python nms算法
作者:互联网
目录
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/a1103688841/article/details/89711120接下来用python写NMS,下面注释的非常详细,有什么不懂得可以留言:
分别从python,Cpython和GPU加速的方面进行。参考
这里我们主要讲解NMS的代码实现,首先我们先讲解一下NMS是干嘛的。我们看下图,可以很明显看出左边的脸3个方框都是代表Ross的脸,右边两个方框是代表小李子的脸。
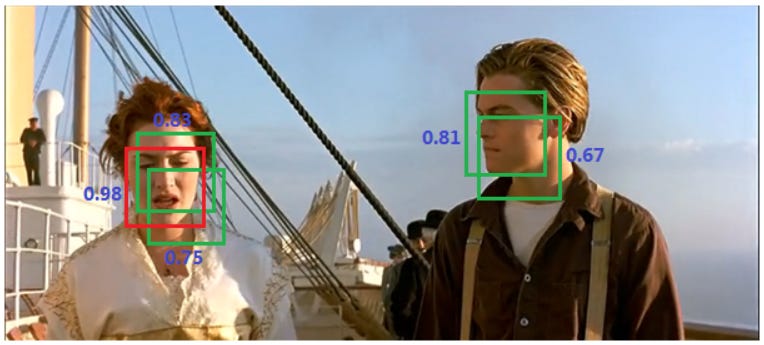
我们选取,得分最高的作为最后我们输出的结果,效果如下图,这就是是非极大值抑制(NMS)。
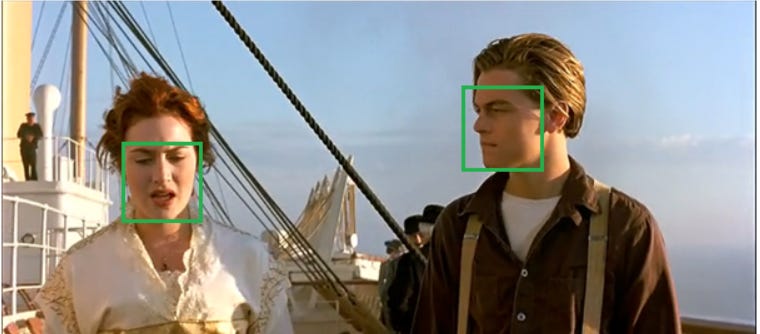
我们实现这个算法有个难点,就是我们怎么知道左边3个方框都是代表Ross的脸呢?我们观察一下发现,左边的三个方框重叠度非常高。然后看一下右边2个,发现右边两个重叠度也高。在看一下左边3个有右边2个毫无重叠,那我们判断他们就是两个物体。
那么NMS算法就出来了,我们首先要计算每个方框和其他方框的重叠度,利用阈值把重叠度高的方框方框进行合并,然后选取合并中分数最高的。
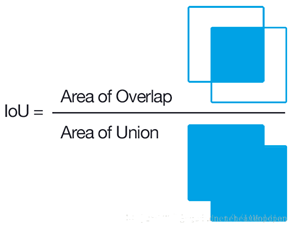
值得一提的是,我们这边定义重叠度用的是IOU算法(交并比),直观图如下:
在代码实现中
1.·····首先计算两个box左上角点坐标的最大值和右下角坐标的最小值 ,计算的是这连个点的坐标 
代码实现· ·x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]])
··· ··· ····y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
···· ··· ···x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
···· ··· ···y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
···· ··· ···w = np.maximum(0, x22-x11+1)
···· ··· ···h = np.maximum(0, y22-y11+1)
实现解析··可以看到我们取两个方框中最大的Xmin和Ymin,最小的Xmax和Ymax。
·········· ··· 当两个方框相交时,我们标出 了11和22的位置,22-11最后得到w,h是正的。

······· ··· 当两个方框不相交的时候,,我们也标出 了11和22的位置,22-11最后得到w,h是负的,我们让他等于0。
PS:这里我们特地找了一个X11,Y11重叠,X22,Y22重叠点,其他不想交的情况虽然X11,Y11不重叠,X22,Y22不重叠,但是X22-X11是负,Y22-Y11是负和前面所说的一样。

2. ·····然后计算交集面积 
3.·····最后把交集面积除以对应的并集面积,这边并集面积是两个相交面积相加减去一个交集面积就等于并集面积
- import numpy as np
- boxes=np.array([[100,100,210,210,0.72],
- [250,250,420,420,0.8],
- [220,220,320,330,0.92],
- [100,100,210,210,0.72],
- [230,240,325,330,0.81],
- [220,230,315,340,0.9]])
上面是生成一段矩形框,我们看到,中间那堆矩形框就是我们NMS去除的目标。
最后的结果应该是 。
- def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):
- #首先数据赋值和计算对应矩形框的面积
- #dets的数据格式是dets[[xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax,scores]....]
- x1 = dets[:,0]
- y1 = dets[:,1]
- x2 = dets[:,2]
- y2 = dets[:,3]
- areas = (y2-y1+1) * (x2-x1+1)
- scores = dets[:,4]
- print('areas ',areas)
- print('scores ',scores)
- #这边的keep用于存放,NMS后剩余的方框
- keep = []
- #取出分数从大到小排列的索引。.argsort()是从小到大排列,[::-1]是列表头和尾颠倒一下。
- index = scores.argsort()[::-1]
- print(index)
- #上面这两句比如分数[0.72 0.8 0.92 0.72 0.81 0.9 ]
- # 对应的索引index[ 2 5 4 1 3 0 ]记住是取出索引,scores列表没变。
- #index会剔除遍历过的方框,和合并过的方框。
- while index.size >0:
- print(index.size)
- #取出第一个方框进行和其他方框比对,看有没有可以合并的
- i = index[0] # every time the first is the biggst, and add it directly
- #因为我们这边分数已经按从大到小排列了。
- #所以如果有合并存在,也是保留分数最高的这个,也就是我们现在那个这个
- #keep保留的是索引值,不是具体的分数。
- keep.append(i)
- print(keep)
- print('x1',x1[i])
- print(x1[index[1:]])
- #计算交集的左上角和右下角
- #这里要注意,比如x1[i]这个方框的左上角x和所有其他的方框的左上角x的
- x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]]) # calculate the points of overlap
- y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
- x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
- y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
- print(x11,y11,x22,y22)
- #这边要注意,如果两个方框相交,X22-X11和Y22-Y11是正的。
- #如果两个方框不相交,X22-X11和Y22-Y11是负的,我们把不相交的W和H设为0.
- w = np.maximum(0, x22-x11+1)
- h = np.maximum(0, y22-y11+1)
- #计算重叠面积就是上面说的交集面积。不相交因为W和H都是0,所以不相交面积为0
- overlaps = w*h
- print('overlaps is',overlaps)
- #这个就是IOU公式(交并比)。
- #得出来的ious是一个列表,里面拥有当前方框和其他所有方框的IOU结果。
- ious = overlaps / (areas[i]+areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)
- print('ious is',ious)
- #接下来是合并重叠度最大的方框,也就是合并ious中值大于thresh的方框
- #我们合并的操作就是把他们剔除,因为我们合并这些方框只保留下分数最高的。
- #我们经过排序当前我们操作的方框就是分数最高的,所以我们剔除其他和当前重叠度最高的方框
- #这里np.where(ious<=thresh)[0]是一个固定写法。
- idx = np.where(ious<=thresh)[0]
- print(idx)
- #把留下来框在进行NMS操作
- #这边留下的框是去除当前操作的框,和当前操作的框重叠度大于thresh的框
- #每一次都会先去除当前操作框,所以索引的列表就会向前移动移位,要还原就+1,向后移动一位
- index = index[idx+1] # because index start from 1
- print(index)
- return keep
- import numpy as np
- boxes=np.array([[100,100,210,210,0.72],
- [250,250,420,420,0.8],
- [220,220,320,330,0.92],
- [100,100,210,210,0.72],
- [230,240,325,330,0.81],
- [220,230,315,340,0.9]])
- def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):
- x1 = dets[:,0]
- y1 = dets[:,1]
- x2 = dets[:,2]
- y2 = dets[:,3]
- areas = (y2-y1+1) * (x2-x1+1)
- scores = dets[:,4]
- keep = []
- index = scores.argsort()[::-1]
- while index.size >0:
- i = index[0] # every time the first is the biggst, and add it directly
- keep.append(i)
- x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]]) # calculate the points of overlap
- y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
- x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
- y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
- w = np.maximum(0, x22-x11+1) # the weights of overlap
- h = np.maximum(0, y22-y11+1) # the height of overlap
- overlaps = w*h
- ious = overlaps / (areas[i]+areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)
- idx = np.where(ious<=thresh)[0]
- index = index[idx+1] # because index start from 1
- return keep
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- def plot_bbox(dets, c='k'):
- x1 = dets[:,0]
- y1 = dets[:,1]
- x2 = dets[:,2]
- y2 = dets[:,3]
- plt.plot([x1,x2], [y1,y1], c)
- plt.plot([x1,x1], [y1,y2], c)
- plt.plot([x1,x2], [y2,y2], c)
- plt.plot([x2,x2], [y1,y2], c)
- plt.title(" nms")
- plt.figure(1)
- ax1 = plt.subplot(1,2,1)
- ax2 = plt.subplot(1,2,2)
- plt.sca(ax1)
- plot_bbox(boxes,'k') # before nms
- keep = py_cpu_nms(boxes, thresh=0.7)
- plt.sca(ax2)
- plot_bbox(boxes[keep], 'r')# after nms
效果:

 liumingchun13
发布了21 篇原创文章 · 获赞 15 · 访问量 3万+
私信
关注
liumingchun13
发布了21 篇原创文章 · 获赞 15 · 访问量 3万+
私信
关注
标签:index,nms,python,方框,y1,算法,np,dets,x1 来源: https://blog.csdn.net/liumingchun13/article/details/104552091