Python for Data Science - DBSCan clustering to identify outliers
作者:互联网
Chapter 4 - Clustering Models
Segment 3 - DBSCan clustering to identify outliers
DBSCAN for Outlier Detection
- Unsupervised method that clusters core samples(dense areas of a dataset) and denotes non-core samples(sparse portions of the dataset)
- Use to identify collective outliers
- Outliers should make up ≤5% of the total observations. Adjust model parameters accordingly
Important DBSCAN model parameters:
- eps
- min_samples
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pylab import rcParams
import seaborn as sb
import sklearn
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
from collections import Counter
%matplotlib inline
rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 5, 4
sb.set_style('whitegrid')
DBSCan clustering to identify outliers
Train your model and identify outliers
# with this example, we're going to use the same data that we used for the rest of this chapter. So we're going to copy and
# paste in the code.
address = '~/Data/iris.data.csv'
df = pd.read_csv(address, header=None, sep=',')
df.columns=['Sepal Length','Sepal Width','Petal Length','Petal Width', 'Species']
data = df.iloc[:,0:4].values
target = df.iloc[:,4].values
df[:5]
| Sepal Length | Sepal Width | Petal Length | Petal Width | Species | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 1 | 4.9 | 3.0 | 1.4 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 2 | 4.7 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 3 | 4.6 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 0.2 | setosa |
| 4 | 5.0 | 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.2 | setosa |
model = DBSCAN(eps=0.8, min_samples=19).fit(data)
print(model)
DBSCAN(eps=0.8, min_samples=19)
Visualize your results
outliers_df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(Counter(model.labels_))
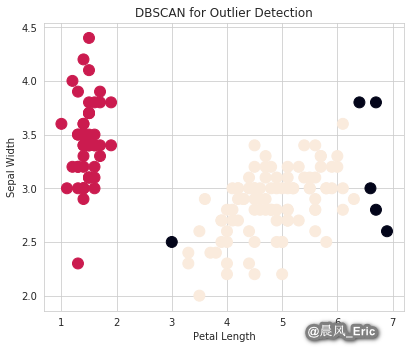
print(outliers_df[model.labels_==-1])
Counter({1: 94, 0: 50, -1: 6})
0 1 2 3
98 5.1 2.5 3.0 1.1
105 7.6 3.0 6.6 2.1
117 7.7 3.8 6.7 2.2
118 7.7 2.6 6.9 2.3
122 7.7 2.8 6.7 2.0
131 7.9 3.8 6.4 2.0
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_axes([.1,.1,1,1])
colors = model.labels_
ax.scatter(data[:,2],data[:,1],c=colors,s=120)
ax.set_xlabel('Petal Length')
ax.set_ylabel('Sepal Width')
plt.title('DBSCAN for Outlier Detection')
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'DBSCAN for Outlier Detection')
标签:clustering,DBSCan,Python,df,DBSCAN,import,model,outliers,data 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/keepmoving1113/p/14320912.html