Python正课16 —— 流程控制之for循环
作者:互联网
本文内容皆为作者原创,如需转载,请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuexianqi/p/12454283.html
一:什么是for循环
循环就是重复做某件事,for循环就是Python提供的第二种循环机制
二:为何要有for循环
理论上for循环能做的事情,while循环都能做
之所以要有for循环,是因为for循环在循环取值(遍历取值)比while循环更简洁
三:如何用for循环
1.基本使用之循环取值
语法:
for 变量名 in 可迭代对象: #可迭代对象可以是:列表、字典、字符串、元组、集合
代码1
代码2
代码3案例1:列表循环取值
# 简单版
l = ['xxq','qwe','asd']
for i in l:
print(i)
xxq
qwe
asd# 复杂版
l = ['xxq','qwe','asd']
i = 0
while i < 3:
print(l[i])
i += 1
xxq
qwe
asd案例2:字典循环取值
# 简单版
dic = {'name':'xxq','age':18,'gender':'male'}
for i in dic:
print(i,dic[i])
name xxq
age 18
gender male# 复杂版
# while循环可以遍历字典,但是太麻烦了案例3:字符串循环取值
# 简单版
msg = 'my name'
for i in msg:
print(i)
m
y
n
a
m
e四:总结for循环与while循环的异同
1.相同之处:都是循环,for循环能做的事,while循环都能做
2.不同之处:
while循环称之为“条件循环”,循环次数取决于条件何时变为假
for循环称之为“取值循环”,循环次数取决in后包含的值的个数
for i in [1,2,3]:
print('=====>')
print('666666')
=====>
666666
=====>
666666
=====>
666666五:for循环控制循环次数:range()
in后直接放一个数据类型来控制循环次数有局限性:
当循环次数过多时,数据类型包含值的格式需要增加
特性:顾头不顾尾
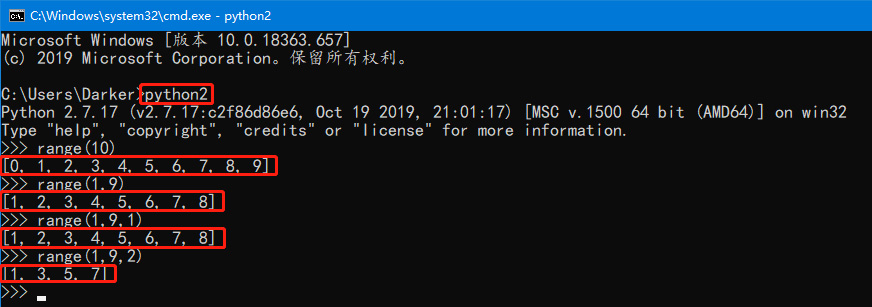
>>> range(10) # 顾头不顾尾,下标是0-9
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> range(1,9) # 从一开始1-9,取不到9,所以是1-8
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
>>> range(1,9,1) # 从一开始1-9,取不到9,步长是1,所以是1-8
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
>>> range(1,9,2) # 从一开始1-9,取不到9,步长是2,所以是1,3,5,7
[1, 3, 5, 7]
>>>for i in range(5):
print("*******")
*******
*******
*******
*******
*******六:案例应用
for + break 的连用,和 while 循环一样
for + else 的连用,和 while 循环一样
username = 'xxq'
password = '123'
count=0
for i in range(3):
inp_name=input('请输入您的账号:')
inp_pwd=input('请输入您的密码:')
if inp_name == username and inp_pwd == password:
print('登录成功')
break
else:
print('帐号或密码错误,请重试')
else:
print('输错3次,退出程序')for循环嵌套:外层循环 循环一次,内层循环 需要完整的循环完毕
for i in range(3):
print('外层循环——>',i)
for j in range(5):
print('内层循环——>', j)
外层循环——> 0
内层循环——> 0
内层循环——> 1
内层循环——> 2
内层循环——> 3
内层循环——> 4
外层循环——> 1
内层循环——> 0
内层循环——> 1
内层循环——> 2
内层循环——> 3
内层循环——> 4
外层循环——> 2
内层循环——> 0
内层循环——> 1
内层循环——> 2
内层循环——> 3
内层循环——> 4for + continue
for i in range(6): #0 1 2 3 4 5
if i == 4:
continue #直接跳过4
print(i)
0
1
2
3
5补充:终止for循环只有break一种方案
print('hello %s' % 'eogn')
print('hello' ,'world', 'eogn')
hello eogn
hello world eognprint('hello\n')
print('world')
hello
worldprint('hello\n',end='')
print('world')
hello
worldprint('hello',end='*')
print('world',end='*')
hello*world*标签:16,Python,while,内层,range,循环,正课,print,hello 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/xuexianqi/p/12454283.html