数据结构与算法--线索化二叉树
作者:互联网
简介
在二叉树中的叶子结点存在两个左右子树为空的指针域,对于有n个结点的二叉树,就有n+1个空指针域。如果将这些空指针域存放某种遍历次序下该节点的前驱结点和后继节点,则将这些指针的指向称为线索,加上线索的二叉树称为线索化二叉树
例如下图的二叉树中前序遍历结果为 1,3,8,10,6,14,其中对于叶子结点8的前驱结点为3,后继节点为10,而对于叶子结点14的前驱结点为6,无后继节点
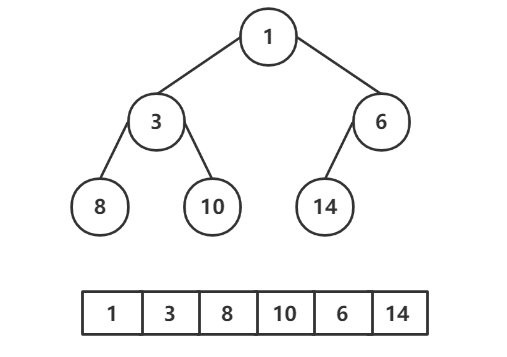
实现线索化二叉树
结点设计
为了方便指明二叉树某个节点它的指向是左右子树还是前驱或后继结点,加入了两个变量
-
左指针指向类型--leftType
-
当
leftType == 0时指向的是左指针,当leftType == 1时指向的是前驱节点
-
-
右指针指向类型--rightType
-
当
rightType == 0时指向的是右指针,当rightType == 1时指向的是后驱节点
-
public class Node<Key,Value> {
/**存储值*/
public Value value;
/**存储键*/
public Key key;
/**记录左子节点*/
public Node<Key,Value> left;
/**记录右子节点*/
public Node<Key,Value> right;
/**
* 左指针指向类型
* 当leftType ==0 时指向的是左指针,当leftType == 1时指向的是前驱节点
* */
public int leftType;
/**
* 右指针指向类型
*当rightType ==0 时指向的是右指针,当rightType == 1时指向的是后驱节点
* */
public int rightType;
public Node(Key key,Value value,Node<Key,Value> left, Node<Key,Value> right) {
this.value = value;
this.key = key;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}基础框架代码
public class ThreadedBinaryTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>,Value> {
/**记录根节点*/
private Node<Key,Value> root;
/**记录树中结点的个数*/
private int n;
/**线索化是记录当前节点的前驱结点*/
private Node<Key,Value> pre;
public ThreadedBinaryTree() {
}
/**向树中插入一个键值对*/
public void put(Key key,Value value){
root = put(root, key, value);
}
/**给指定树x上,添加一个键值对,并返回添加后的新树*/
private Node<Key,Value> put(Node<Key,Value> x,Key key,Value value){
//1.如果x子树为空
if (x == null) {
n++;
return new Node(key,value,null,null);
}
//2.如果x子树不为空,比较x的键和key的大小
int compare = key.compareTo((Key) x.key);
if (compare < 0){
//2.1如果key小于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的左子树
x.left = put(x.left,key,value);
}else if (compare > 0){
//2.2如果key大于x结点的键,则继续找x结点的右子树
x.right = put(x.right,key,value);
}else{
//2.3如果key等于x结点的键,则替换x结点的值
x.value = value;
}
return x;
}
}构建线索化二叉树
构建线索化二叉树本质上就是遍历二叉树,在遍历过程中,增加检测当前节点的左右节点是否为空;将它们改为指向前驱结点和后继节点的线索,为了实现这个过程,需要添加一个 pre 指针,将 pre 指针每次指向上次访问的节点。然后就可以使用 pre 指向它的前驱结点,使用当前访问的节点指向 pre 也就是后继结点
前序线索化二叉树
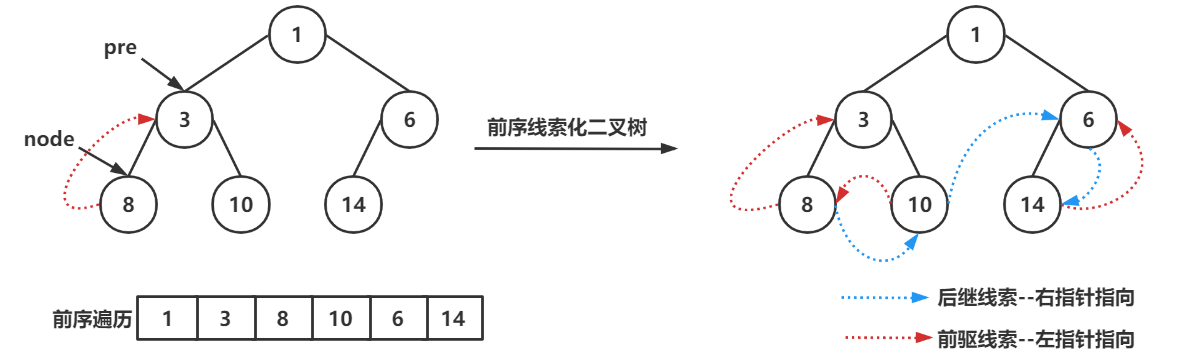
public void preThreadedBinaryTree(){
this.preThreadedBinaryTree(root);
}
public void preThreadedBinaryTree(Node<Key,Value> node){
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//线索化当前结点
//1.处理当前结点的前驱结点
if (node.left == null) {
//让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.left = pre;
//修改当前结点的左指针类型为前驱结点
node.leftType = 1;
}
//2.处理当前结点的后继结点
if (pre != null && pre.right == null) {
//让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.right = node;
//修改前驱结点的右指针类型
pre.rightType = 1;
}
//3.每处理一个节点后,让当前结点是下一个结点的前驱结点
pre = node;
//线索化左子树
if (node.leftType == 0) {
preThreadedBinaryTree(node.left);
}
//线索化右子树
if (node.rightType == 0) {
preThreadedBinaryTree(node.right);
}
}中序线索化二叉树
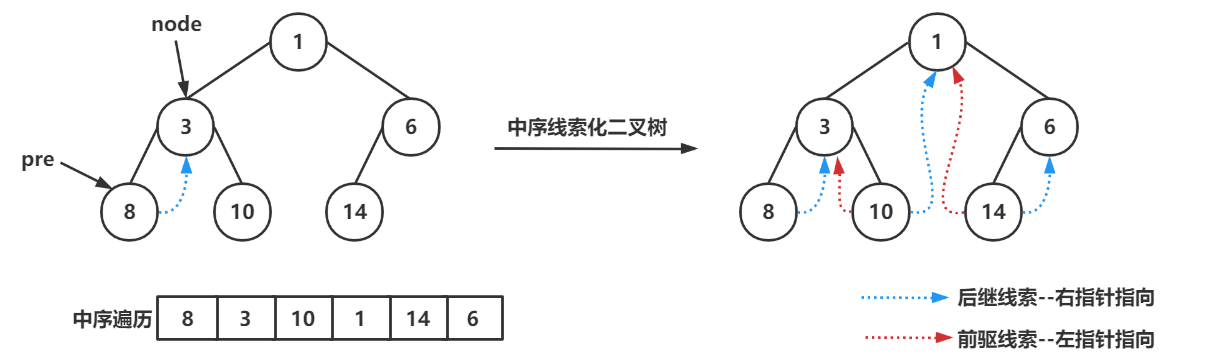
public void midThreadedBinaryTree(){
this.midThreadedBinaryTree(root);
}
public void midThreadedBinaryTree(Node<Key,Value> node){
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//先线索化左子树
midThreadedBinaryTree(node.left);
//线索化当前结点
//1.处理当前结点的前驱结点
if (node.left == null) {
//让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.left = pre;
//修改当前结点的左指针类型为前驱结点
node.leftType = 1;
}
//2.处理当前结点的后继结点
if (pre != null && pre.right == null) {
//让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.right = node;
//修改前驱结点的右指针类型
pre.rightType = 1;
}
//3.每处理一个节点后,让当前结点是下一个结点的前驱结点
pre = node;
//再线索化右子树
midThreadedBinaryTree(node.right);
}后序线索化二叉树
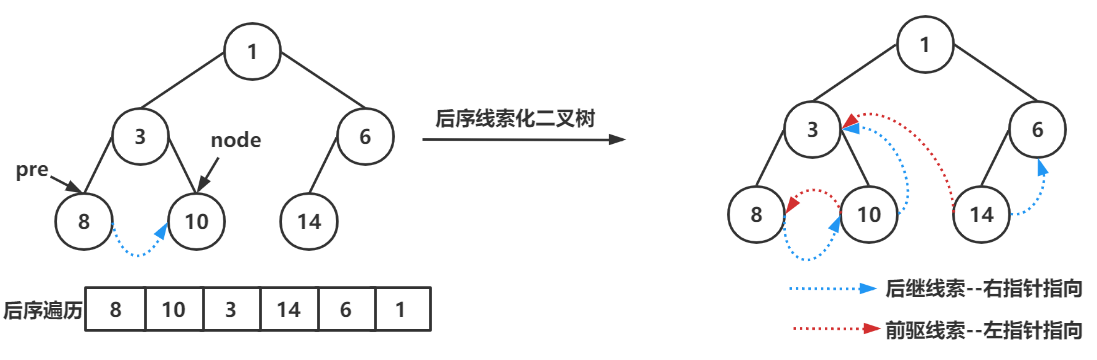
public void afterThreadedBinaryTree(){
this.afterThreadedBinaryTree(root);
}
public void afterThreadedBinaryTree(Node<Key,Value> node){
if (node == null) {
return;
}
//线索化左子树
afterThreadedBinaryTree(node.left);
//线索化右子树
afterThreadedBinaryTree(node.right);
//线索化当前结点
//1.处理当前结点的前驱结点
if (node.left == null) {
//让当前结点的左指针指向前驱结点
node.left = pre;
//修改当前结点的左指针类型为前驱结点
node.leftType = 1;
}
//2.处理当前结点的后继结点
if (pre != null && pre.right == null) {
//让前驱结点的右指针指向当前结点
pre.right = node;
//修改前驱结点的右指针类型
pre.rightType = 1;
}
//3.每处理一个节点后,让当前结点是下一个结点的前驱结点
pre = node;
}遍历线索化二叉树
前序遍历
public Queue<Key> preThreadedErgodic(){
Queue<Key> queue = new LinkedList<>();
preThreadedErgodic(root,queue);
return queue;
}
public void preThreadedErgodic(Node<Key,Value> node,Queue<Key> queue){
while (node != null) {
//循环找到leftType == 1的结点(leftType == 1说明该结点是按照线索化)
while (node.leftType == 0) {
//输出当前结点
queue.add(node.key);
node = node.left;
}
//输出当前结点
queue.add(node.key);
//替换这个遍历的结点
node = node.right;
}
}中序遍历
public Queue<Key> midThreadedErgodic(){
Queue<Key> queue = new LinkedList<>();
midThreadedErgodic(root,queue);
return queue;
}
public void midThreadedErgodic(Node<Key,Value> node,Queue<Key> queue){
while (node != null) {
//循环找到leftType == 1的结点(leftType == 1说明该结点是按照线索化)
while (node.leftType == 0) {
node = node.left;
}
//输出当前结点
queue.add(node.key);
//如果当前结点的右指针指向的后继节点,就一直输出
while (node.rightType == 1) {
//获取当前结点的后继节点
node = node.right;
queue.add(node.key);
}
//替换这个遍历的结点
node = node.right;
}
}测试
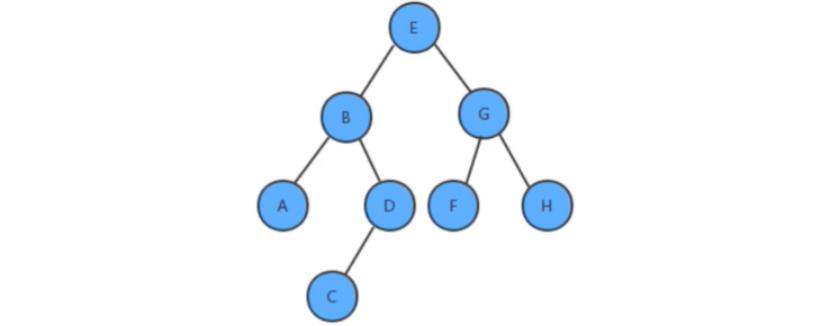
前序线索化二叉树遍历
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadedBinaryTree<String, String> bt = new ThreadedBinaryTree<>();
bt.put("E", "5");
bt.put("B", "2");
bt.put("G", "7");
bt.put("A", "1");
bt.put("D", "4");
bt.put("F", "6");
bt.put("H", "8");
bt.put("C", "3");
bt.preThreadedBinaryTree();
Queue<String> keys = bt.preThreadedErgodic();
for (String key : keys) {
System.out.print(key+" ");
}
}
}中序线索化二叉树遍历
import Queue.LinearQueue.LinearQueue;
import Tree.BinaryTree;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadedBinaryTree<String, String> bt = new ThreadedBinaryTree<>();
bt.put("E", "5");
bt.put("B", "2");
bt.put("G", "7");
bt.put("A", "1");
bt.put("D", "4");
bt.put("F", "6");
bt.put("H", "8");
bt.put("C", "3");
bt.midThreadedBinaryTree();
Queue<String> keys = bt.midThreadedErgodic();
for (String key : keys) {
System.out.print(key+" ");
}
}
}标签:node,pre,结点,--,前驱,二叉树,key,数据结构,public 来源: https://www.cnblogs.com/52-IT-y/p/16578199.html