go-zero微服务实战系列(三、API定义和表结构设计)
作者:互联网
前两篇文章分别介绍了本系列文章的背景以及根据业务职能对商城系统做了服务的拆分,其中每个服务又可分为如下三类:
- api服务 - BFF层,对外提供HTTP接口
- rpc服务 - 内部依赖的微服务,实现单一的业务功能
- rmq服务 - 负责流式任务的处理,如消费kafka等等
- admin服务 - 对内部管理后台提供HTTP接口,通常数据操作权限比较高
如果没看过前两篇文章可通过如下传送门查看
前两篇文章比较偏理论,以至于文章发出去后有些同学觉得写得比较水,非常理解大家迫切想要写代码的心情,我也进行了深刻的反思哈哈哈。所以从本篇开始就要进入万众期待的代码环节了。但是,所谓磨刀不误砍柴工,在真正的生产开发过程中,我们一般都会花大量的时间在需求的理解和协议的设计上,如果需求理解的不透彻或者协议设计的不合理就会大大增加我们项目返工的可能,甚至还没上线就得重构。所以前期多投入一些时间也完全是值得的。当我们把需求理解透彻,项目结构和协议定义清晰后,其实写代码就是顺水推舟的事情,速度那是大大滴快。闲言少叙,我们开始今天的内容。
API定义
可能大家在工作中都遇到过这样的场景,就是代码更新了但是文档没有更新,从而产生一些问题导致一些扯皮事情的发生。这个问题的本质是服务和文档是割裂的。我们期望的是文档即协议,协议即服务,这个理念与go-zero的api定义不谋而合。
我们定义了BFF层,BFF是对外提供HTTP接口的统一出口,所以我们这里API的定义主要是针对BFF服务的API的定义。
API的兼容性
我们定义或修改API的时候一定要考虑向前兼容,如下几种情况是向前兼容的:
- 增加新的API接口协议
- 请求参数添加字段,需要保证新老客户端对该字段的处理方式不同
- 响应结果添加字段,该字段信息只会在新版本客户端中展示
如下几种情况是向前不兼容的:
- 删除或重命名服务、字段、方法等,从本质上说,如果客户端代码可以引用某些内容,那么删除或者重命名它都是不兼容的变化,这时必须修改major版本号
- 修改字段类型,这会导致客户端库生成的代码发生变化,因此必须增加major版本号,对于编译型静态语言来说,可能会编译错误
- 修改现有请求的可见行为,客户端通常依赖于API行为和语义,即使这样的行为没有被明确支持或记录。因此,在大多数情况下,修改API数据的行为或语义将被消费者视为是破坏性的
- 给资源消息添加 读取/写入 字段
首页API定义
首页功能主要分为四个部分,搜索、Banner图、限时抢购和推荐商品列表,点击搜索框会跳转到搜索页,推荐部分是分页展示的,用户通过不断地往上滑动可以加载下一页。通过分析首页我们大致需要提供三个接口,分别是Banner接口,限时抢购接口和推荐接口。
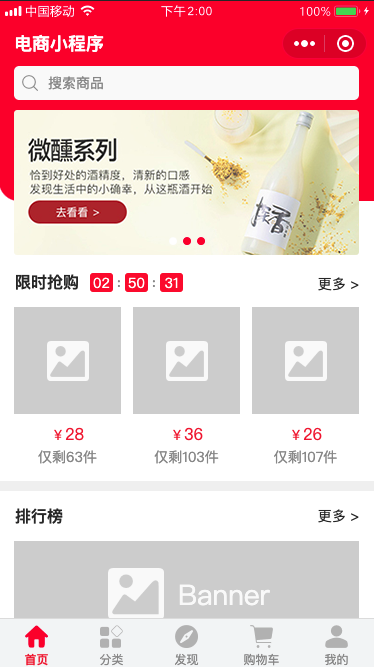
这里需要注意的是推荐接口,推荐接口返回的数据是需要支持分页的,这里分页采用游标的方式,Ps参数为每页返回数据条数,默认一页返回20条数据,注意在服务端一定需要再次校验Ps值,防止Ps恶意值导致的性能问题,比如Ps传了10000,当为非法值的时候需要把Ps置为默认值,Cursor为游标值,游标为每页最后一条数据的RecommendTime。
返回值中Products定义了返回的商品列表,IsEnd表示是否是最后一页,客户端通过判断IsEnd是否为true决定是否终止请求,RecommendTime为本页返回数据最后一条数据的推荐时间,推进列表按照推荐时间倒序返回。
RecommendRequest {
Cursor int64 `json:"cursor"`
Ps int64 `form:"ps,default=20"` // 每页大小
}
RecommendResponse {
Products []*Product `json:"products"`
IsEnd bool `json:"is_end"` // 是否最后一页
RecommendTime int64 `json:"recommend_time"` // 商品列表最后一个商品的推荐时间
}
Product {
ID int64 `json:"id"` // 商品ID
Name string `json:"name"` // 产品名称
Description string `json:"description"` // 商品描述
Price float64 `json:"price"` // 商品价格
Stock int64 `json:"stock"` // 库存
Category string `json:"category"` // 分类
Status int64 `json:"status"` // 状态:1-正常,2-下架
CreateTime int64 `json:"create_time"` // 创建时间
UpdateTime int64 `json:"update_time"` // 更新时间
}
抢购有一个倒计时的功能,我们这里返回抢购开始时间,客户端计算剩余时间进行倒计时。
FlashSaleResponse {
StartTime int64 `json:"start_time"` // 抢购开始时间
Products []*Product `json:"products"`
}
分类API定义
分类列表中可以切换不同的tab来选择不同的分类,同时在每一种分类下面又可以按照不同的维度进行排序,且支持分页。
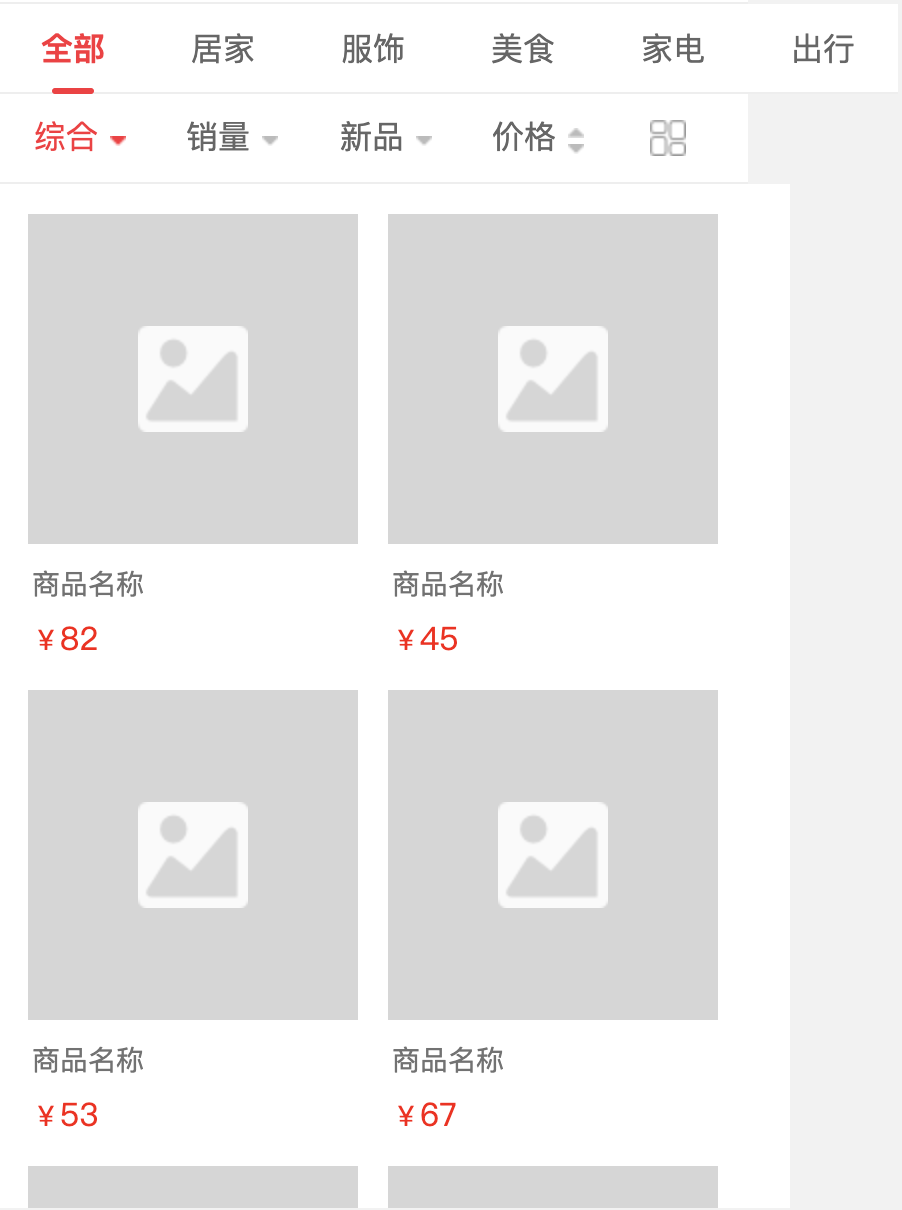
分类商品列表和推荐接口的分页方式一样,都是采用游标的方式,同时分类商品列表需要根据不同的分类和排序属性进行排序,此类需要排序的列表我们一般会通过redis的sorted set来实现,score为需要排序的属性,比如销量,member为对应商品的id。
CategoryListRequest {
Cursor int64 `form:"cursor"` // 分页游标
Ps int64 `form:"ps,default=20"` // 每页大小
Category string `form:"category"` // 分类
Sort string `form:"sort"` // 排序
}
CategoryListResponse {
Products []*Product `json:"products"`
IsEnd bool `json:"is_end"`
LastVal int64 `json:"last_val"`
}
提到sorted set在这里说一个笔者使用sorted set曾经踩过的一个坑。我们使用缓存的常用姿势是cache aside模式,即先读缓存,如果缓存命中则直接从缓存中返回数据,如果读取缓存miss了,则回源到DB中读数据,且为了后面更快的读取数据,从DB中读取的数据会回塞到缓存中,且会给缓存设置一个过期时间。
而为了保证缓存和数据库数据的一致性,当我们新增数据的时候需要把这条数据也写到缓存中从而保证缓存和数据库数据一致,一般代码会这么写,先通过Exists判断缓存对应的key是否存在,如果存在就往sorted set中增加一条数据,如果不存在则不处理,等待下次来读取列表的时候重新加载列表数据到缓存中。我们发现有时候缓存中列表数据会变成一条,但是数据其实是有多条的,当时感觉是很诡异的,通过排查最终定位到问题,原来是Exists操作和Zadd两个操作不是原子的操作导致的,也就是在Exists的时候缓存的Key还没有过期,但是在Exists后和进行Zadd前这个key过期了,然后再执行Zadd就导致缓存列表中就只有本次新增的这条数据了。解决这个问题的办法也很简单,不使用Exists判断key是否存在,而是通过Expire给这个key续期,如果key不存在则Expire返回0,key存在则Expire返回1,续期成功。缓存的使用我们还踩过很多坑,特别是在高并发的场景下,这个后续文章再详细介绍。
购物车API定义
在这里我们对购物车的数量做一下限制,我们限制购物车最多只能加200个商品,这样做是为了在全选的时候下单不会导致过高的写放大,由于加了200条的限制,所以购物车列表不需要分页。
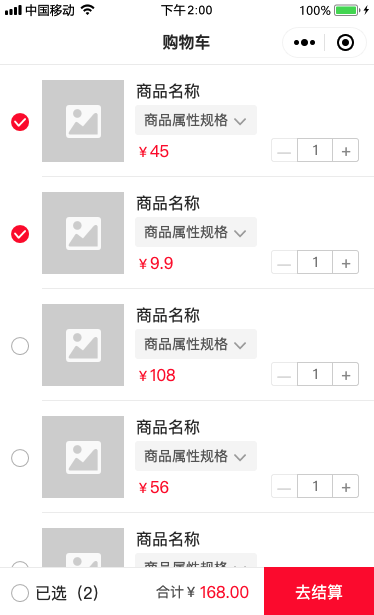
购物车列表请求和返回定义如下:
CartListRequest {
UID int64 `form:"uid"`
}
CartListResponse {
Products []*CartProduct `json:"products"`
}
CartProduct {
Product *Product `json:"product"`
Count int64 `json:"count"` // 购买数量
}
商品评价API定义
商品评价的功能同样也是需要支持分页的,采用游标的方式进行分页,同时按照评论时间进行倒序

评论列表定义如下:
ProductCommentRequest {
ProductID int64 `form:"product_id"`
Cursor int64 `form:"cursor"`
Ps int64 `form:"ps,default=20"`
}
ProductCommentResponse {
Comments []*Comment `json:"comments"`
IsEnd bool `json:"is_end"` // 是否最后一页
CommentTime int64 `json:"comment_time"` // 评论列表最后一个评论的时间
}
Comment {
ID int64 `json:"id"` // 评论ID
ProductID int64 `json:"product_id"` // 商品ID
Content string `json:"content"` // 评论内容
Images []*Image `json:"images"` // 评论图片
User *User `json:"user"` // 用户信息
CreateTime int64 `json:"create_time"` // 评论时间
UpdateTime int64 `json:"update_time"` // 更新时间
}
User {
ID int64 `json:"id"` // 用户ID
Name string `json:"name"` // 用户名
Avatar string `json:"avatar"` // 头像
}
Image {
ID int64 `json:"id"`
URL string `json:"url"`
}
以上列出了一些核心的API的定义,商城的功能点非常多,很难短时间内全部定义完,笔者会在工作之余不断的完善。定义接口返回数据的时候我们要尽量的收敛只返回必要的数据。
定义好api后,我们使用如下命令重新生成项目代码,输出如下信息表明生成成功
$ goctl api go -api api.api -dir .
etc/api-api.yaml exists, ignored generation
internal/config/config.go exists, ignored generation
api.go exists, ignored generation
internal/svc/servicecontext.go exists, ignored generation
internal/handler/homebannerhandler.go exists, ignored generation
internal/handler/flashsalehandler.go exists, ignored generation
internal/handler/recommendhandler.go exists, ignored generation
internal/handler/categorylisthandler.go exists, ignored generation
internal/handler/cartlisthandler.go exists, ignored generation
internal/handler/productcommenthandler.go exists, ignored generation
internal/logic/homebannerlogic.go exists, ignored generation
internal/logic/flashsalelogic.go exists, ignored generation
internal/logic/recommendlogic.go exists, ignored generation
internal/logic/categorylistlogic.go exists, ignored generation
internal/logic/cartlistlogic.go exists, ignored generation
internal/logic/productcommentlogic.go exists, ignored generation
Done.
RPC定义
因为BFF只负责数据的组装工作,数据真正的来源是各个微服务通过RPC接口提供,接下来我们来定义各个微服务的proto。如下展示的订单列表页面由两部分数据组成,分别是订单数据和商品数据,也就是我们的BFF需要依赖order-rpc和product-rpc来完成该页面数据的组装,下面我们分别来定义order-rpc和product-rpc
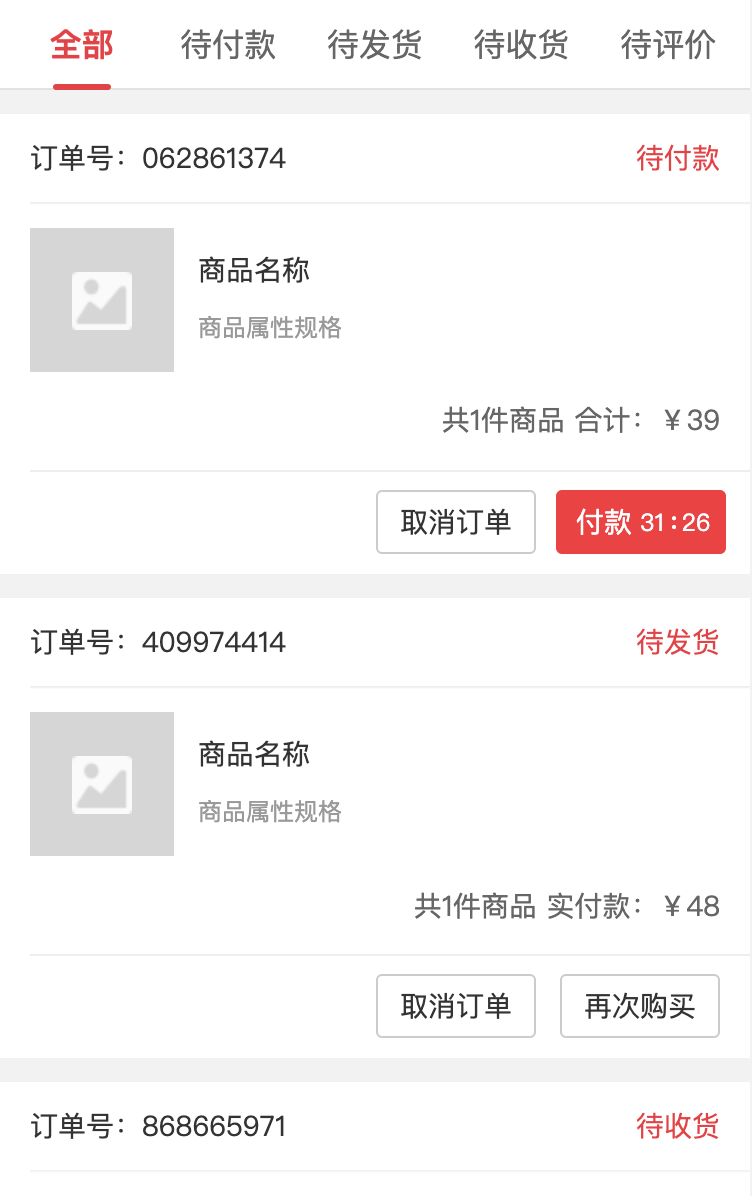
order.proto定义如下,service名字为Order,添加了Orders获取订单列表rpc接口。
syntax = "proto3";
package order;
option go_package="./order";
service Order {
rpc Orders(OrdersRequest) returns(OrdersResponse);
}
message OrdersRequest {
int64 user_id = 1;
int32 status = 2;
int64 cursor = 3;
int32 ps = 4;
}
message OrdersResponse {
repeated OrderItem orders = 1;
bool is_end = 2;
string create_time = 3;
}
message OrderItem {
string order_id = 1;
int64 quantity = 2;
float payment = 3;
int64 product_id = 4;
int64 user_id = 5;
int64 create_time = 6;
}
使用如下命令重新生成代码,注意这里需要依赖protoc-gen-go和protoc-gen-go-grpc两个插件,木有安装的话执行下面命令会报错
$ goctl rpc protoc order.proto --go_out=. --go-grpc_out=. --zrpc_out=.
生成好后然后启动order-rpc服务,输出如下:
$ go run order.go
Starting rpc server at 127.0.0.1:8080...
{"level":"warn","ts":"2022-06-09T15:42:21.680+0800","logger":"etcd-client","caller":"v3@v3.5.4/retry_interceptor.go:62","msg":"retrying of unary invoker failed","target":"etcd-endpoints://0xc000029c00/127.0.0.1:2379","attempt":0,"error":"rpc error: code = DeadlineExceeded desc = latest balancer error: last connection error: connection error: desc = \"transport: Error while dialing dial tcp 127.0.0.1:2379: connect: connection refused\""}
{"@timestamp":"2022-06-09T15:42:21.682+08:00","caller":"zrpc/server.go:90","content":"context deadline exceeded","level":"error"}
panic: context deadline exceeded
什么情况?竟然报错了,还好日志输出的比较详细,通过日志可以看出来好像是本地的etcd没有启动,那我们就把本地的etcd启动,启动后再次运行order rpc服务,已经侦听在默认的8080端口上
$ go run order.go
Starting rpc server at 127.0.0.1:8080...
product.proto定义如下
syntax = "proto3";
package product;
option go_package="./product";
service Product {
rpc Products(ProductRequest) returns(ProductResponse);
}
message ProductRequest {
string product_ids = 1;
}
message ProductResponse {
repeated ProductItem products = 1;
}
message ProductItem {
int64 product_id = 1;
string name = 2;
string description = 3;
string image_url = 4;
}
执行如下命令生成product rpc的代码
$ goctl rpc protoc product.proto --go_out=. --go-grpc_out=. --zrpc_out=.
注意,goctl生成的rpc服务默认侦听在8080端口,因为我们现在是在本地测试,所以把product rpc默认的端口改为8081,然后启动服务。
Name: product.rpc
ListenOn: 127.0.0.1:8081
Etcd:
Hosts:
- 127.0.0.1:2379
Key: product.rpc
$ go run product.go
Starting rpc server at 127.0.0.1:8081...
因为我们的BFF需要依赖order.rpc和product.rpc,我们需要先添加配置文件,如下:
Name: api-api
Host: 0.0.0.0
Port: 8888
OrderRPC:
Etcd:
Hosts:
- 127.0.0.1:2379
Key: order.rpc
ProductRPC:
Etcd:
Hosts:
- 127.0.0.1:2379
Key: product.rpc
然后在ServiceContext中添加RPC的客户端,如下:
type ServiceContext struct {
Config config.Config
OrderRPC order.Order
ProductRPC product.Product
}
func NewServiceContext(c config.Config) *ServiceContext {
return &ServiceContext{
Config: c,
OrderRPC: order.NewOrder(zrpc.MustNewClient(c.OrderRPC)),
ProductRPC: product.NewProduct(zrpc.MustNewClient(c.ProductRPC)),
}
}
最后只要在订单接口的logic方法中添加逻辑就可以啦,这里只是演示,所以会比较简单:
func (l *OrderListLogic) OrderList(req *types.OrderListRequest) (resp *types.OrderListResponse, err error) {
orderRet, err := l.svcCtx.OrderRPC.Orders(l.ctx, &order.OrdersRequest{UserId: req.UID})
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
var pids []string
for _, o := range orderRet.Orders {
pids = append(pids, strconv.Itoa(int(o.ProductId)))
}
productRet, err := l.svcCtx.ProductRPC.Products(l.ctx, &product.ProductRequest{ProductIds: strings.Join(pids, ",")})
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
var orders []*types.Order
for _, o := range orderRet.Orders {
if p, ok := productRet.Products[o.ProductId]; ok {
orders = append(orders, &types.Order{
OrderID: o.OrderId,
ProductName: p.Name,
})
}
}
return &types.OrderListResponse{Orders: orders}, nil
}
然后在浏览器中请求订单接口,就可以看到输出了如下的数据,说明从BFF到RPC的链路已经打通:
http://127.0.0.1:8888/v1/order/list?uid=123
{
"orders": [
{
"order_id": "20220609123456",
"status": 0,
"quantity": 0,
"payment": 0,
"total_price": 0,
"create_time": 0,
"product_id": 0,
"product_name": "测试商品名称",
"product_image": "",
"product_description": ""
}
],
"is_end": false,
"order_time": 0
}
表结构定义
不同的微服务间需要做数据的隔离,每个微服务独占数据库资源,通过RPC调用来获取数据依赖,整体架构如下图所示:
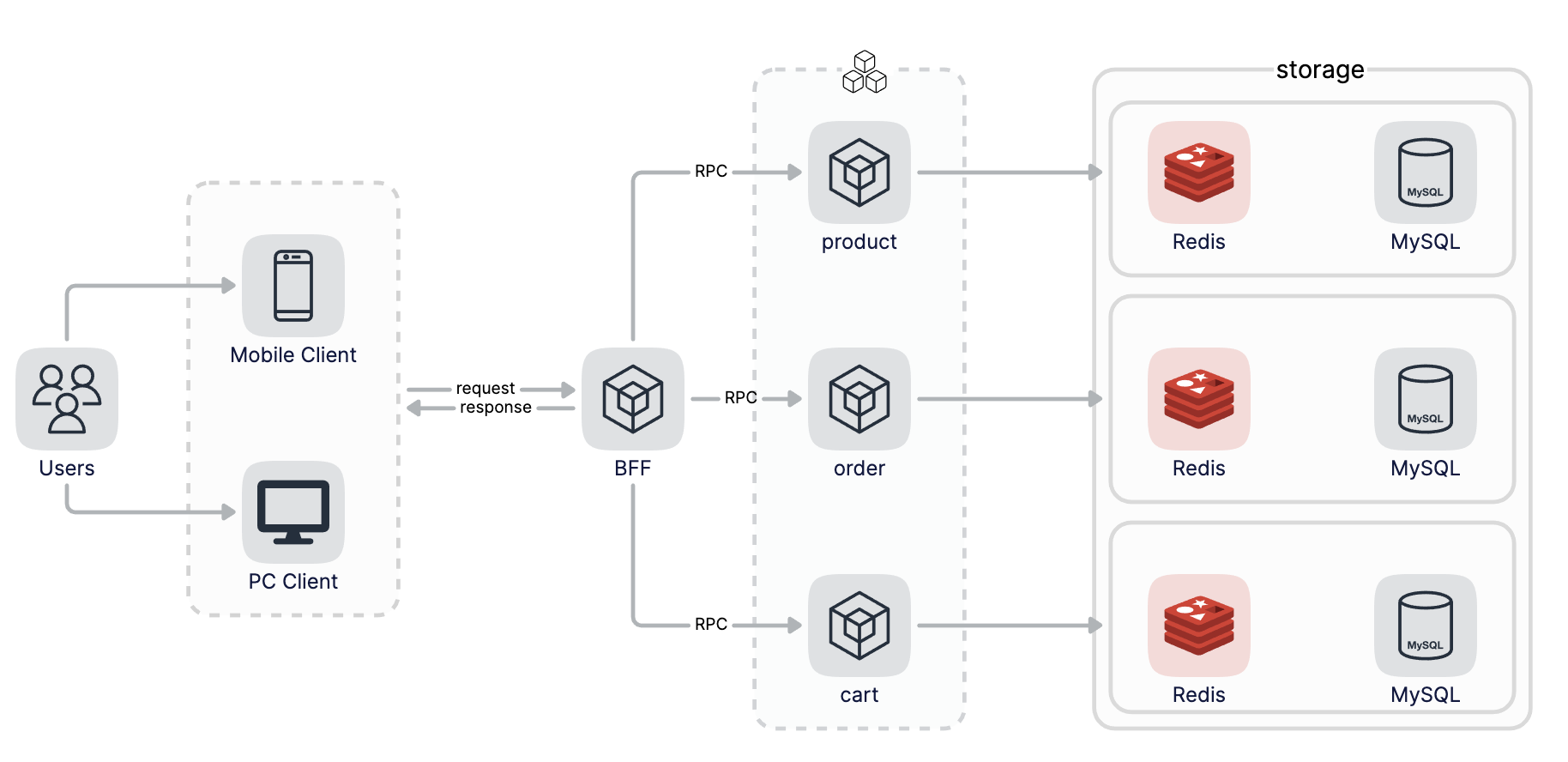
通过以上对API的定义我们大致了解了需要哪些数据字段,下面开始进行数据表的设计,建表语句放在项目根目录下data.sql文件中,该文件会不断更新,主要涉及的库和表定义如下:
用户表主要保存用户信息,在user库中后续可能还会扩展比如用户积分,用户等级等功能
CREATE DATABASE user;
USE user;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户ID',
`username` varchar(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '用户名',
`password` varchar(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '用户密码,MD5加密',
`phone` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '手机号',
`question` varchar(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '找回密码问题',
`answer` varchar(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '找回密码答案',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `ix_update_time` (`update_time`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='用户表';
商品库中主要涉及商品表和商品分类表:
CREATE DATABASE product;
USE product;
CREATE TABLE `product` (
`id` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '商品id',
`cateid` smallint(6) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '类别Id',
`name` varchar(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '商品名称',
`subtitle` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '商品副标题',
`images` text COMMENT '图片地址,json格式,扩展用',
`detail` text COMMENT '商品详情',
`price` decimal(20,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '价格,单位-元保留两位小数',
`stock` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '库存数量',
`status` int(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 1 COMMENT '商品状态.1-在售 2-下架 3-删除',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `ix_cateid` (`cateid`),
KEY `ix_update_time` (`update_time`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='商品表';
CREATE TABLE `category` (
`id` smallint(6) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '分类id',
`parentid` smallint(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '父类别id当id=0时说明是根节点,一级类别',
`name` varchar(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '类别名称',
`status` tinyint(4) NOT NULL DEFAULT 1 COMMENT '类别状态1-正常,2-已废弃',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='商品类别表';
购物车
CREATE DATABASE cart;
USE cart;
CREATE TABLE `cart` (
`id` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '购物车id',
`userid` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '用户id',
`proid` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '商品id',
`quantity` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '数量',
`checked` int(11) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '是否选择,1=已勾选,0=未勾选',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `ix_userid` (`userid`),
KEY `ix_proid` (`proid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='购物车表';
订单相关:
CREATE DATABASE order;
USE order;
CREATE TABLE `orders` (
`id` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '订单id',
`userid` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '用户id',
`shoppingid` bigint(20) NOT NUMBER DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '收货信息表id',
`payment` decimal(20,2) DEFAULT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '实际付款金额,单位是元,保留两位小数',
`paymenttype` tinyint(4) NOT NULL DEFAULT 1 COMMENT '支付类型,1-在线支付',
`postage` int(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '运费,单位是元',
`status` smallint(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 10 COMMENT '订单状态:0-已取消-10-未付款,20-已付款,30-待发货 40-待收货,50-交易成功,60-交易关闭',
`payment_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00' COMMENT '支付时间',
`send_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00' COMMENT '发货时间',
`end_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00' COMMENT '交易完成时间',
`close_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT '0000-00-00 00:00:00' COMMENT '交易关闭时间',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='订单表';
CREATE TABLE `orderitem` (
`id` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL COMMENT '订单子表id',
`orderid` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '订单id',
`userid` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '用户id',
`proid` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '商品id',
`proname` varchar(100) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '商品名称',
`proimage` varchar(500) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '商品图片地址',
`currentunitprice` decimal(20,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '生成订单时的商品单价,单位是元,保留两位小数',
`quantity` int(10) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '商品数量',
`totalprice` decimal(20,2) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '商品总价,单位是元,保留两位小数',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `ix_orderid` (`orderid`),
KEY `ix_userid` (`userid`),
KEY `ix_proid` (`proid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='订单明细表';
CREATE TABLE `shopping` (
`id` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL COMMENT '收货信息表id',
`orderid` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '订单id',
`userid` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '用户id',
`receiver_name` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '收货姓名',
`receiver_phone` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '收货固定电话',
`receiver_mobile` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '收货移动电话',
`receiver_province` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '省份',
`receiver_city` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '城市',
`receiver_district` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '区/县',
`receiver_address` varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '详细地址',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `ix_orderid` (`orderid`),
KEY `ix_userid` (`userid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='收货信息表';
支付相关:
CREATE DATABASE pay;
USE pay;
CREATE TABLE `payinfo` (
`id` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL COMMENT '支付信息表id',
`orderid` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '订单id',
`userid` bigint(20) UNSIGNED NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '用户id',
`payplatform` tinyint(4) NOT NULL DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '支付平台:1-支付宝,2-微信',
`platformnumber` varchar(200) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '支付流水号',
`platformstatus` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '支付状态',
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `ix_orderid` (`orderid`),
KEY `ix_userid` (`userid`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='支付信息表';
结束语
本篇文章介绍了如何定义API,并根据定义好的api文件通过 goctl 生成服务代码,整个项目涉及的api非常多,没办法一次性定义完,后续还会不断的补充。
接着演示了如何在BFF服务中调用RPC服务,把整个调用链路打通,这里只是为了演示所以写死了代码,后面RPC返回的数据会从缓存或者数据库中获取。
最后定义了整个项目主要涉及的库和表,我们采用了微服务的架构,服务间数据做了隔离,每个服务独享了数据库。
到这里前期的准备工作基本完成了,后面主要就是按照需求完成业务功能,和应对高并发来做优化。
由于笔者水平有限,难免会出现理解有误的地方,如果你发现有可以改进的地方,希望能够得到你宝贵的意见。
另外,如果你感兴趣,非常欢迎你加入,我们一起来完成这个项目,为社区献出自己的一份力。
希望本篇文章对你有所帮助,谢谢。
每周一、周四更新
代码仓库 https://github.com/zhoushuguang/lebron
项目地址
https://github.com/zeromicro/go-zero
欢迎使用 go-zero 并 star 支持我们!
微信交流群
关注『微服务实践』公众号并点击 交流群 获取社区群二维码。
标签:COMMENT,DEFAULT,json,和表,zero,API,go,NULL,id 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/kevinwan/p/16369542.html