Good Bye 2019(前五题题解)
作者:互联网
这套也是后来补得。
我太菜了,第三题就卡着了。想了好久才做出来,要是参加了绝对掉分。
D题是人生中做完的第一道交互题,不容易。
A.Card Game
题目大意:一共有n张互不相同的牌,玩家1有k1张牌,玩家2有k2张牌。两个人每次都会拿出一张牌,牌号大的人会得到这张牌,直到一方没牌。问第一个人能否会获胜。
这就是我们从小玩的比大小游戏。
在广大劳动人民的实践后得出来结论是有最大的牌的人获胜。
代码如下:

1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstdio>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 #include <cstring>
5 #include <vector>
6 #define rep(x, l, r) for(int x = l; x <= r; x++)
7 #define repd(x, r, l) for(int x = r; x >= l; x--)
8 #define clr(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
9 #define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
10 #define pb push_back
11 #define mp make_pair
12 #define MAXN
13 #define fi first
14 #define se second
15 #define SZ(x) ((int)x.size())
16 using namespace std;
17 typedef long long ll;
18 typedef vector<int> vi;
19 typedef pair<int, int> pii;
20 const int INF = 1 << 30;
21 const int p = 1000000009;
22 int lowbit(int x){ return x & (-x);}
23 int fast_power(int a, int b){ int x; for(x = 1; b; b >>= 1){ if(b & 1) x = 1ll * x * a % p; a = 1ll * a * a % p;} return x % p;}
24
25 int main(){
26 int t;
27 scanf("%d", &t);
28 rep(times, 1, t){
29 int n, k1, k2;
30 scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &k1, &k2);
31 int maxx1 = 0, maxx2 = 0;
32 rep(i, 1, k1){
33 int x;
34 scanf("%d", &x);
35 maxx1 = max(maxx1, x);
36 }
37 rep(i, 1, k2){
38 int x;
39 scanf("%d", &x);
40 maxx2 = max(maxx2, x);
41 }
42 if(maxx1 > maxx2) puts("YES");
43 else puts("NO");
44 }
45 return 0;
46 }
View Code-A
B.Interesting Subarray
题目大意:有一个数列a,让你找任意一个子段满足子段的最大值减最小值大于等于子段长度。
感觉这套的B题也比之前的难了点,看着屏幕愣了半天,可能最近脑子不对劲。
如果子段(l,r)满足条件,那么必定存在i,j满足a[i] - i < a[j] - j ,或者a[i] + i > a[j] + j。
那么只需记录下在所有的i,j( i <= j ),最小的a[i] - i和最大的a[i] + i,如果满足上面的条件就输出这一对。
代码如下:

1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstdio>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 #include <cstring>
5 #include <vector>
6 #define rep(x, l, r) for(int x = l; x <= r; x++)
7 #define repd(x, r, l) for(int x = r; x >= l; x--)
8 #define clr(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
9 #define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
10 #define pb push_back
11 #define mp make_pair
12 #define MAXN 200005
13 #define fi first
14 #define se second
15 #define SZ(x) ((int)x.size())
16 using namespace std;
17 typedef long long ll;
18 typedef vector<int> vi;
19 typedef pair<int, int> pii;
20 const int INF = 1 << 30;
21 const int p = 1000000009;
22 int lowbit(int x){ return x & (-x);}
23 int fast_power(int a, int b){ int x; for(x = 1; b; b >>= 1){ if(b & 1) x = 1ll * x * a % p; a = 1ll * a * a % p;} return x % p;}
24
25 int a[MAXN];
26
27 int main(){
28 int t;
29 scanf("%d", &t);
30 rep(times, 1, t){
31 int n;
32 scanf("%d", &n);
33 rep(i, 1, n) scanf("%d", &a[i]);
34 int s = INF, id = 0, ans = 0;
35 rep(i, 1, n){
36 if(s < a[i] - i){
37 printf("YES\n%d %d\n", id, i);
38 ans = 1;
39 break;
40 }
41 if(a[i] - i < s){
42 s = a[i] - i;
43 id = i;
44 }
45 }
46 if(!ans){
47 s = 0, id = 0;
48 rep(i, 1, n){
49 if(s > a[i] + i){
50 printf("YES\n%d %d\n", id, i);
51 ans = 1;
52 break;
53 }
54 if(a[i] + i > s){
55 s = a[i] + i;
56 id = i;
57 }
58 }
59 }
60 if(!ans) puts("NO");
61 }
62 return 0;
63 }
View Code-B
C.Make Good
题目大意:给你一串数字,让你在其中插入最多3个数字,使得这些数字的总和等于异或的2倍,只要给出任何一种方案即可。
首先这串数字是和我们没关系了,我们需要的只是它们的异或以及和。
很显然,必定存在一种方案只放一个数字就能成立(不要问我为什么,程序员不需要证明)。
然后么将异或的乘个二,按照二进制来计算。
对于每一位,要是该位的为1,会对和产生1的贡献,对异或产生2的贡献,那么对于一个二进制位,要是这两个数不同,插入的数该位一定为1。
感觉解释的有点模糊……那就来个样例解释一下。
以下以[1,2,3,7]为例:
和:13 二进制:01101
异或:7 二进制:00111
异或的先乘个2也就是右移一位,为01110
0110 | 1
0111 | 0
两位置不同,答案该位为1,即加上1 << 0,变成1
和变成01110,异或变成01100,最后一位已经相同了,舍掉
011 | 1
011 | 0
不同,答案变成3,两数分别变成1000和0100,同样舍最后一位
10 | 0
01 | 0 相同
1 | 0
0 | 1 不同,答案变成11
| 1
| 1 相同
插入后数列为 1, 2, 3, 7 , 11符合条件
具体代码实现:

1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstdio>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 #include <cstring>
5 #include <vector>
6 #define rep(x, l, r) for(int x = l; x <= r; x++)
7 #define repd(x, r, l) for(int x = r; x >= l; x--)
8 #define clr(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
9 #define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
10 #define pb push_back
11 #define mp make_pair
12 #define MAXN
13 #define fi first
14 #define se second
15 #define SZ(x) ((int)x.size())
16 using namespace std;
17 typedef long long ll;
18 typedef vector<int> vi;
19 typedef pair<int, int> pii;
20 const int INF = 1 << 30;
21 const int p = 1000000009;
22 int lowbit(int x){ return x & (-x);}
23 int fast_power(int a, int b){ int x; for(x = 1; b; b >>= 1){ if(b & 1) x = 1ll * x * a % p; a = 1ll * a * a % p;} return x % p;}
24
25 int main(){
26 int t;
27 scanf("%d", &t);
28 rep(times, 1, t){
29 int n;
30 scanf("%d", &n);
31 ll s1 = 0, s2 = 0;
32 rep(i, 1, n){
33 ll x;
34 scanf("%lld", &x);
35 s1 += x;
36 s2 ^= x;
37 }
38 s2 <<= 1;
39 ll ans = 0;
40 for(int i = 0; s1 != s2; i++){
41 if((s1 & 1) ^ (s2 & 1)){
42 s1 += 1;
43 s2 ^= 2;
44 ans += 1ll << i;
45 }
46 s1 >>= 1;
47 s2 >>= 1;
48 }
49 printf("1\n%lld\n", ans);
50 }
51 return 0;
52 }
View Code-D
D.Strange Device
题目大意:有一个长为n数列a,值已确定,但是你不知道。现在有个设备,你可以输入长为k的上升序列p1,p2,…,pk,进行询问,它会回答ap1,ap2,...,apk中第m小的数在原数列的坐标和这个数的值。现在给你n和k,让你在最多询问n次后回答m的大小。
作为以往交互题直接跳的人,这题拿到一脸懵,后来还是看题解才有的思路。
我们只需要询问k+1次,第i次询问序列为{ x | 1 <= x <= k + 1, x <> i }
假设n = 4, k = 3,询问分别为
2 3 4
1 3 4
1 2 4
1 2 3
这样问有一个好处,第i次询问,若是i <= m,那么返回的必然是[a1..ak +1]中第m + 1小的数,否则返回的数必然是第m小的数。
那么在k+1次询问后,m+1小的数恰好返回了m次,于是我们答案就是返回的较大的一个数的次数。
代码如下:

1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstdio>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 #include <cstring>
5 #include <vector>
6 #include <map>
7 #define rep(x, l, r) for(int x = l; x <= r; x++)
8 #define repd(x, r, l) for(int x = r; x >= l; x--)
9 #define clr(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
10 #define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
11 #define pb push_back
12 #define mp make_pair
13 #define MAXN
14 #define fi first
15 #define se second
16 #define SZ(x) ((int)x.size())
17 using namespace std;
18 typedef long long ll;
19 typedef vector<int> vi;
20 typedef pair<int, int> pii;
21 const int INF = 1 << 30;
22 const int p = 1000000009;
23 int lowbit(int x){ return x & (-x);}
24 int fast_power(int a, int b){ int x; for(x = 1; b; b >>= 1){ if(b & 1) x = 1ll * x * a % p; a = 1ll * a * a % p;} return x % p;}
25
26 map<int, int> f;
27
28 int main(){
29 int n, k;
30 scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
31 int maxx = 0;
32 rep(i, 1, k + 1){
33 putchar('?');
34 rep(j, 1, k + 1){
35 if(i == j) continue;
36 printf(" %d", j);
37 }
38 puts("");
39 fflush(stdout);
40 int x, y;
41 scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
42 f[y]++;
43 maxx = max(maxx, y);
44 }
45 printf("! %d\n", f[maxx]);
46 return 0;
47 }
View Code-D
E.Divide Points
题目大意:给你n个点和它们的坐标,现在给它们两两连上边,如果在同一组为黄色,不同组为蓝色。现在让你给出任意一种分组方案,使得所有长度相同的边颜色相同。
相信大家看到这题目想的都是二分图啊,并查集啊……但我不一样,我想的是:这题目能做嘛……
大佬的做法真是高超,先放上题解里截来的图。

主要思路就是奇偶分类。
我们将点按照横纵坐标的奇偶性,分成4个集合。
其中点上的0,1表示坐标的奇偶性,边上的0,1表示长度平方的奇偶性。
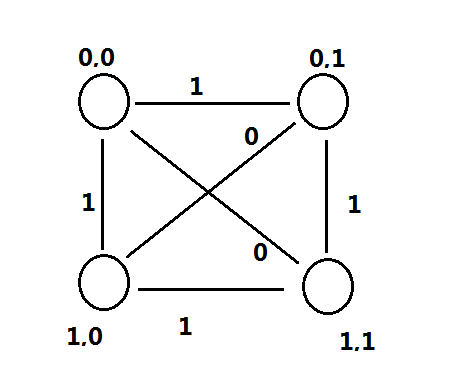
不难得出以上不同集合的点的关系,另外同一集合中的边当然也为0。
那么我们只要将(0,0)和(1,1)放入一组,(0,1)和(1,0)放入另一组,那么偶边(即长度平方为偶数的边)必定是同一组的两点,奇边必定是不同组的两点。当然这有个前提,就是每组都不能为空。
那若是有一组为空呢,图片就变成了这个样子

两个集合连起来也是偶边,自己集合连自己集合也是偶边,似乎无法连接了。
但是我们发现自己连自己横坐标差和纵坐标差都为偶数,和别的集合连得差都为偶数。
我们设同一集合的横坐标差为2k1,纵坐标差为2k2,不同集合的横坐标差为2k1+1,纵坐标差是2k2+1
根据距离公式d = √((x1 - x2) × (x1 + x2) + (y1 - y2) × (y1 - y2))进行计算(方便起见,直接算边长度的平方)。
同一集合相连 = (2k1)2 + (2k2)2 = 4(k12 + k22)
不同集合相连 = (2k1 + 1)2 + (2k2 + 1)2 = 4(k12 + k22 + k1 + k2) + 2
很显然这两个是不会相等的。
那么如果不符合上一个情况,那么按x的奇偶性分组。
可是万一数据只有一个集合呢?
没事把数据缩小一倍就好了,到时候一定会有答案因为点坐标两两不同。
这样为什么可行呢?
因为同一个集合中的点的奇偶性都是相同的,那么我们将它们的最后一位舍弃也是符合原来的大小情况。
代码如下:

1 #include <iostream>
2 #include <cstdio>
3 #include <algorithm>
4 #include <cstring>
5 #include <vector>
6 #define rep(x, l, r) for(int x = l; x <= r; x++)
7 #define repd(x, r, l) for(int x = r; x >= l; x--)
8 #define clr(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
9 #define all(x) x.begin(), x.end()
10 #define pb push_back
11 #define mp make_pair
12 #define MAXN 1005
13 #define fi first
14 #define se second
15 #define SZ(x) ((int)x.size())
16 using namespace std;
17 typedef long long ll;
18 typedef vector<int> vi;
19 typedef pair<int, int> pii;
20 const int INF = 1 << 30;
21 const int p = 1000000009;
22 int lowbit(int x){ return x & (-x);}
23 int fast_power(int a, int b){ int x; for(x = 1; b; b >>= 1){ if(b & 1) x = 1ll * x * a % p; a = 1ll * a * a % p;} return x % p;}
24
25 vi ans;
26 int x[MAXN], y[MAXN], cnt[2][2];
27
28 int main(){
29 int n;
30 scanf("%d", &n);
31 rep(i, 1, n) scanf("%d%d", &x[i], &y[i]);
32 while(1){
33 clr(cnt, 0);
34 rep(i, 1, n) cnt[x[i] & 1][y[i] & 1]++;
35 if(cnt[0][1] + cnt[1][0] > 0 && cnt[0][0] + cnt[1][1] > 0){
36 rep(i, 1, n)
37 if((x[i] & 1) ^ (y[i] & 1)) ans.pb(i);
38 printf("%d\n", SZ(ans));
39 rep(i, 0, SZ(ans) - 1) printf("%d ", ans[i]);
40 puts("");
41 return 0;
42 }
43 if(cnt[0][0] + cnt[0][1] > 0 && cnt[1][0] + cnt[1][1] > 0){
44 rep(i, 1, n)
45 if(x[i] & 1) ans.pb(i);
46 printf("%d\n", SZ(ans));
47 rep(i, 0, SZ(ans) - 1) printf("%d ", ans[i]);
48 puts("");
49 return 0;
50 }
51 rep(i, 1, n){
52 x[i] >>= 1;
53 y[i] >>= 1;
54 }
55 }
56 return 0;
57 }
View Code-E
标签:typedef,include,int,题解,rep,Good,ans,Bye,define 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/nblyz2003/p/12161998.html
