CSAPP读书笔记第二章
作者:互联网
计算机的字长
每一台计算机都有字长,指明指针数据的标称大小,字长决定了的最重要的系统参数是虚拟地址空间的最大大小。
-
字长决定了指针的存储大小,32位的字长的指针存储空间是4字节,64位是8个字节;
-
字长决定了虚拟地址的最大大小,所以32位的寻址空间最大是\(2^{32}\)Byte = 4GB,64位的是\(2^{64}\)Byte = 16EB。
典型的C语言的数据类型的大小参考下表
| C声明 | 32bit | 64bit |
|---|---|---|
| char | 1 | 1 |
| short int | 2 | 2 |
| int | 4 | 4 |
| long int | 4 | 8 |
| long long int | 8 | 8 |
| char * | 4 | 8 |
| float | 4 | 4 |
| double | 8 | 8 |
查看上面的表格,32bit和64bit的大部分数据类型的字节长度是一样的,仅有两个不同,long int和char *。可以使用下面的代码查看每个不同类型的字节的大小
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("size of char is %d\n", sizeof(char));
printf("size of short is %d\n", sizeof(short));
printf("size of int is %d\n", sizeof(int));
printf("size of long is %d\n", sizeof(long));
printf("size of long long is %d\n", sizeof(long long));
printf("size of double is %d\n", sizeof(double));
printf("size of float is %d\n", sizeof(float));
printf("size of char* is %d\n", sizeof(char *));
return 0;
}
我在自己的64位字长的win10电脑上试了下,除了char *的字节数是4,其他的与上面表格的结果一样。
整数的表示和转换
整数范围
整数分为无符号和有符号整数,如果表示整数\(w\)位比特,那么无符号表示的范围是\([0, 2^w-1]\),有符号整数表示的范围是\([-2^{w-1},2^{w-1}-1]\)。下面是一些典型值,

参考下表,可以在自己的PC上可以通过下面的代码,得到上面的值
| Macro | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CHAR_BIT | 8 | Defines the number of bits in a byte. |
| SCHAR_MIN | -128 | Defines the minimum value for a signed char. |
| SCHAR_MAX | +127 | Defines the maximum value for a signed char. |
| UCHAR_MAX | 255 | Defines the maximum value for an unsigned char. |
| CHAR_MIN | -128 | Defines the minimum value for type char and its value will be equal to SCHAR_MIN if char represents negative values, otherwise zero. |
| CHAR_MAX | +127 | Defines the value for type char and its value will be equal to SCHAR_MAX if char represents negative values, otherwise UCHAR_MAX. |
| MB_LEN_MAX | 16 | Defines the maximum number of bytes in a multi-byte character. |
| SHRT_MIN | -32768 | Defines the minimum value for a short int. |
| SHRT_MAX | +32767 | Defines the maximum value for a short int. |
| USHRT_MAX | 65535 | Defines the maximum value for an unsigned short int. |
| INT_MIN | -2147483648 | Defines the minimum value for an int. |
| INT_MAX | +2147483647 | Defines the maximum value for an int. |
| UINT_MAX | 4294967295 | Defines the maximum value for an unsigned int. |
| LONG_MIN | -9223372036854775808 | Defines the minimum value for a long int. |
| LONG_MAX | +9223372036854775807 | Defines the maximum value for a long int. |
| ULONG_MAX | 18446744073709551615 | Defines the maximum value for an unsigned long int. |
代码如下
#include<stdio.h>
#include<limits.h>
int main()
{
printf("int max is %d, int min is %d\n", INT_MAX, INT_MIN);
printf("char max is %d, char min is %d\n", CHAR_MAX, CHAR_MIN);
return 0;
}
补码表示
\(w\)bit的有符号整数数学表示如下,
\[B 2 T_{w}(\vec{x}) \doteq-x_{w-1} 2^{w-1}+\sum_{i=0}^{w-2} x_{i} 2^{i} \]有一个理解的小技巧,与无符号的整数相比,对于这\(w\)位bit解读差异仅仅在最高位\(x_{w-1}\),有符号数的权重是\(-2^{w-1}\),无符号数的权重是\(2^{w-1}\)。这个是理解书本里面内容的技巧。典型数值的补码表示如下所示,
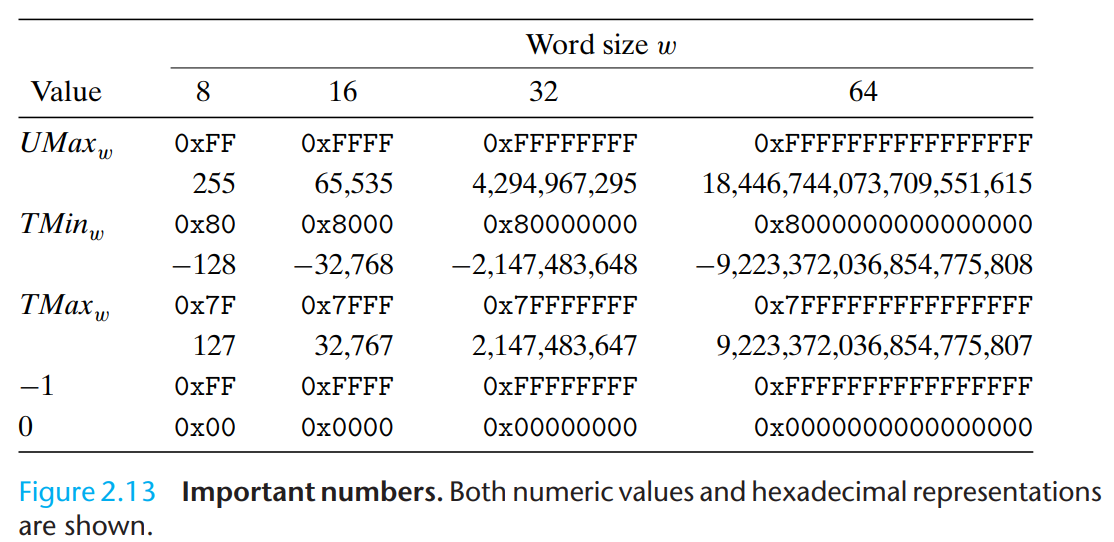
从上面的表格可以看出,
-
相同位宽的无符号整数最大值与有符号整数的-1的底层bit一样;
-
\(TMin_w = -TMax_w - 1\)。
C语言中无符号和有符号的转换
-
位宽一样的无符号和有符号的整数之间的转换,遵循底层的bit不变的原则,互相进行转换,也就是说无论如何转换,仅仅是底层bit的解读方法不同而已。
-
C语言中的无符号数和有符号数的二元计算,都会将有符号数强制转换为无符号整数进行计算。
整数的扩展和截断
整数的扩展分为无符号扩展和有符号数的扩展,
-
无符号数的扩展就往高位bit填充0;
-
有符号数的扩展方式是符号扩展,即最高位符号位填充空位。
整数截断逻辑很简单,就是底层的bit表示按照目的的位宽直接截断。这一小节有一个技巧,如果是位宽较小的无符号转换成为位宽较宽的有符号数,则是先改变大小,再进行转换,比如下面的代码
short sx = -12345;
unsigned uy = sx;
printf("uy = %u: \t", uy);
上面的代码中,第2行等价于(unsigned int)(int)sx,先应用符号扩展将short扩展到int,然后再使用等宽bit位的无符号的转换。
编程建议
在实际的软件开发中,尤其要注意无符号整数和有符号整数的转换,比如下面的代码的第4行
float sum_element(float a[], unsigned length) {
int i;
float result = 0.0f;
for (i = 0; i < length - 1; ++i) result += a[i];
return result;
}
如果length的初始值为0,那么length - 1会是一个非常大的正数,导致对于数组a的越界访问。
整数计算
标签:CSAPP,符号,int,MAX,读书笔记,value,char,第二章,Defines 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/bugxch/p/16187317.html