出到存储系统或下一个Flume Agent,Sink就利用Channel提交事务。事务一旦被提交,该Channel从自己的内部缓冲区删除事件。
Sink组件目的地包括hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、null、HBase、solr、自定义。官方提供的Sink类型已经很多,但是有时候并不能满足实际开发当中的需求,此时我们就需要根据实际需求自定义某些Sink。
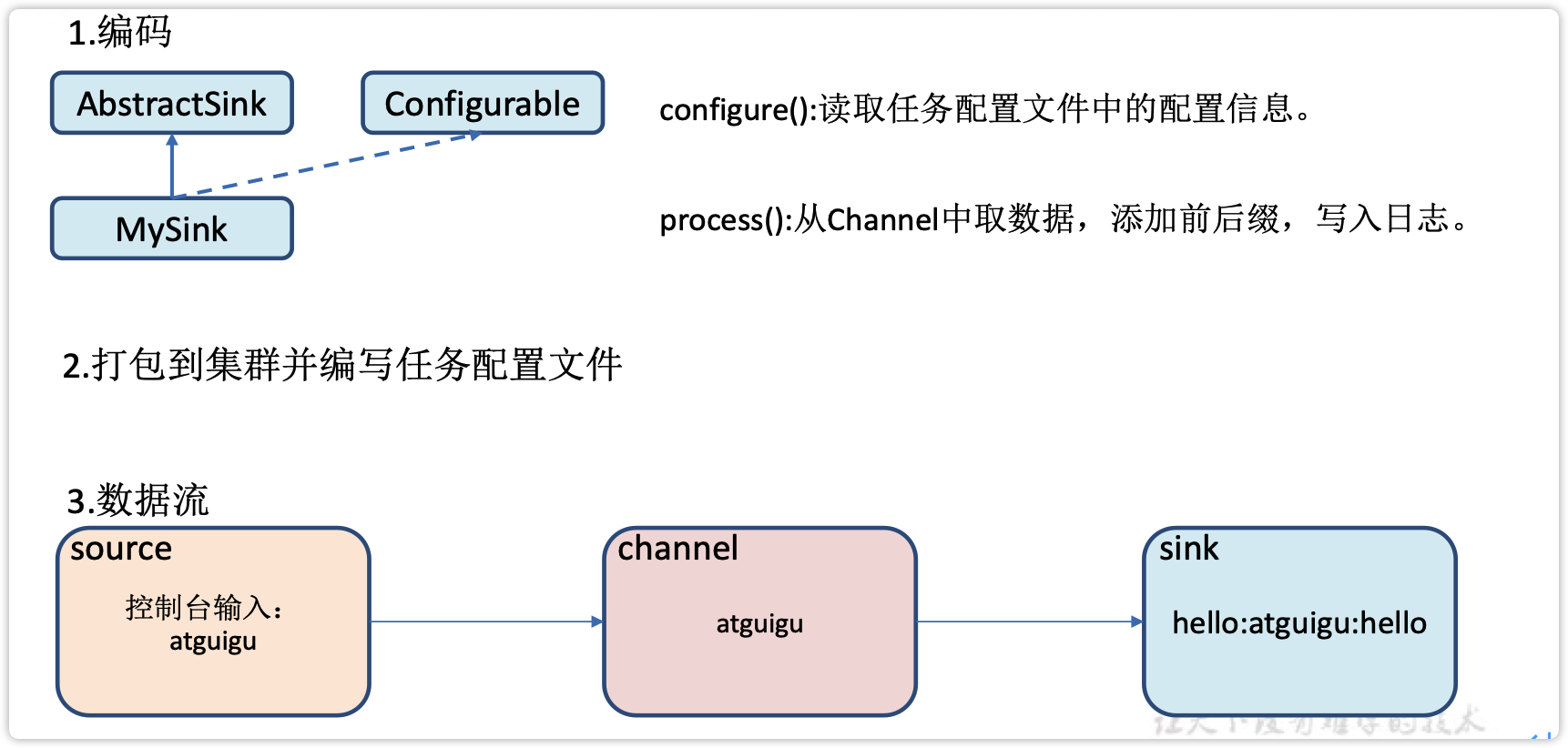
官方也提供了自定义sink的接口:https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#sink根据官方说明自定义MySink需要继承AbstractSink类并实现Configurable接口。
实现相应方法:
configure(Context context)//初始化context(读取配置文件内容)
process()//从Channel读取获取数据(event),这个方法将被循环调用。
使用场景:读取Channel数据写入MySQL或者其他文件系统。
2)需求
使用flume接收数据,并在Sink端给每条数据添加前缀和后缀,输出到控制台。前后缀可在flume任务配置文件中配置。
流程分析:
3)编码
package com.bdreasercher.bigdata;
import org.apache.flume.*;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.sink.AbstractSink;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class MySink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable {
//创建Logger对象
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbstractSink.class);
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
//声明返回值状态信息
Status status;
//获取当前Sink绑定的Channel
Channel ch = getChannel();
//获取事务
Transaction txn = ch.getTransaction();
//声明事件
Event event;
//开启事务
txn.begin();
//读取Channel中的事件,直到读取到事件结束循环
while (true) {
event = ch.take();
if (event != null) {
break;
}
}
try {
//处理事件(打印)
LOG.info(prefix + new String(event.getBody()) + suffix);
//事务提交
txn.commit();
status = Status.READY;
} catch (Exception e) {
//遇到异常,事务回滚
txn.rollback();
status = Status.BACKOFF;
} finally {
//关闭事务
txn.close();
}
return status;
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
//读取配置文件内容,有默认值
prefix = context.getString("prefix", "hello:");
//读取配置文件内容,无默认值
suffix = context.getString("suffix");
}
}
4)测试
(1)打包
将写好的代码打包,并放到flume的lib目录(/opt/module/flume-1.9.0/lib)下。
(2)配置文件
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = com.bdreasercher.bigdata.MySink
#a1.sinks.k1.prefix = root:
a1.sinks.k1.suffix = :root
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
(3)开启任务
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ bin/flume-ng agent -c conf/ -f job/mysink.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[root@hadoop102 ~]$ nc localhost 44444
hello
OK
root
OK
(4)结果展示
3.8 Flume数据流监控
3.8.1 Ganglia的安装与部署
Ganglia由gmond、gmetad、gweb三部分组成。
-
gmond(Ganglia Monitoring Daemon)是一种轻量级服务,安装在每台需要收集指标数据的节点主机上。使用gmond,你可以很容易收集很多系统指标数据,如CPU、内存、磁盘、网络和活跃进程的数据等。
-
gmetad(Ganglia Meta Daemon)整合所有信息,并将其以RRD格式存储至磁盘的服务。
-
gweb(Ganglia Web)Ganglia可视化工具,gweb是一种利用浏览器显示gmetad所存储数据的PHP前端。在Web界面中以图表方式展现集群的运行状态下收集的多种不同指标数据。
1)安装ganglia
(1)规划
hadoop102: web gmetad gmod
hadoop103: gmod
hadoop104: gmod
(2)在102 103 104分别安装epel-release
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo yum -y install epel-release
[root@hadoop103 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo yum -y install epel-release
[root@hadoop104 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo yum -y install epel-release
(3)在102 安装 web gmetad gmod
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmetad
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo yum -y install ganglia-web
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmond
(4)在103 和 104 安装 gmod
[root@hadoop103 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmond
[root@hadoop104 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmond
2)在102修改配置文件 /etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.conf
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.conf
修改为红颜色的配置:
# Ganglia monitoring system php web frontend
Alias /ganglia /usr/share/ganglia
<Location /ganglia>
# Require ip 10.1.2.3
# Require host example.org
Require all granted
</Location>
5)在102修改配置文件/etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo vim /etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf
修改为:
data_source "my cluster" hadoop102
6)在102 103 104分别修改配置文件/etc/ganglia/gmond.conf
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo vim /etc/ganglia/gmond.conf
修改为:
cluster {
name = "my cluster"
owner = "unspecified"
latlong = "unspecified"
url = "unspecified"
}
udp_send_channel {
#bind_hostname = yes # Highly recommended, soon to be default.
# This option tells gmond to use a source address
# that resolves to the machine's hostname. Without
# this, the metrics may appear to come from any
# interface and the DNS names associated with
# those IPs will be used to create the RRDs.
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
# 数据发送给hadoop102
host = hadoop102
port = 8649
ttl = 1
}
udp_recv_channel {
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
port = 8649
# 接收来自任意连接的数据
bind = 0.0.0.0
retry_bind = true
# Size of the UDP buffer. If you are handling lots of metrics you really
# should bump it up to e.g. 10MB or even higher.
# buffer = 10485760
}
7)在102修改配置文件 /etc/selinux/config
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo vim /etc/selinux/config
修改为:
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
尖叫提示:selinux本次生效关闭必须重启,如果此时不想重启,可以临时生效之:
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo setenforce 0
8)启动ganglia
(1)在102 103 104 分别启动
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo systemctl start gmond
[root@hadoop104 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo systemctl status gmond
● gmond.service - Ganglia Monitoring Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/gmond.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 二 2022-01-25 20:32:00 CST; 2 weeks 4 days ago
Process: 43115 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/gmond (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 43116 (gmond)
CGroup: /system.slice/gmond.service
└─43116 /usr/sbin/gmond
1月 25 20:32:00 hadoop104 systemd[1]: Starting Ganglia Monitoring Daemon...
1月 25 20:32:00 hadoop104 systemd[1]: Started Ganglia Monitoring Daemon.
(2)在102 启动
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo systemctl start httpd
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo systemctl status httpd
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 二 2022-01-25 20:41:19 CST; 2 weeks 4 days ago
Docs: man:httpd(8)
man:apachectl(8)
Process: 86976 ExecStop=/bin/kill -WINCH ${MAINPID} (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 3268 ExecReload=/usr/sbin/httpd $OPTIONS -k graceful (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 86981 (httpd)
Status: "Total requests: 0; Current requests/sec: 0; Current traffic: 0 B/sec"
CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service
├─ 3273 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─ 3274 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─ 3275 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─ 3276 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─ 3277 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
└─86981 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo systemctl start gmetad
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo systemctl status gmetad
● gmetad.service - Ganglia Meta Daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/gmetad.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since 二 2022-01-25 20:32:17 CST; 2 weeks 4 days ago
Main PID: 86918 (gmetad)
CGroup: /system.slice/gmetad.service
└─86918 /usr/sbin/gmetad -d 1
9)打开网页浏览ganglia页面
尖叫提示:如果完成以上操作依然出现权限不足错误,请修改/var/lib/ganglia目录的权限。
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ sudo chmod -R 777 /var/lib/ganglia
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/cosmos-wong/p/11980500.html
3.8.2 操作Flume测试监控
1)启动Flume任务
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ bin/flume-ng agent \
-c conf/ \
-n a1 \
-f job/netcat-flume-logger.conf \
-Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console \
-Dflume.monitoring.type=ganglia \
-Dflume.monitoring.hosts=hadoop102:8649
2)发送数据观察ganglia监测图
[root@hadoop102 flume-1.9.0]$ nc localhost 6666
样式如图:
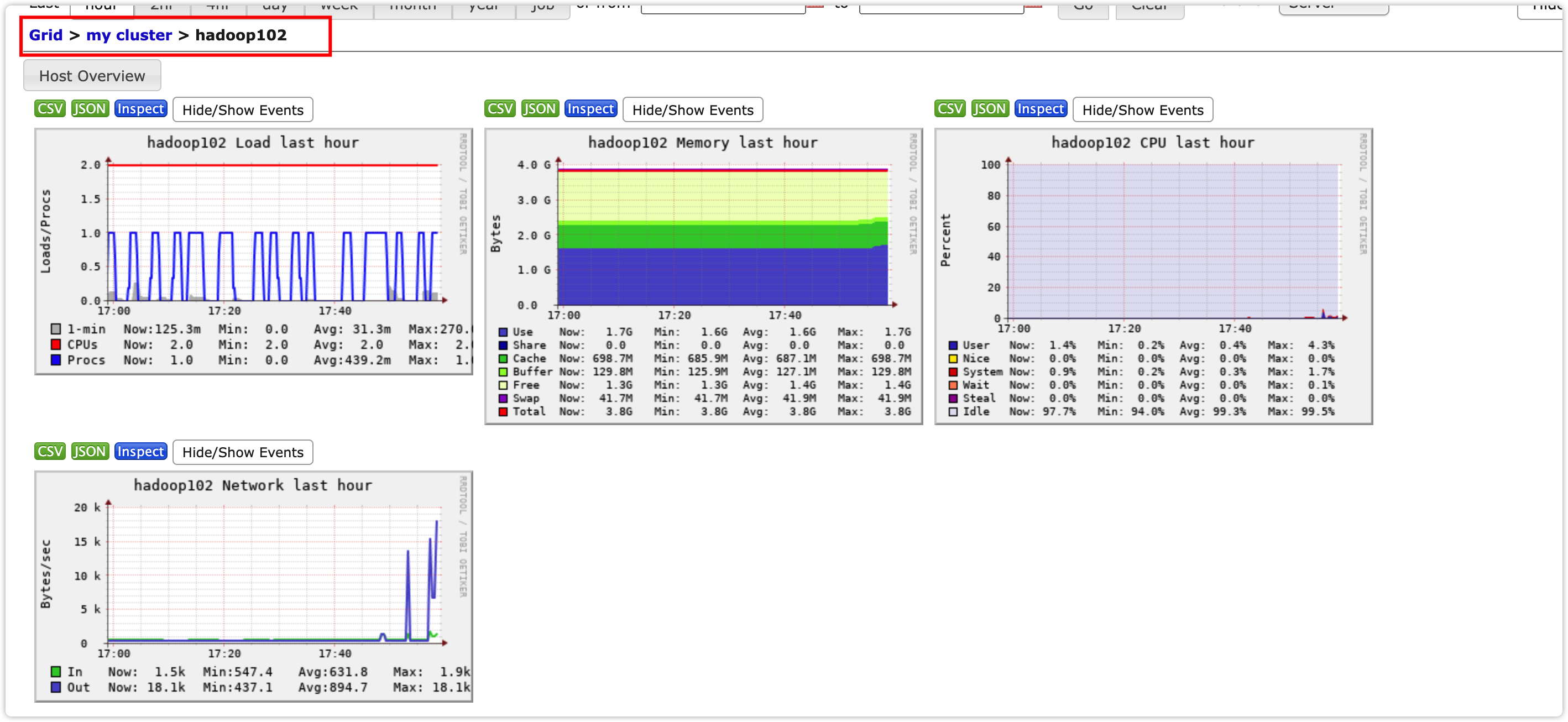
图例说明:
| 字段(图表名称) | 字段含义 |
|---|---|
| EventPutAttemptCount | source尝试写入channel的事件总数量 |
| EventPutSuccessCount | 成功写入channel且提交的事件总数量 |
| EventTakeAttemptCount | sink尝试从channel拉取事件的总数量。 |
| EventTakeSuccessCount | sink成功读取的事件的总数量 |
| StartTime | channel启动的时间(毫秒) |
| StopTime | channel停止的时间(毫秒) |
| ChannelSize | 目前channel中事件的总数量 |
| ChannelFillPercentage | channel占用百分比 |
| ChannelCapacity | channel的容量 |
IT学习网站
Spring Cloud Alibaba学习资源推荐
Spring Cloud Alibaba 微服务架构实战
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1nJpfbjPyf3n339INybjOQQ?pwd=8t11 提取码: 8t11
--来自百度网盘超级会员v4的分享
失效加V:x923713
标签:Flume,flume,进阶,a1,r1,c1,数据,channels,sinks 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/niuniu2022/p/16350388.html