2021-06-20
作者:互联网
学习目标:
1. 何为 CSS
CSS是级联样式表(Cascading Style Sheets)的缩写。HTML 用于撰写页面的内容,而 CSS 将决定这些内容该如何在屏幕上呈现。
2. CSS 语法
一条CSS样式规则由两个主要的部分构成:选择器,以{}包裹的一条或多条声明: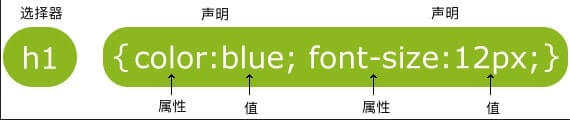
这条规则表明,页面中所有的一级标题都显示为蓝色,字体大小为12像数。
说明:
选择器是您需要改变样式的对象(上图的规则就一级标题生效)。
每条声明由一个属性和一个值组成。(无论是一条或多条声明,都需要用{}包裹,且声明用;分割)
属性(property)是您希望设置的样式属性(style attribute)。每个属性有一个值。属性和值被冒号分开。
3. CSS 如何生效
上节我们学习了如何定义 CSS样式,那么如何让这些规则对页面生效?
我们一般有三种方法:外部样式表,内部样式表,内联样式
4. 颜色, 尺寸, 对齐
颜色
颜色在网页中的重要性不言而喻。
我们可以采用颜色名称也可以使用颜色RGB16进制值,来设定前景或背景的颜色。如:
<!-- 颜色名称 -->
<h3 style="background-color:Tomato;">Tomato</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:Orange;">Orange</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:DodgerBlue;">DodgerBlue</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:MediumSeaGreen;">MediumSeaGreen</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:Gray;">Gray</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:SlateBlue;">SlateBlue</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:Violet;">Violet</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:LightGray;">LightGray</h3>
<hr>
<!-- 颜色值,3个字节分别代表RGB(Red,Green,Blue)的0~255的值 -->
<h3 style="background-color:#ff0000;">#ff0000</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:#0000ff;">#0000ff</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:#3cb371;">#3cb371</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:#ee82ee;">#ee82ee</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:#ffa500;">#ffa500</h3>
<h3 style="background-color:#6a5acd;">#6a5acd</h3>
<!-- 文本颜色 -->
<h3 style="color:Tomato;">Hello World</h3>
<p style="color:DodgerBlue;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit, amet consectetur adipisicing elit.</p>
<p style="color:MediumSeaGreen;">Ad facilis est ducimus rem consectetur, corporis omnis, eveniet esse dolor molestiae numquam odio corrupti, sed obcaecati praesentium accusamus? Tempora, dolor a?</p>
尺寸
我们可以用 height 和 width 设定元素内容占据的尺寸。常见的尺寸单位有:像数 px,百分比 %等。
新建如下 HTML 文件:
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./mycss.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="example-1">
这个元素高 200 pixels,占据全部宽度
</div>
<div class="example-2">
这个元素宽200像素,高300像素
</div>
</body>
</html>
再建对应的 CSS 文件如下:
.example-1 {
width: 100%;
height: 200px;
background-color: powderblue;
text-align: center;
}
.example-2 {
height: 100px;
width: 500px;
background-color: rgb(73, 138, 60);
text-align: right;
}
对齐
对于元素中的文本,我们可以简单的设置text-align属性为left, center, right即可(显然缺省的是左对齐),上例中已有相关的应用。
对于元素本身如何对齐,我们后面再学习。
5. 盒子模型
盒子模型指的是一个 HTML 元素可以看作一个盒子。从内到外,这个盒子是由内容 content, 内边距 padding, 边框 border, 外边距 margin构成的,
说明:
Content 盒子的内容,如文本、图片等
Padding 填充,也叫内边距,即内容和边框之间的区域
Border 边框,默认不显示
Margin 外边距,边框以外与其它元素的区域
新建如下 HTML 文件:
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./mycss.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">我是内容一,外面红色的是我的边框。注意边框的内外都有25px的距离。</div>
<div class="box2">我是内容二,外面蓝色的是我的边框。注意与上面元素的外边距,发生了叠加,不是50px而是25px。</div>
</body>
</html>
再建对应的 CSS 文件如下:
.box1 {
height: 200px;
width: 200px;
background-color:#615200;
color: aliceblue;
border: 10px solid red;
padding: 25px;
margin: 25px;
}
.box2 {
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
background-color:#004d61;
color: aliceblue;
border: 10px solid blue;
padding: 25px;
margin: 25px;
}
6. 定位
position属性用于对元素进行定位。该属性有以下一些值:
static 静态
relative 相对
fixed 固定
absolute 绝对
设置了元素的position属性后,我们才能使用top, bottom, left, right属性,否则定位无效。
static
设置为静态定位position: static;,这是元素的默认定位方式,也即你设置与否,元素都将按正常的页面布局进行。
即:按照元素在 HTML出现的先后顺序从上到下,从左到右进行元素的安排。
relative
设置为相对定位position: relative;,这将把元素相对于他的静态(正常)位置进行偏移
7. 溢出
当元素内容超过其指定的区域时,我们通过溢出overflow属性来处理这些溢出的部分。
溢出属性有一下几个值:
visible 默认值,溢出部分不被裁剪,在区域外面显示
hidden 裁剪溢出部分且不可见
scroll 裁剪溢出部分,但提供上下和左右滚动条供显示
auto 裁剪溢出部分,视情况提供滚动条
以上内容较好理解,请自行进行验证。
关于滚动,我们还可以单独对上下或左右方向进行,如下代码所示:
<!-- HTML -->
<div class="example-overflow-scroll-y">You can use the overflow property when you want to have better control of the
layout. The overflow property specifies what happens if content overflows an element's box.
</div>
<!-- CSS -->
.example-overflow-scroll-y {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: #eee;
overflow-y: scroll;
}
8. 不透明度
我们可以用opacity对任何元素(不过常用于图片)设置不透明度。
值在[0.0~1.0]之间,值越低,透明度越高
9. 组合选择器
前面我们学习了 CSS有三种选择器:元素、id 和 class 。但我们也可以进行组合,以得到简洁精确的选择。
下面我们介绍两种组合选择器。
后代选择器
以空格作为分隔,如:.haha p 代表在div元素内有.haha这种类的所有元素。
参见如下代码:
<html>
<head>
<style>
.haha p {
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="haha">
<p>Paragraph 1 in the div .haha.</p>
<p>Paragraph 2 in the div .haha>.</p>
<span>
<p>Paragraph 3 in the div .haha.</p>
</span>
</div>
<p>Paragraph 4. Not in a div .haha.</p>
<p>Paragraph 5. Not in a div .haha.</p>
</body>
</html>
段落1、2、3都将有黄色的背景,而段落4、5没有。
子选择器
也称为直接后代选择器,以>作为分隔,如:.haha > p 代表在有.haha类的元素内的直接
元素。
参见如下代码:
<html>
<head>
<style>
.haha > p {
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="haha">
<p>Paragraph 1 in the div .haha.</p>
<p>Paragraph 2 in the div .haha.</p>
<span>
<p>Paragraph 3 in the div .haha - it is descendant but not immediate child.</p>
</span> <!-- not Child but Descendant -->
</div>
<p>Paragraph 4. Not in a div .haha.</p>
<p>Paragraph 5. Not in a div .haha.</p>
</body>
</html>
虽然段落3在.haha类中,但它的直接父元素是span,不是.haha的直接后代,所以不能选择。只有段落1、2有黄色背景。
10. 伪类和伪元素
伪类(pseudo-class)或伪元素(pseudo-element)用于定义元素的某种特定的状态或位置等。
比如我们可能有这样的需求:
鼠标移到某元素上变换背景颜色
超链接访问前后访问后样式不同
离开必须填写的输入框时出现红色的外框进行警示
保证段落的第一行加粗,其它正常
标签:06,color,元素,haha,Paragraph,2021,20,div,CSS 来源: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_59150966/article/details/118071174