MIT 6.830 LAB3 Query Optimization查询优化器
作者:互联网
MIT 6.830 LAB3 Query Optimization查询优化器
目录2021/04/12-2021/04/17
前言
课程地址:http://db.lcs.mit.edu/6.830/sched.php
代码:https://github.com/MIT-DB-Class/simple-db-hw
讲义:https://github.com/MIT-DB-Class/course-info-2018/
快要期末考了,所以赶着时间把Lab3写完了。Lab3的代码量其实并不是很多,但是难度会比前两个Lab大,系统提供了整体的框架,所以主要在于理解。课程网站中的PPT十分有借鉴价值。
本次实验主要内容:
- 实现TableStats类中的方法,使得可以估计过滤器的选择率和遍历的代价,使用直方图或者你发明的其他方式展示结果。
- 实现JoinOptimizer类中的方法,使得可以估计cost和join的选择率
- 实现JoinOptimizer类中的orderJoins方法。这个方法会根据前两步计算出的数据,生成一个最佳的joins顺序
CBO(cost-based optimizer)
在学习本次实验之前,需要了解查询优化器的一些相关知识
RBO & CBO
SQL优化的发展,则可以分为两个阶段,即RBO(Rule Base Optimization),和CBO(Cost Base Optimization)。
RBO,RBO主要是开发人员在使用SQL的过程中,有些发现有些通用的规则,可以显著提高SQL执行的效率
例如,我们都知道join是非常耗时的一个操作,且性能与join双方数据量大小呈线性关系(通常情况下)。那么很自然的一个优化,就是尽可能减少join左右双方的数据量,于是就想到了先filter再join这样一个rule。而非常多个类似的rule,就构成了RBO。
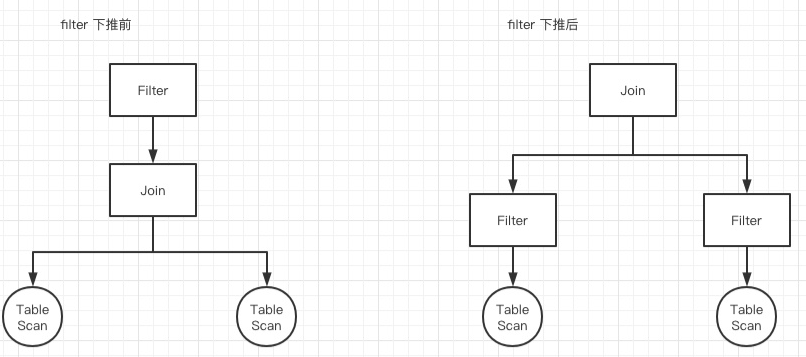
main idea of CBO
- 利用关于表的统计数据,来估计不同查询计划的cost。通常来说,cost与join、selection的基数、filter的选择率和join的谓词有关。
- 使用数据来对join和select进行排序,并选择最佳的实现方式
LAB3
exercise1
作为辅助类,提供方法来记录table的数据,用于后期进行估算。
构造时候需要提供(buckets桶个数, min最小值, max最大值)
之后可以不断往里面添加数据,然后调用
estimateSelectivity(Predicate.Op op, int v)方法进行数据统计
实现
- IntHistogram.java
- StringHistogram.java
主要根据讲义中的这个图进行实现
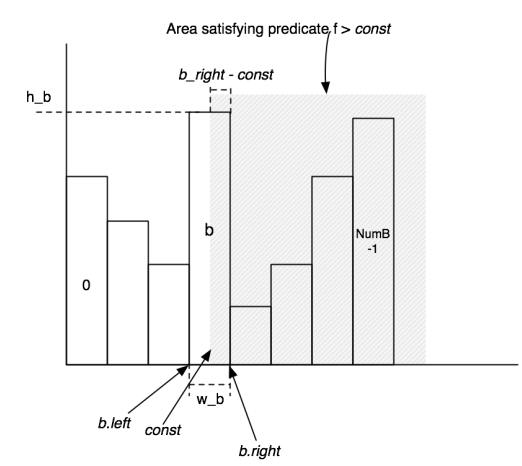
这里我引入了内部类Bucket进行辅助实现
难点在于区间怎么定义,边界条件要小心,必要时可以特判
private class Bucket {
private int left;
private int right;
private int count;
public Bucket(int left, int right) {
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
// getter and setter
}
核心方法实现,注意width计算,要从Bucket里获得,而不是直接拿this.width,这个bug在exercise2才发现
/**
* Estimate the selectivity of a particular predicate and operand on this table.
* <p>
* For example, if "op" is "GREATER_THAN" and "v" is 5,
* return your estimate of the fraction of elements that are greater than 5.
*
* @param op Operator
* @param v Value
* @return Predicted selectivity of this particular operator and value
*/
public double estimateSelectivity(Predicate.Op op, int v) {
int index;
double sum;
Bucket bucket;
switch (op) {
case EQUALS:
index = getIndex(v);
if(index<0||index>=numBuckets){
return 0;
}else{
bucket = buckets.get(index);
return (1.0*bucket.getCount() / bucket.getWidth()) / ntup;
}
case GREATER_THAN:
index = getIndex(v);
if (index < 0) {
return 1;
} else if (index >= numBuckets) {
return 0;
} else {
bucket = buckets.get(index);
sum = 1.0*bucket.getCount() * (bucket.getRight() - v) / bucket.getWidth();
for (int i = index+1; i < numBuckets; i++) {
sum += buckets.get(i).getCount();
}
return sum / ntup;
}
case LESS_THAN:
index = getIndex(v);
if (index < 0) {
return 0;
} else if (index >= numBuckets) {
return 1;
} else {
bucket = buckets.get(index);
sum = 1.0*bucket.getCount() * (v - bucket.getLeft()) / bucket.getWidth();
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
sum += buckets.get(i).getCount();
}
return sum / ntup;
}
case GREATER_THAN_OR_EQ:
return estimateSelectivity(Predicate.Op.GREATER_THAN,v-1);
case NOT_EQUALS:
return 1-estimateSelectivity(Predicate.Op.EQUALS,v);
case LESS_THAN_OR_EQ:
return estimateSelectivity(Predicate.Op.LESS_THAN,v+1);
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
exercise2
TableStats类用于统计某个Table的数据,包括选择率、开销等
实现
- TableStats.java中的
- 构造函数
estimateSelectivity(int field, Predicate.Op op, Field constant)estimateScanCost()estimateTableCardinality(double selectivityFactor)
在成员变量中引入
/**
* <FiledIndex,Histogram>
*/
private Map<Integer,StringHistogram> stringHistogramMap;
private Map<Integer,IntHistogram> integerIntHistogramMap;
为每一个field建立Histogram并调用即可
exercise3
计算JOIN的cost和cardinality,也就是join操作的开销和join后的基数预估
实现
- JoinOptimizer.java
-
estimateJoinCost(LogicalJoinNode j, int card1, int card2, double cost1, double cost2) -
estimateJoinCardinality(LogicalJoinNode j, int card1, int card2, boolean t1pkey, boolean t2pkey)
-
基本按照框架走就可
计算JoinCost使用讲义中的公式
joincost(t1 join t2) = scancost(t1) + ntups(t1) x scancost(t2) //IO cost
+ ntups(t1) x ntups(t2) //CPU cost
计算基数,也是使用讲义中简化后的估算方法
-
对于equality joins
当一个属性是primary key,由表连接产生的tuples数量不能大于non-primary key属性的选择数。
对于没有primary key的equality joins,很难说连接输出的大小是多少,可以是两表被选择数的乘积(如果两表的所有tuples都有相同的值),或者也可以是0。
-
对于范围scans,很难说清楚明确的数量。
输出的数量应该与输入的数量是成比例的,可以预估一个固定的分数代表range scans产生的向量叉积(cross-product),比如30%。总的来说,range join的开销应该大于相同大小两表的non-primary key equality join开销。
exercise4
LAB中为我们实现了几个辅助方法,我们只需要按照讲义中的伪代码将其串联起来即可,虽然听起来唬人,但需要动手写的东西比较简单,框架性的代码已经给出了。
实现
- JoinOptimizer.java
Vector<LogicalJoinNode> orderJoins( HashMap<String, TableStats> stats, HashMap<String, Double> filterSelectivities, boolean explain)
核心就是翻译这段伪代码
j = set of join nodes
for (i in 1...|j|):
for s in {all length i subsets of j}
bestPlan = {}
for s' in {all length d-1 subsets of s}
subplan = optjoin(s')
plan = best way to join (s-s') to subplan
if (cost(plan) < cost(bestPlan))
bestPlan = plan
optjoin(s) = bestPlan
return optjoin(j)
这里使用到了一个十分巧妙的动态规划算法,课件上的描述如下:
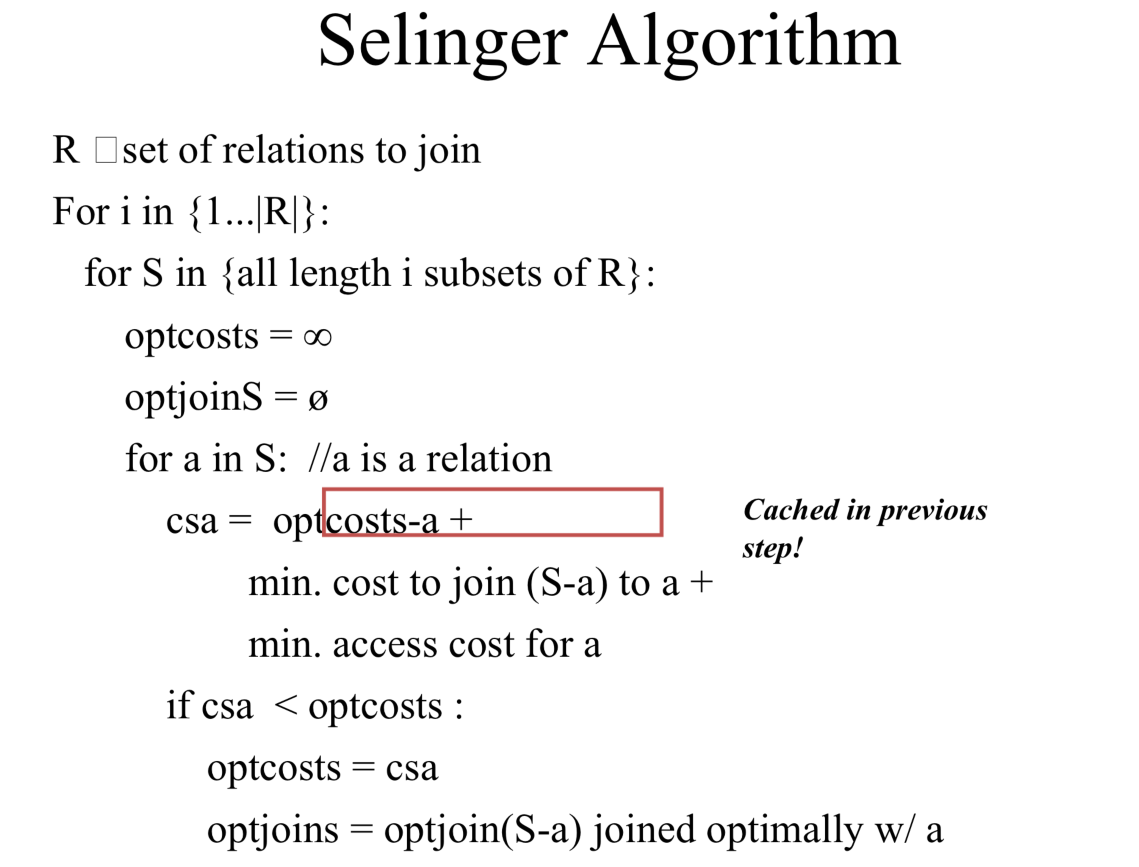
直接将其翻译即可实现
public Vector<LogicalJoinNode> orderJoins(
HashMap<String, TableStats> stats,
HashMap<String, Double> filterSelectivities, boolean explain)
throws ParsingException {
PlanCache pc = new PlanCache();
Set<Set<LogicalJoinNode>> nodeSets = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= joins.size(); i++) {
nodeSets = enumerateSubsets(joins,i);
for(Set<LogicalJoinNode> nodeSet:nodeSets){
double optCosts = Double.MAX_VALUE;
int optCards =0;
Vector<LogicalJoinNode> optJoins = null;
for(LogicalJoinNode n:nodeSet){
CostCard costCard = computeCostAndCardOfSubplan(stats,filterSelectivities,n,nodeSet,optCosts,pc);
if(costCard!=null){
optCosts = costCard.cost;
optJoins = costCard.plan;
optCards = costCard.card;
}
}
pc.addPlan(nodeSet,optCosts,optCards,optJoins);
}
}
Vector<LogicalJoinNode> res = null;
for(Set<LogicalJoinNode> nodes:nodeSets){
res = pc.getOrder(nodes);
}
if(explain){
printJoins(res,pc,stats,filterSelectivities);
}
return res;
}
优化点:Set<Set<T>> enumerateSubsets(Vector<T> v, int size)方法
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/159688029这篇博文中提到了joinOrder运行慢的原因主要在于enumerateSubsets的方法,讲义上也有这样的描述:This method is not particularly efficient; you can earn extra credit by implementing a more efficient enumerator
于是,我们来优化一下这个方法
优化前:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> Set<Set<T>> enumerateSubsets(Vector<T> v, int size) {
Set<Set<T>> els = new HashSet<Set<T>>();
els.add(new HashSet<T>());
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Set<Set<T>> newels = new HashSet<Set<T>>();
for (Set<T> s : els) {
for (T t : v) {
if(s.contains(t)){
continue;
}
Set<T> news = (Set<T>) (((HashSet<T>) s).clone());
if (news.add(t))
newels.add(news);
}
}
els = newels;
}
return els;
}
优化后:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> Set<Set<T>> enumerateSubsets(Vector<T> v, int size) {
Set<Set<T>> els = new HashSet<Set<T>>();
Vector<Boolean> used = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
used.add(false);
}
enumerateSubsetsHelper(els,v,used,0,0,size);
}
private <T> void enumerateSubsetsHelper(Set<Set<T>> res,Vector<T> v,Vector<Boolean> used,int next,int count,int size){
if(count==size){
Set<T> tmp = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
if(used.get(i)){
tmp.add(v.get(i));
}
}
res.add(tmp);
return;
}
for (int i = next; i <v.size()-(size-count-1); i++) {
used.set(i,true);
enumerateSubsetsHelper(res,v,used,i+1,count+1,size);
used.set(i,false);
}
}
reference
MIT 6.830 Database System 数据库系统 Lab 3 实验报告https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/159688029
6.830 Lab 3: Query Optimizationhttps://blog.csdn.net/hjw199666/article/details/103639262
标签:6.830,index,Set,return,int,bucket,LAB3,Optimization,join 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/cpaulyz/p/14671793.html