简单web架构实例应用
作者:互联网
一、架构图
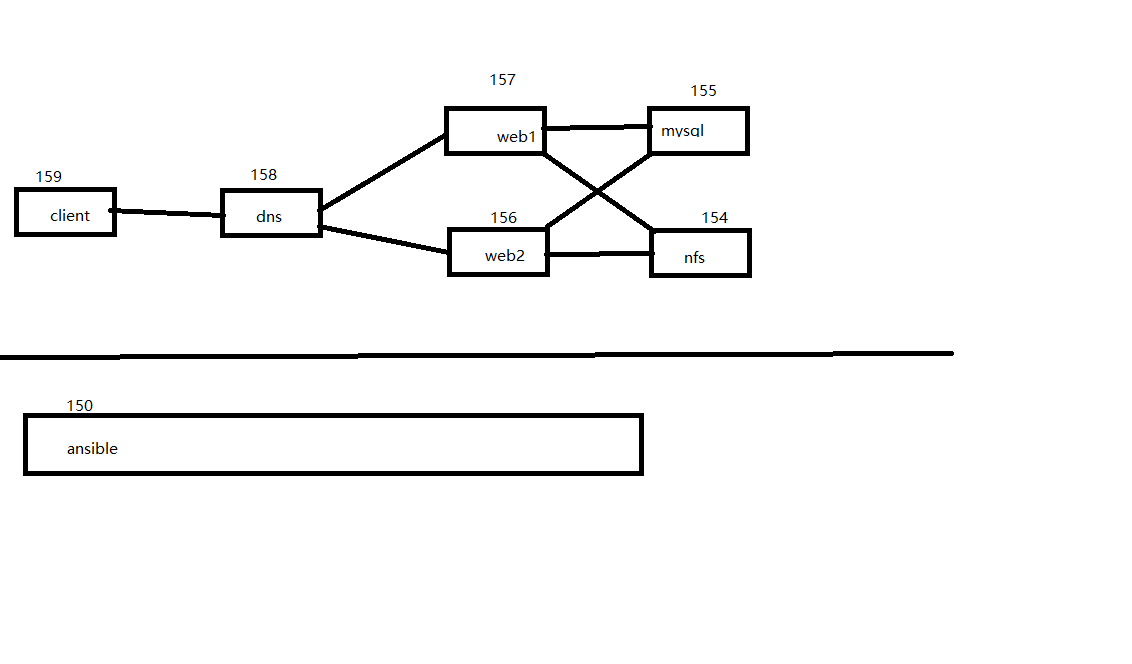
- dns完成解析web1,web2来实现负载均衡
- web1,web2使用后台的mysql数据库
- web1,web2的页面数据全部放在nfs数据上,实现自动挂载
- nfs服务器为web1,web2提供网页数据
10.7.2. 准备工作
设置ip信息
nmcli con add ifname ens33 con-name ens33 type ethernet ipv4.method manual \
ipv4.address 192.158.46.150/24 ipv4.gateway 192.168.46.1
Note
我使用的nmcli修改的ip,当然也是可以手工修改的。
10.7.3. ansible的配置
10.7.3.1. 安装ansible
[root@localhost ~]# yum install ansible
10.7.3.2. 添加主机
需要添加如下内容到/etc/ansible/hosts文件中去。
[client]
192.168.46.159
[dns]
192.168.46.158
[web]
192.168.46.157
192.168.46.156
[db]
192.168.46.155
[nfs]
192.168.46.154
[self]
192.168.46.150
10.7.3.3. 配置免密码登陆
这里我之前写有一个脚本自动完成免密码登陆的脚本,参考我的博客
[root@localhost ~]# cat hosts.txt
192.168.46.150 root oracle
192.168.46.151 root oracle
192.168.46.152 root oracle
192.168.46.153 root oracle
192.168.46.154 root oracle
192.168.46.155 root oracle
192.168.46.156 root oracle
192.168.46.157 root oracle
192.168.46.158 root oracle
192.168.46.159 root oracle
192.168.46.160 root oracle
[root@localhost ~]# cat mima.sh
#!/bin/bash
#================================================
#FileName :expect_ssh.sh
#Author :zhaojiedi
#Description:
#DateTime :2018-01-05 08:26:06
#Version :V1.0
#Other :
#================================================
host_username_password_file=hosts.txt
# install expect
rpm -q expect &>/dev/null || yum install -yq expect &>/dev/null
# create id_rsa.pub file
pubkey=~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
if [ ! -e "$pubkey" ] ; then
ssh-keygen -P "" -t rsa -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa
fi
while read host username password ; do
con=${username}"@"${host}
echo $password
expect <<EOF
set timeout 20
spawn ssh-copy-id $con
expect {
"yes/no" { send "yes\n" ; exp_continue }
"password:" { send "${password}\n"; exp_continue }
}
EOF
done < $host_username_password_file
# 执行下脚本,自动完成公钥copy工作了
[root@localhost ~]# bash mima.sh
# 测试下
[root@localhost ~]# ssh 192.168.46.151 'ip a show ens33'
10.7.3.4. 设置主机名(可选)
我这里的机器全是刚刚克隆出来的虚拟机,为了管理方便设置下主机名,防止误操作。
# 创建一个设置主机名的脚本
[root@localhost ~]# vim set_hostname.sh
[root@localhost ~]# cat set_hostname.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "start"
hostname
name=centos-$(ip a show ens33 |grep 'inet.*ens33' | sed -r -n 's@.*\.([0-9]{1,3})/.*@\1@p').linuxpanda.tech
echo $name
hostnamectl set-hostname $name
echo "end"
[root@centos-localhost ~]# ansible all -m script -a '/root/set_hostname.sh'
这个脚本也是设置了ansible主机的ip。
10.7.3.5. 防火墙和selinux关闭
# 关闭防火墙
[root@centos-150 ~]# ansible all -m service -a 'name=firewalld enabled=no'
[root@centos-150 ~]# ansible all -m service -a 'name=firewalld state=stopped'
[root@centos-150 ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'sed -i -r 's@SELINUX=.*@SELINUX=disabled@' /etc/sysconfig/selinux'
[root@centos-150 ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'setenforce 0'
Note
如果原有selinux就是disabled,使用setenforce 0会报错误的,不用管它。
10.7.4. dns主机设置
10.7.4.1. dns配置
[root@centos-158 ~]# yum install bind bind-utils
[root@centos-158 ~]# vim /etc/named.conf
# 注释如下5行
// listen-on port 53 { 127.0.0.1; };
// listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
// allow-query { localhost; };
// dnssec-enable yes;
// dnssec-validation yes;
[root@centos-158 ~]# vim /etc/named.rfc1912.zones
# 添加如下内容,注意之后的分号
zone "linuxpanda.tech" IN {
type master;
file "linuxpanda.tech.zone";
};
[root@centos-158 ~]# cd /var/named/
[root@centos-158 named]# cp -a named.localhost linuxpanda.tech.zone
[root@centos-158 named]# vim linuxpanda.tech.zone
[root@centos-158 named]# cat linuxpanda.tech.zone
$TTL 1D
@ IN SOA ns1 admin (
0 ; serial
1D ; refresh
1H ; retry
1W ; expire
3H ) ; minimum
NS ns1
ns1 A 192.168.46.158
web A 192.168.46.157
web A 192.168.46.156
www CNAME web
10.7.4.2. dns本机测试
[root@centos-158 named]# dig www.linuxpanda.tech @localhost
; <<>> DiG 9.9.4-RedHat-9.9.4-51.el7_4.2 <<>> www.linuxpanda.tech @localhost
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 57957
;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 3, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 2
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 4096
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;www.linuxpanda.tech. IN A
;; ANSWER SECTION:
www.linuxpanda.tech. 86400 IN CNAME web.linuxpanda.tech.
web.linuxpanda.tech. 86400 IN A 192.168.46.156
web.linuxpanda.tech. 86400 IN A 192.168.46.157
;; AUTHORITY SECTION:
linuxpanda.tech. 86400 IN NS ns1.linuxpanda.tech.
;; ADDITIONAL SECTION:
ns1.linuxpanda.tech. 86400 IN A 192.168.46.158
;; Query time: 0 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1)
;; WHEN: Sun Feb 18 21:05:05 CST 2018
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 132
10.7.5. client主机测试
# 修改客户端的dns指向为我们自己的dns主机
[root@centos-159 ~]# nmcli con modify ens33 ipv4.dns 192.168.46.158
# 重启网络,或者重新加载
[root@centos-159 ~]# service network restart
# ping下我们的web主机,看是否能解析出来157,156两个ip
[root@centos-159 ~]# ping www.linuxpanda.tech
PING web.linuxpanda.tech (192.168.46.157) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.46.157 (192.168.46.157): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.330 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.46.157 (192.168.46.157): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.255 ms
64 bytes from 192.168.46.157 (192.168.46.157): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.292 ms
[root@centos-159 ~]# ping www.linuxpanda.tech
PING web.linuxpanda.tech (192.168.46.156) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 192.168.46.156 (192.168.46.156): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.421 ms
Note
ping命令去测试有点不专业的,需要多次测试才能2个地址都出现,这里就不安装dig工具了,毕竟客户端。
10.7.6. nfs主机配置
10.7.6.1. 添加用户
[root@centos-154 ~]# groupadd -g 48 apache
[root@centos-154 ~]# useradd -u 48 -g 48 apache
[root@centos-154 ~]# id apache
uid=48(apache) gid=48(apache) groups=48(apache)
10.7.6.2. 修改权限
[root@centos-154 ~]# chown -R apache.apache /data/html
10.7.6.3. 共享出去
[root@centos-154 ~]# yum install nfs-utils
[root@centos-154 ~]# vim /etc/exports
[root@centos-154 ~]# cat /etc/exports
/data/html 192.168.46.156(rw,all_squash,anonuid=apache,anongid=apache)
/data/html 192.168.46.156(rw,all_squash,anonuid=apache,anongid=apache)
[root@centos-154 ~]# systemctl restart nfsd
[root@centos-154 ~]# exportfs -v
/data/html 192.168.46.156(rw,sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,anonuid=48,anongid=48,sec=sys,secure,root_squash,all_squash)
/data/html 192.168.46.157(rw,sync,wdelay,hide,no_subtree_check,anonuid=48,anongid=48,sec=sys,secure,root_squash,all_squash)
10.7.7. mysql主机配置
10.7.7.1. 安装软件
[root@centos-155 ~]# yum install mariadb-server mariadb
10.7.7.2. 启动服务
[root@centos-155 ~]# systemctl start mariadb
[root@centos-155 ~]# netstat -tunlp |grep 3306
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3306 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 13680/mysqld
10.7.7.3. 添加应用用户
[root@centos-155 ~]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 10
Server version: 5.5.56-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> create database web ;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> grant all on web.* to web@'192.168.46.%' identified by 'oracle';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
10.7.7.4. 安全初始化
[root@centos-155 ~]# mysql_secure_installation
10.7.8. web主机配置
这里是2个主机。
10.7.8.1. 安装软件
# 安装
[root@centos-150 ~]# ansible web -m yum -a 'name=httpd,php-fpm,php-mysql,mod_fcgid state=installed'
# 启动服务
[root@centos-150 ~]# ansible web -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started'
[root@centos-150 ~]# ansible web -m service -a 'name=php-fpm state=started'
10.7.8.2. 挂载目录
# 安装必要的挂载相关的软件
[root@centos-156 httpd]# yum install nfs-utils cifs-utils
# 启动rpc服务
[root@centos-156 httpd]# systemctl restart rpcbind
# 查看远程的导出情况
[root@centos-156 httpd]# showmount -e 192.168.46.154
Export list for 192.168.46.154:
/data/html 192.168.46.157,192.168.46.156
# 挂载
[root@centos-156 httpd]# mount 192.168.46.154:/data/html /var/www/html
# 自动挂载
[root@centos-156 httpd]# tail -n 1 /etc/mtab
192.168.46.154:/data/html /var/www/html nfs4 rw,relatime,vers=4.1,rsize=65536,wsize=65536,namlen=255,hard,proto=tcp,port=0,timeo=600,retrans=2,sec=sys,clientaddr=192.168.46.156,local_lock=none,addr=192.168.46.154 0 0
[root@centos-156 httpd]# tail -n 1 /etc/mtab >> /etc/fstab
# 查看下样例网页
[root@centos-156 httpd]# cat /var/www/html/index.html
hellow world
10.7.8.3. 配置httpd
本部分内容需要在2个机器都要做一遍。
# 下载一个样例的php页面
[root@centos-156 httpd]# wget download.linuxpanda.tech/lamp/index.php.sample -O /var/www/html/index.php
# 编辑下样例php页面的数据库连接用户和密码
[root@centos-156 httpd]# vim /var/www/html/index.php
[root@centos-156 httpd]# cat /var/www/html/index.php
<?php
$mysqli=new mysqli("192.168.46.155","web","oracle");
if(mysqli_connect_errno()){
echo "失败了";
$mysqli=null;
exit;
}
echo "成功了";
$mysqli->close();
?>
# fcgi编辑
[root@centos-156 conf.d]# vim fcgid.conf
# 添加如下3行
DirectoryIndex index.php
ProxyRequests Off
ProxyPassMatch ^/(.*\.php)$ fcgi://127.0.0.1:9000/var/www/html/$1
# 重启网络服务
[root@centos-156 conf.d]# service httpd restart
10.7.8.4. 本机测试
本部分内容需要在2个机器都要做一遍。
[root@centos-156 conf.d]# curl localhost/index.php
成功了
10.7.9. client测试
[root@centos-159 ~]# curl http://www.linuxpanda.tech/index.php
成功了
# 把156的web停掉
[root@centos-159 ~]# curl http://www.linuxpanda.tech/index.php
成功了
# 再把157的web停掉
[root@centos-159 ~]# curl http://www.linuxpanda.tech/index.php
curl: (7) Failed connect to www.linuxpanda.tech:80; Connection refused
10.7.10. 总结
这个作业,看起来挺简单的,做起来还是遇到些麻烦的。
需要改进的地方:
dns解析太不稳定,如果web1停掉,dns还可能解析到这个停掉的主机,就会导致web没法访问。
mysql实例后面学习了主从可以考虑完善下。
lamp没有使用xcache加速下
本练习都是使用的yum安装的lamp环境,可以考虑使用编译安装方法。
数据通过nfs共享,本质还是一个磁盘的数据,可以考虑使用rsync来替代nfs。
数据文件可以考虑放到raid上,来提供文件的访问性能
标签:web,架构,centos,httpd,156,192.168,实例,php,root 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/tanxiaojun/p/12151739.html