Codeforces Round #787 (Div. 3) 解题报告
作者:互联网
A. Food for Animals
题意:商店有a个狗粮,b个猫粮 ,c个通用粮,需要x个狗粮,y个猫粮,问是否能满足需要
判断猫和狗能否都被满足即可
ac代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include <sstream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
//#include <unordered_map>
#define x first
#define y second
#define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define endl '\n'
#define pi 3.14159265358979323846
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 200010,M = 500010,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f,mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
const double INFF = 0x7f7f7f7f7f7f7f7f;
int main()
{
ios;
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --)
{
int a,b,c,x,y;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> x >> y;
if(a >= x) ;
else c -= x - a;
if(c < 0 )
{
cout << "NO" << endl;
continue;
}
if(b + c >= y) cout << "YES" << endl;
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B. Make It Increasing
题意:给定一个数列a,定义操作:对任意一个a[i] / 2(向下取整),问能够将这个数列构造成严格递增数列的最小操作数。
从后往前搜一遍,只要a[i] >= a[i + 1] 就进行一次操作。最后判断一下是否严格递增。
注意:如果a[i] < 0 ,操作会使其变大。
ac代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include <sstream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
//#include <unordered_map>
#define x first
#define y second
#define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define endl '\n'
#define pi 3.14159265358979323846
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 200010,M = 500010,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f,mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
const double INFF = 0x7f7f7f7f7f7f7f7f;
int n,a[N];
int main()
{
ios;
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --)
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++) cin >> a[i];
bool f = true;
LL res = 0;
for(int i = n - 2;i >= 0;i --)
{
while(a[i] && a[i] >= a[i + 1])
{
res ++;
a[i] /= 2;
}
}
for(int i = 1;i < n;i ++) if(a[i] <= a[i - 1]) f = false;
if(f) cout << res << endl;
else cout << -1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
C. Detective Task
题意:n个人依次进房间看画,有一个人偷了画,按看画次序问,结果为(1:还在,0:不在, ?:不记得),除小偷外其他人都说的实话,问嫌疑人个数。
如果一个人是小偷,那么其他人说的都是实话,那么他前面的人肯定是没有人说不在的,后面的人肯定没有说还在的
即对于一个可能的点其前面没有0,后面没有1,所以只要找到第一个出现的0的位置r,再找到其第一个为1的位置l,则中间的全是嫌疑人,ans = r - l + 1;

ac代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include <sstream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
//#include <unordered_map>
#define x first
#define y second
#define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define endl '\n'
#define pi 3.14159265358979323846
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 200010,M = 500010,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f,mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
const double INFF = 0x7f7f7f7f7f7f7f7f;
int n,a[N],b[N];
int main()
{
ios;
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --)
{
string s;
cin >> s;
int l,r;
for(r = 0;r < s.size() - 1;r ++)
{
if(s[r] == '0') break;
}
for(l = r;l;l --)
{
if(s[l] == '1') break;
}
cout << r - l + 1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
D. Vertical Paths
题意:给定一颗树,问把这颗树拆成几条路径的最小值,并输出路径
dfs回溯过程中如果接着往深处走,就是一条新路径
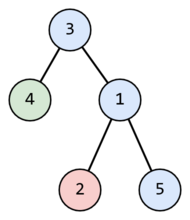
ac代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include <sstream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
//#include <unordered_map>
#define x first
#define y second
#define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define endl '\n'
#define pi 3.14159265358979323846
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 200010,M = 500010,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f,mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
const double INFF = 0x7f7f7f7f7f7f7f7f;
int n,p[N];
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx,idxx;
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx] = b,ne[idx] = h[a],h[a] = idx ++;
}
map<int,int> mp;
int path[N];
bool st[N];
vector<int > a[ N ];
void dfs(int u,int c)
{
path[c] = u;
if(h[u] == -1)
{
a[idxx].clear();
for(int i = 0;i <= c;i ++) a[idxx].push_back(path[i]);
idxx ++;
c = -1;
return ;
}
for(int i = h[u];i != -1;i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
dfs(j,c + 1);
}
}
int main()
{
ios;
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --)
{
int tt;
idx = idxx = 0;
mp.clear();
cin >> n;
memset(h,-1,(n + 1) * 4);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
mp[x] = 1;
if(x == i)
{
tt = i;
continue;
}
add(x,i);
}
dfs(tt,0);
memset(st,0,sizeof st);
cout << idxx << endl;
for(int i = 0;i < idxx;i ++)
{
int pos;
for(pos = 0;pos < a[i].size();pos ++) if(!st[a[i][pos]]) break;
cout << a[i].size() - pos << endl;
for(;pos < a[i].size(); pos ++) cout << a[i][pos] << ' ',st[a[i][pos]] = true;
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
E. Replace With the Previous, Minimize
题意:给定一个字符串,定义操作:
if(s[i] == 'a') s[i] = 'z';
else s[i] -= 1;
并且整个字符串中与s[i]相同的字符,都会一起变化,问用k个操作所能得到的字典序最小字符串。
大体思路即尽量让前面的字母变成'a',变不了就尽量往小减。
同时注意到如果一个字符可以变成'a',并且前面的字母都比他小,那么只需对它操作就可以让前面全变为'a'。
不难想到字符串是这样的

红色的结尾是那个第一个不能变成'a'的字符,其前面的只需找到最大的那个对其操作即可。
ac代码
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include <sstream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
//#include <unordered_map>
#define x first
#define y second
#define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define endl '\n'
#define pi 3.14159265358979323846
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 200010,M = 500010,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f,mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
const double INFF = 0x7f7f7f7f7f7f7f7f;
map<char,char> mp;
bool st[N];
int main()
{
ios;
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --)
{
int n,k;
string s;
cin >> n >> k >> s;
for(char i = 'a';i <= 'z';i ++) mp[i] = i;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++)
{
if(s[i] - 'a'> k)
{
char l = s[i] - k + res;
char r = s[i];
if(l > r) break;
for(int j = 0;j < n;j ++)
{
if(s[j] >= l && s[j] <= r)
{
s[j] = l;
}
}
break;
}
res = max(res,s[i] - 'a');
}
for(int j = 0;j < n;j ++) if(s[j] <= 'a' + res) s[j] = 'a';
cout << s << endl;
}
return 0;
}
F. Vlad and Unfinished Business
题意:给定一颗无根树,以及起点x,终点y。从起点要先经过一系列点然后最终到y,问最短距离。
bfs标记每个节点的父节点并计算距起点的最短距离。
如果想要在一个树上,要求从根出发,经过若干个点的话,最后回到根,基本想法就是从要经过的点往根遍历,没经过一条边,就要代价 +2,因为一次是往下,第二次是经过了该子树要经过的点,然后回去
所以这题就套用这个想法,把 y 也作为要经过的点,然后再减去 x 到 y 的距离,就变成最后是在 y 点停下
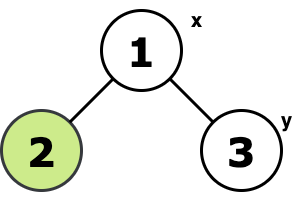
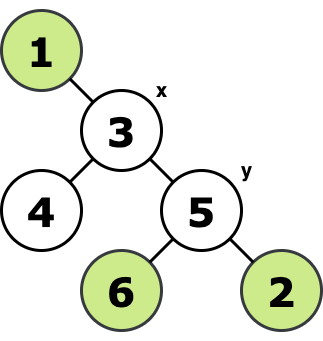
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
#include <sstream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
//#include <unordered_map>
#define x first
#define y second
#define ios ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
#define endl '\n'
#define pi 3.14159265358979323846
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 200010,M = 500010,INF = 0x3f3f3f3f,mod = 1e9 + 7 ;
const double INFF = 0x7f7f7f7f7f7f7f7f;
int h[N], e[N * 2], ne[N * 2], idx;
int p[N],d[N];
int n,k,x,y;
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx] = b,ne[idx] = h[a],h[a] = idx ++;
}
void bfs(int s)
{
//memset(d,-1,sizeof (int) * (n + 4) ) ;
memset(p,-1,sizeof (int) * (n + 4));
p[s] = 0;
queue<PII> q;
q.push((PII){s,0});
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
int u = t.x;
d[t.x] = t.y;
for(int i = h[u];i != -1;i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(p[j] == -1)
{
p[j] = u;
q.push({j,d[t.x] + 1});
}
}
}
}
int a[N];
bool st[N];
int main()
{
ios;
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --)
{
cin >> n >> k;
cin >> x >> y;
memset(h,-1,sizeof (int) * (n + 4));
memset(st,0,sizeof (bool) * (n + 4));
idx = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < k;i ++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 0;i < n - 1;i ++)
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a,b),add(b,a);
}
bfs(x);
int res = 0;
a[k ++] = y;
st[x] = true;
for(int i = 0;i < k;i ++)
{
int t = a[i];
while(!st[t])
{
st[t] = true;
t = p[t];
res += 2;
}
}
cout << res - d[y]<< endl;
}
return 0;
}
标签:typedef,787,int,ios,Codeforces,cin,Div,include,define 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/notyour-young/p/16228362.html